-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 170
How to Use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Advanced Hunting With WDAC App Control
Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC), also referred to as Application Control for Business, is a highly effective security feature that empowers you to manage the execution of applications on your endpoints.
The application whitelisting approach serves as a potent defense against emerging and unknown threats. By emphasizing the identification of trusted applications, it automatically blocks any software that falls outside this trusted realm.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) is one of the tools that can be used by enterprises and organizations to develop the trusted applications policy and mange it at scale. MDE provides the intelligence and insights needed to create and maintain a robust application control policy through its Advanced Hunting feature. This feature uses KQL (Kusto Query Language) to query the data collected by MDE and using the WDACConfig module, we can turn this actionable data into WDAC policies. We can then use Intune to deploy these policies to our endpoints. All of these tools are built for scalability.
Note
You can access Intune portal by navigating to: https://intune.microsoft.com
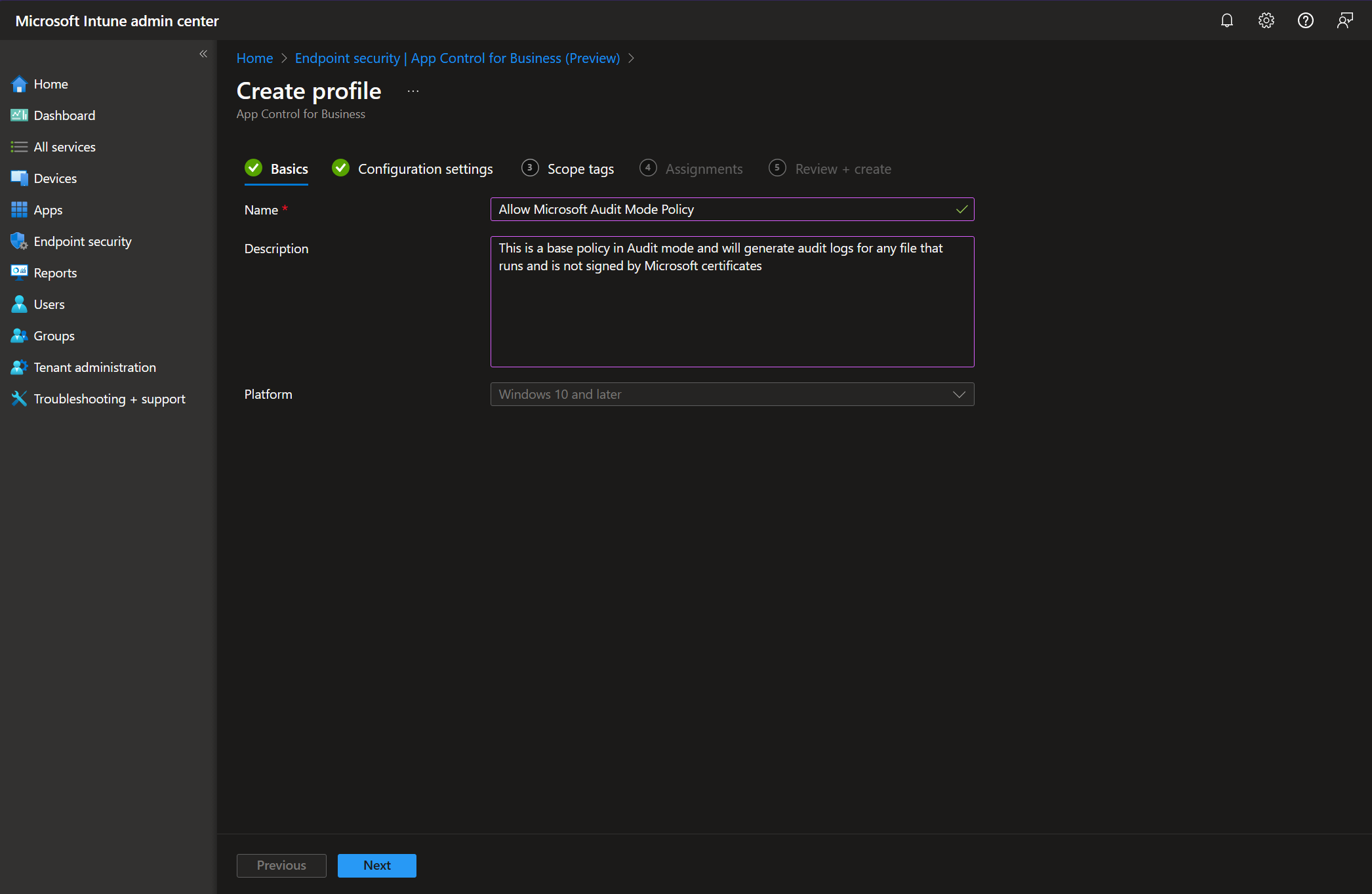
To start, we need our endpoints to be generating data and intelligence we can work with. These data points are the Code Integrity and AppLocker events. These events are generated when an application or file is blocked or audited by WDAC, or when a script or MSI file is blocked or audited by AppLocker. We can trigger the data generation by deploying WDAC policies to our endpoints in Audit mode. This mode will not block any applications, instead it will generate data points for any application, file, script, MSI file and so on that would have been blocked if the policy was in Enforce mode.
You can create Audit mode policies using the WDACConfig module based on different levels of trust.
For instance, the following command will create an Audit mode policy that once deployed on an endpoint, starts generating Audit logs for any file that runs but is not part of the Windows by default.
New-WDACConfig -PrepDefaultWindowsAuditAnother option would be the following command, which will create an Audit mode policy that once deployed, starts generating Audit logs for any file that runs but is not signed by Microsoft certificates.
New-WDACConfig -PrepMSFTOnlyAuditPlease refer to this document for further info about the commands.
You will then use Intune to deploy the generated policies to as many endpoints as you want.
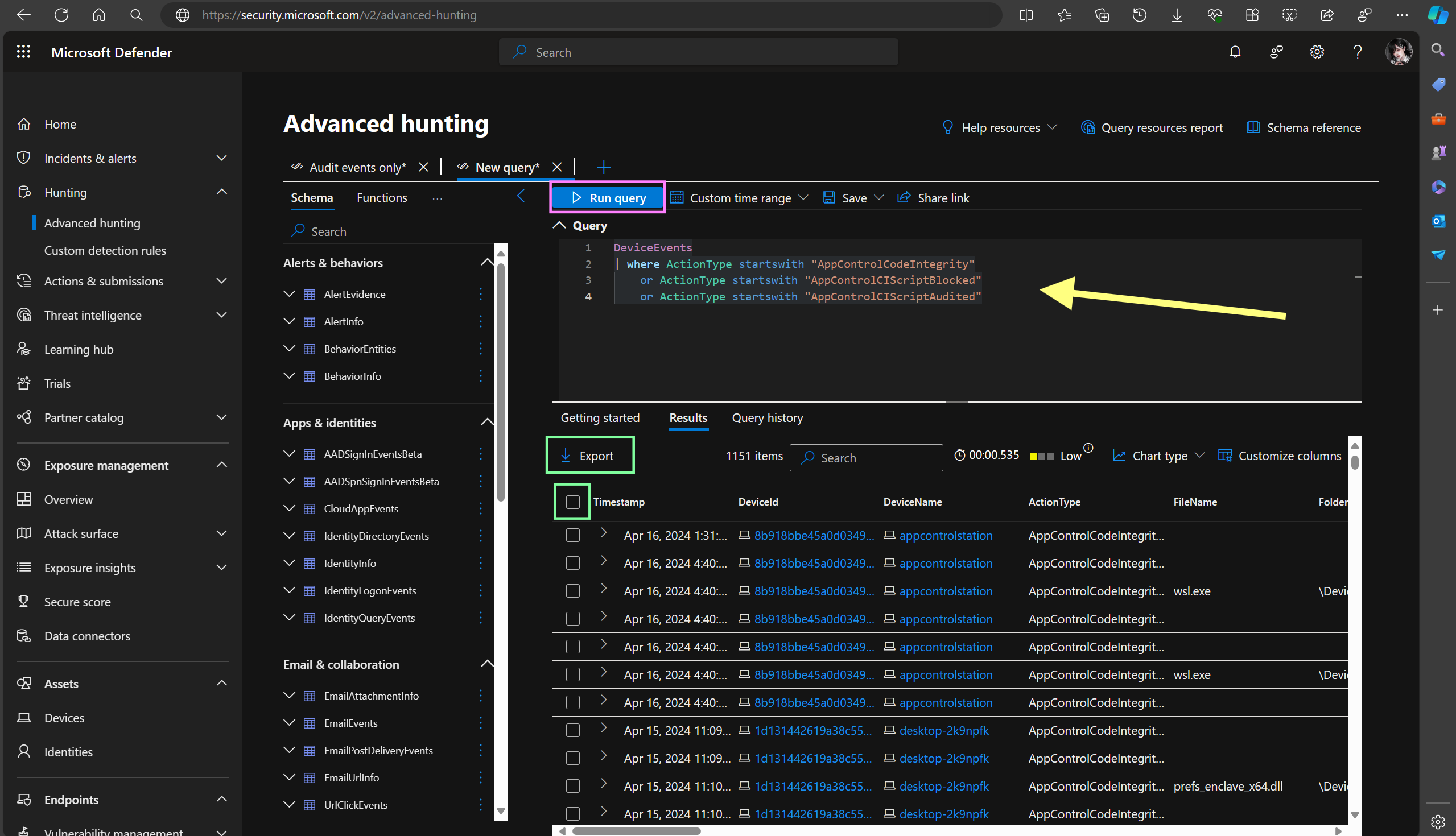
Now we need to collect the data from MDE Advanced Hunting. We can customize this query to be more specific to our environment, for instance by targeting specific devices and so on, but the following query will give us a good starting point by collecting all of the Code Integrity and AppLocker events:
DeviceEvents
| where ActionType startswith "AppControlCodeIntegrity"
or ActionType startswith "AppControlCIScriptBlocked"
or ActionType startswith "AppControlCIScriptAudited"Note
You can access Microsoft Defender for Endpoint's portal by navigating to: https://security.microsoft.com
That query generates a standard output of the data in CSV file format which is compatible with what the WDACConfig module requires in order to generate WDAC policies. If you want to customize the query further, make sure the subsequent filters are applied after the initial query to ensure correct data format.
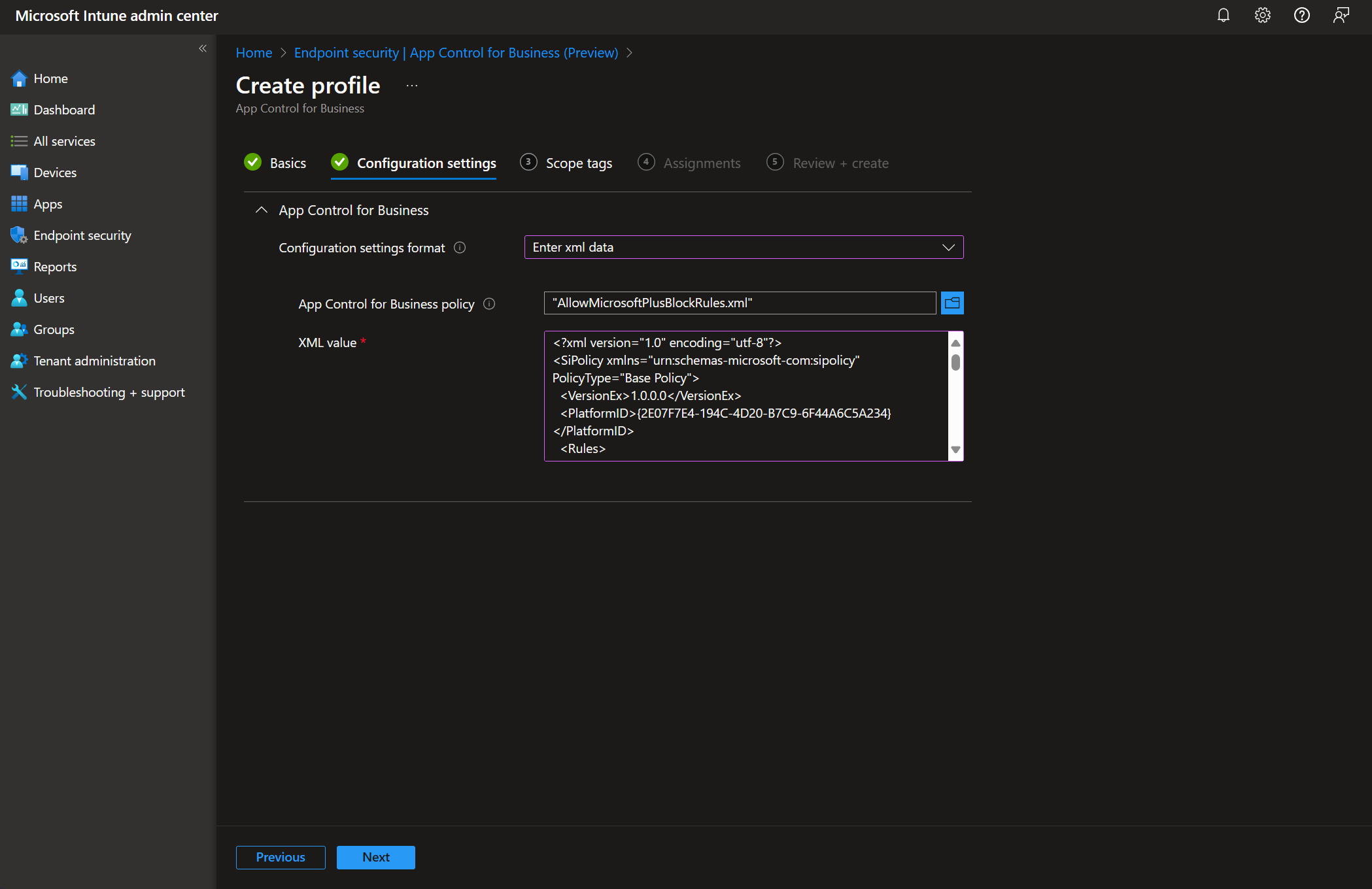
After exporting the data from MDE Advanced Hunting, we can use the WDACConfig module to generate WDAC policies. We need to feed the CSV file(s) we collected MDE Advanced Hunting data into the module like so:
ConvertTo-WDACPolicy -Source MDEAdvancedHunting -MDEAHLogs <Path to one or more CSV files> -BasePolicyGUID <Base policy GUID>It is only one example of how you can utilize the WDACConfig for policy generation based on MDE AH data, for more information about the cmdlet please refer to its documentations available here.
The command we used above will process the CSV file(s) and open a GUI window where you can filter the logs based on many criteria, and then either select all or only select some of the logs to be included in the WDAC policy.
Note that the generated policy will be a Supplemental policy.
- Systematic approach for converting the MDE AH data to WDAC policy with high precision and performance
- Uses parallel processing to speed up the policy generation process
- Provides a GUI for filtering the logs based on various criteria
- Never includes duplicate rules in the policy, regardless of the number of the duplicate logs you give it
- If a file is unsigned then a hash rule will be created for it.
- If a file is signed then there are multiple possibilities:
- If the file is signed and the MDE AH results contain the file's version as well as at least one of the following file attributes (Original Name, Internal Name, Description, Product Name), then a File Publisher rule will be created for it.
- If the file is signed but the file attributes are not present in the results, Publisher level rule will be created for it.
These levels are selected based on their security. You can read more about the levels security comparison in this article.
The following video demonstrates the process of collecting the data from MDE Advanced Hunting and generating WDAC policies using the WDACConfig module
After generating the Supplemental policies based off of the MDE Advanced Hunting data, you need to remove the Audit mode policies you deployed to your endpoints initially and replace them with Enforced mode policies.
New-WDACConfig -MakeAllowMSFTWithBlockRulesNew-WDACConfig -MakeDefaultWindowsWithBlockRulesImportant
Ensure that the Enforced mode policies align with the type of policies set during Audit mode. For example, if you utilized an Audit mode policy that permits Microsoft-signed files, it is crucial to employ an Enforced mode policy that also allows such files. Conversely, when dealing with the default Windows policy, consistency is key. Mixing these policies can result in files that were allowed during Audit mode being unexpectedly blocked during Enforce mode.
You can deploy the policies using Intune, SCCM, or any other MDM solution you are using.
After deploying the base policies, you will then deploy the Supplemental policies generated from MDE AH data, these policies are responsible for allowing any 3rd party apps or files that your endpoints need to use.
You can put your endpoints into different groups and each group can receive different Supplemental policy based on their needs.
If you have any questions, feature requests or feedback regarding this guide or the WDACConfig module, please feel free to reach out to me on GitHub by opening a new issue or discussion.
- Create AppControl Policy
- Create Supplemental Policy
- System Information
- Configure Policy Rule Options
- Simulation
- Allow New Apps
- Build New Certificate
- Create Policy From Event Logs
- Create Policy From MDE Advanced Hunting
- Create Deny Policy
- Merge App Control Policies
- Deploy App Control Policy
- Get Code Integrity Hashes
- Get Secure Policy Settings
- Update
- Sidebar
- Validate Policies
- View File Certificates
- Introduction
- How To Generate Audit Logs via App Control Policies
- How To Create an App Control Supplemental Policy
- The Strength of Signed App Control Policies
- App Control Notes
- How to use Windows Server to Create App Control Code Signing Certificate
- Fast and Automatic Microsoft Recommended Driver Block Rules updates
- App Control policy for BYOVD Kernel mode only protection
- EKUs in App Control for Business Policies
- App Control Rule Levels Comparison and Guide
- Script Enforcement and PowerShell Constrained Language Mode in App Control Policies
- How to Use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Advanced Hunting With App Control
- App Control Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Create Bootable USB flash drive with no 3rd party tools
- Event Viewer
- Group Policy
- How to compact your OS and free up extra space
- Hyper V
- Overrides for Microsoft Security Baseline
- Git GitHub Desktop and Mandatory ASLR
- Signed and Verified commits with GitHub desktop
- About TLS, DNS, Encryption and OPSEC concepts
- Things to do when clean installing Windows
- Comparison of security benchmarks
- BitLocker, TPM and Pluton | What Are They and How Do They Work
- How to Detect Changes in User and Local Machine Certificate Stores in Real Time Using PowerShell
- Cloning Personal and Enterprise Repositories Using GitHub Desktop
- Only a Small Portion of The Windows OS Security Apparatus
- Rethinking Trust: Advanced Security Measures for High‐Stakes Systems
- Clean Source principle, Azure and Privileged Access Workstations
- How to Securely Connect to Azure VMs and Use RDP
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 2
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 3
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 4
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 5
- How To Access All Stream Outputs From Thread Jobs In PowerShell In Real Time
- PowerShell Best Practices To Follow When Coding
- How To Asynchronously Access All Stream Outputs From Background Jobs In PowerShell
- Powershell Dynamic Parameters and How to Add Them to the Get‐Help Syntax
- RunSpaces In PowerShell
- How To Use Reflection And Prevent Using Internal & Private C# Methods in PowerShell

