-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 121
Adding a MySQL target
This page explains the process of adding a new MySQL target host to Warpgate and allowing users to connect to it.
Currently, Wargate can connect to MySQL and MariaDB servers with a username/password via the mysql_native_password auth mode.
As a MySQL protocol server, Warpgate only allows secure (TLS) connections and uses mysql_clear_password auth mode.
Enable the MySQL protocol in your config file (default: /etc/warpgate.yaml) if you didn't do so during the initial setup:
+ mysql:
+ enable: true
+ certificate: /var/lib/warpgate/tls.certificate.pem
+ key: /var/lib/warpgate/tls.key.pemYou can reuse the same certificate and key that are used for the HTTP listener.
Log into the Warpgate admin UI and navigate to Config > Targets > Add target and give the new MySQL target a name:
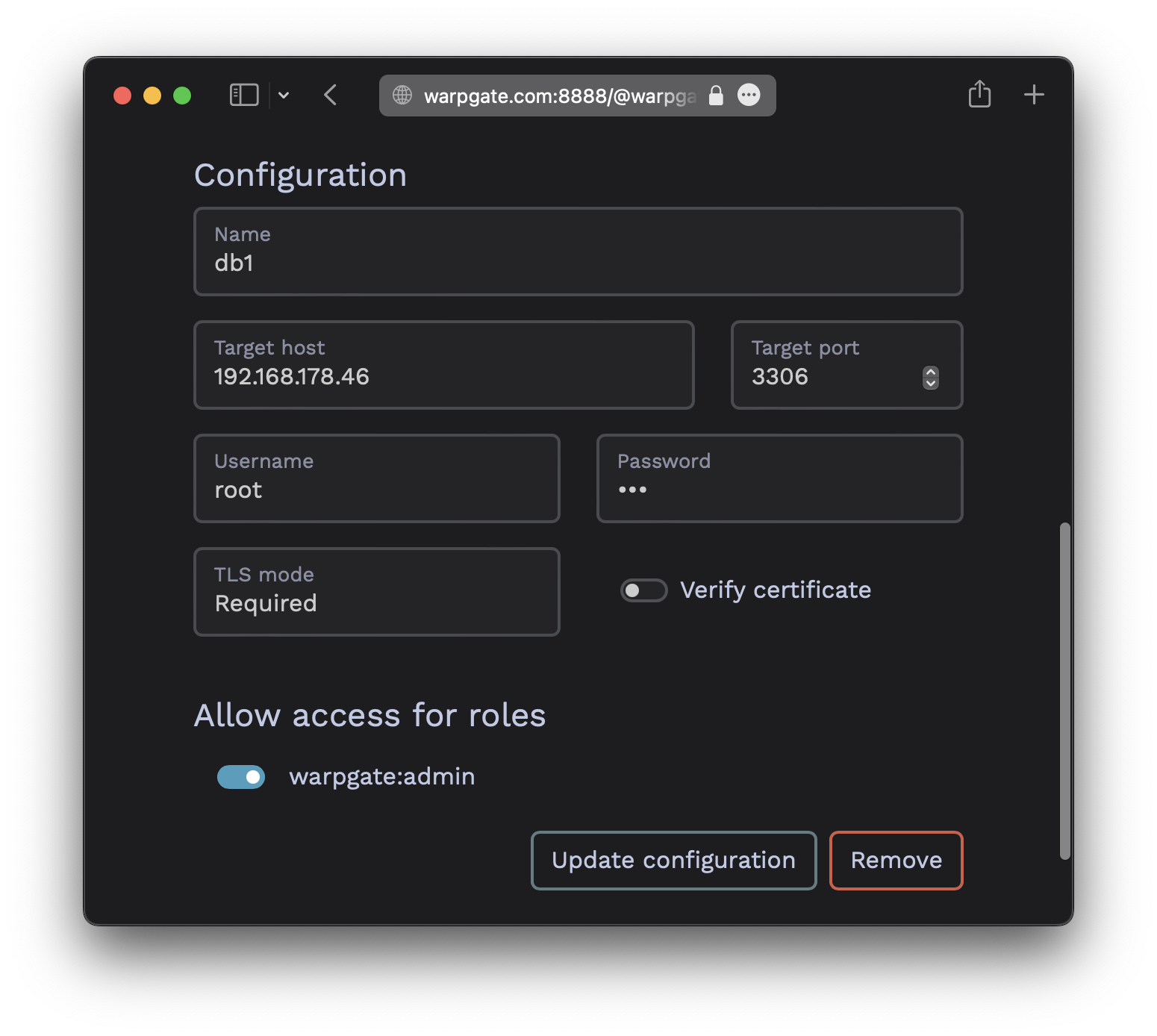
Fill out the configuration:
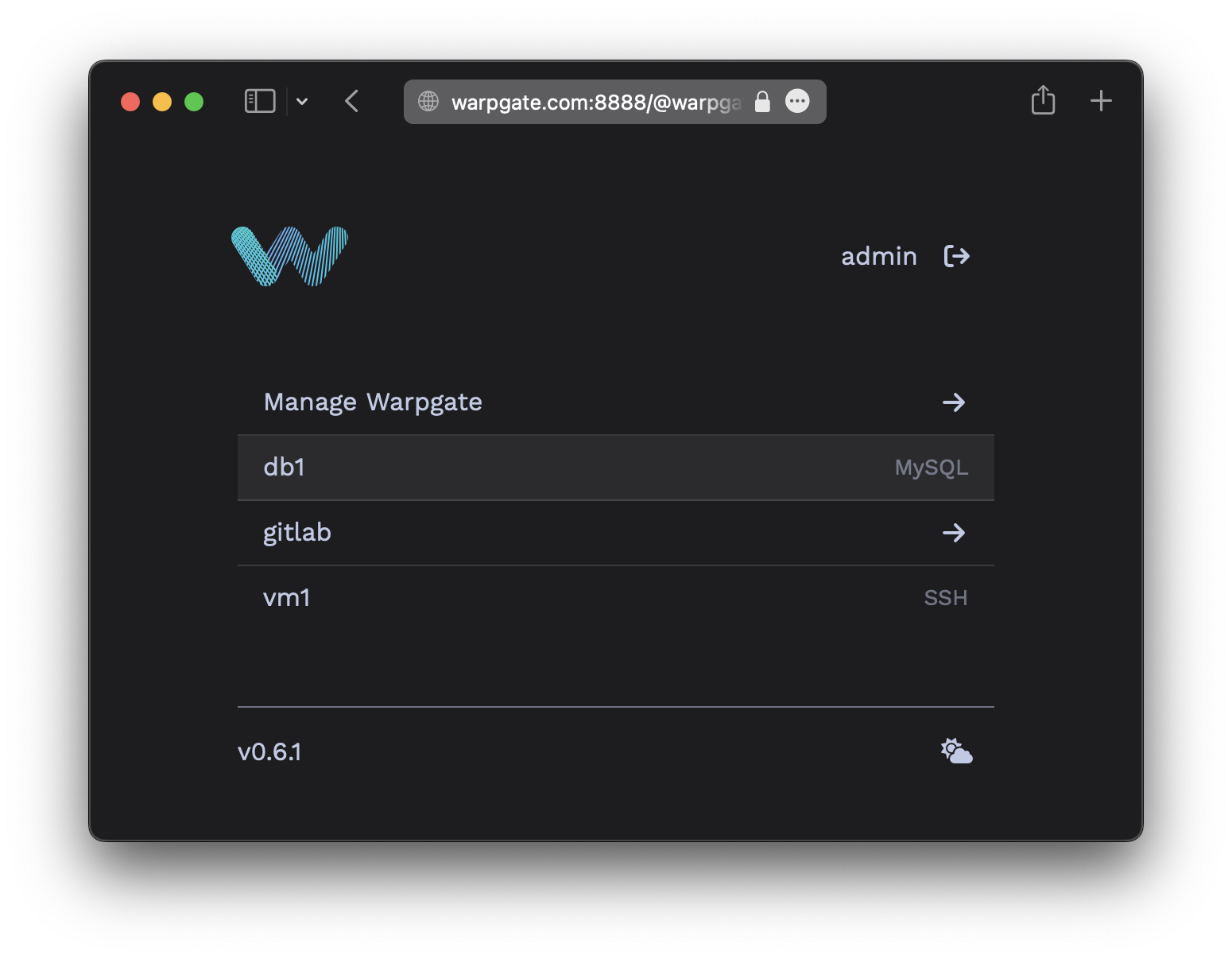
The target should show up on the Warpgate's homepage:
Users will be able to click the entry to obtain connection instructions:
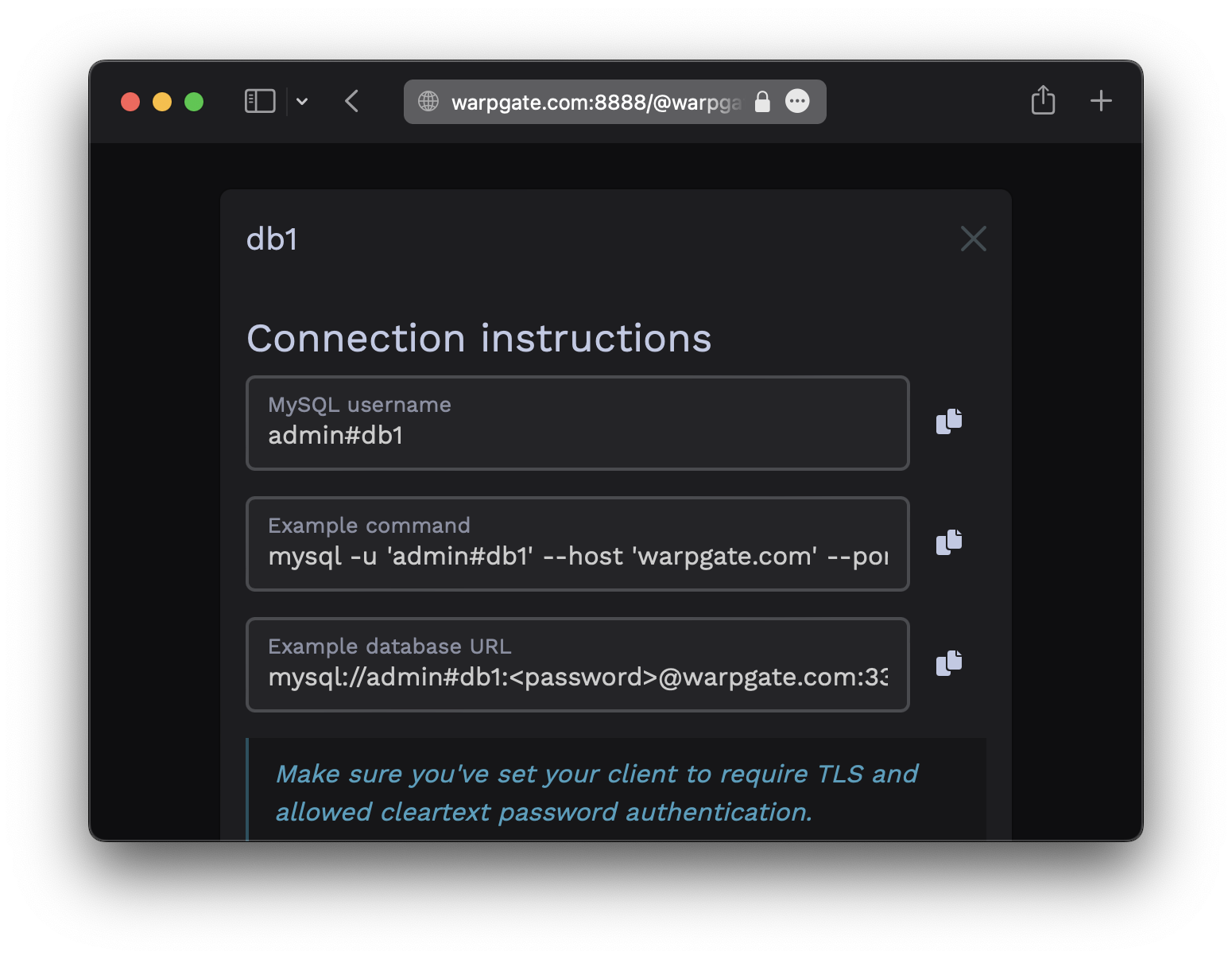
You can now use any MySQL/MariaDB client applications to connect through Warpgate with the following settings:
- Host: the Warpgate host
- Port: the Warpgate MySQL port (default: 33306)
- Username:
admin#<target-name>oradmin:<target-name>, in this example:admin#db1 - Password: your Warpgate admin password
- TLS: enabled
- Cleartext password authentication: allowed
If your client uses a database URL, use: mysql://<username>#<target>:<password>@<warpgate host>:<warpgate mysql port>?sslMode=required
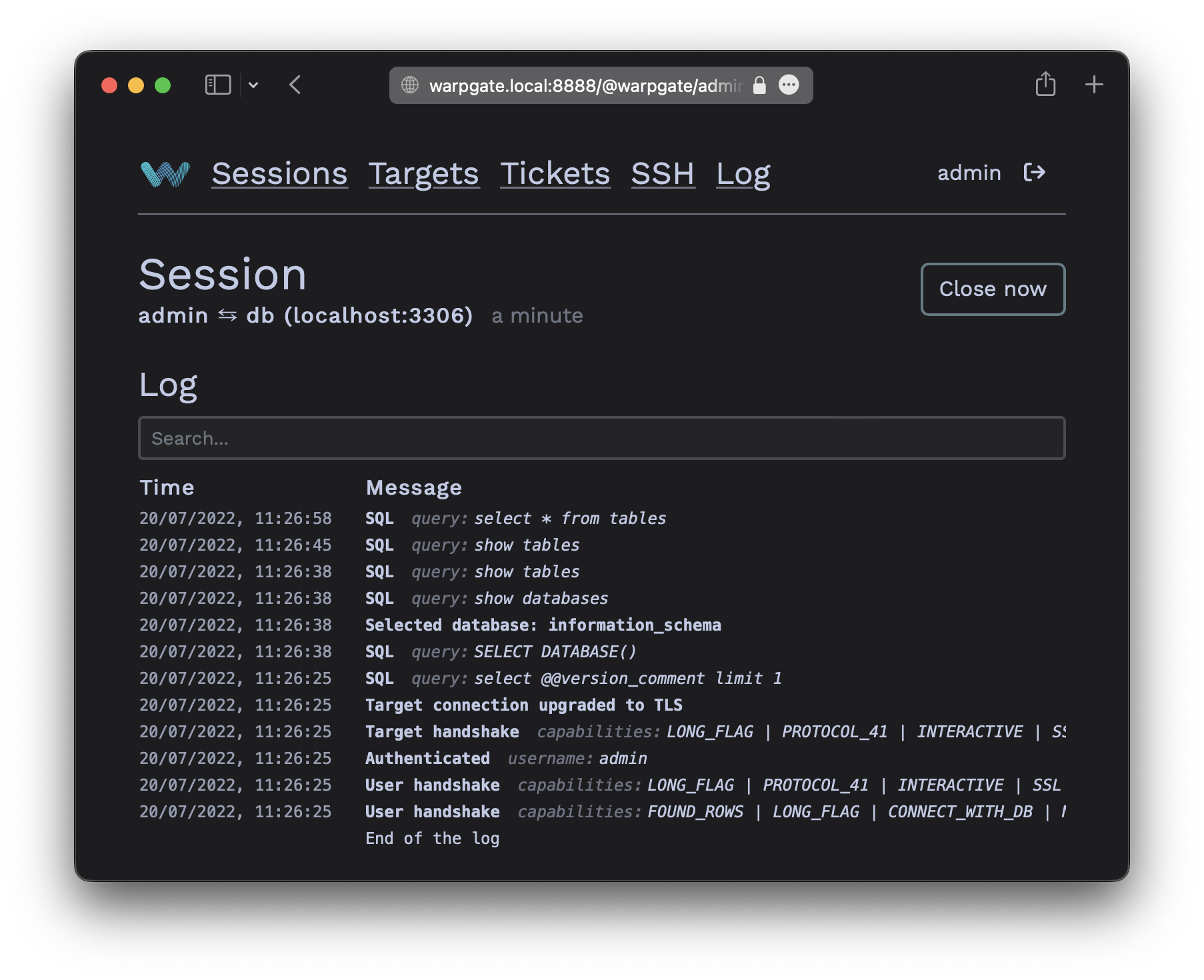
While your MySQL session is running, you'll be able to see its status in the Admin UI, including the query log: