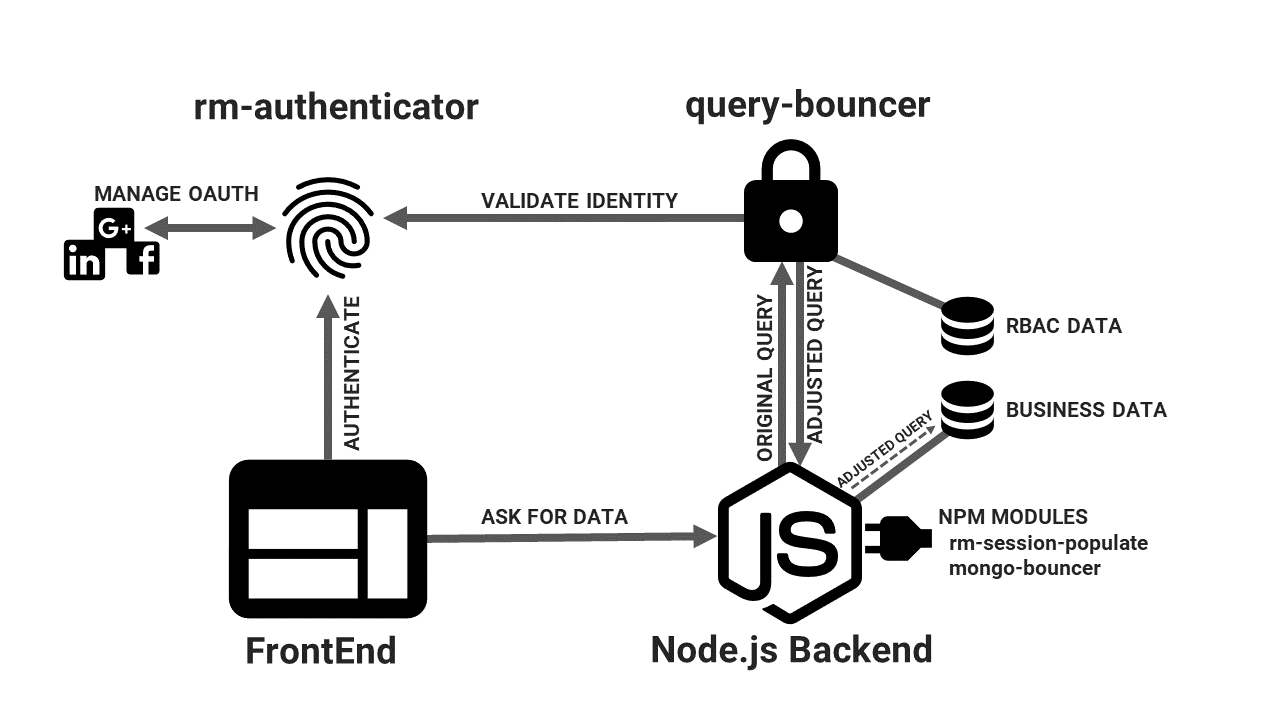
The Mongoose Plugin for Query Bouncer (MongoBouncer) integrates with rm-authenticator, Query Bouncer and rm-session-populate. It's goal is to integrate the Role Based Access Control System you define in Query Bouncer easily in your Backend without having to worry about making the correct http requests and modify queries by yourself. The tasks of these components are
- rm-authenticator: Easy way to authenticate your user with just a Docker Container. Works with different OAuth providers like facebook, linkedin and google+.
- rm-session-populator: Middleware for Express. It will automatically communicate with the Authenticator and add a user object to your Express req with all the information you need
- Query Bouncer: Set up your Role Based Access System with a comfortable REST-API and use it to automatically modify queries and payloads based on your users permissions.
- Query Bouncer Mongoose Plugin: A Plugin that handles all the communication with the authorizer automatically so you can focus on writing your application.
This Overview illustrates a possible architecture for your application and the integration of those 4 components.
Just install with npm
npm i --save query-bouncer-mongoose-pluginYou need a running instance of Query Bouncer to connect to. The Query Bouncer supplies the plugin with the correct queries accordingly to the users permissions. you can see how to set it up here
Query Bouncer will be used to easily set up your roles, permissions and roleAssignments for your Application. It supplies endpoints to send your query and payload to. The Query Bouncer will then validate the information based on your users permissions and will e.g. send back an adjusted query based on the users permissions. So what does that mean. Lets assume we have a collection called blogposts. Each BlogPost has a Title, Description and a Category. The user only has access to BlogPosts of the Category "Cars". So when a request to the Query Bouncer is made with the query to get all BlogPosts The Query
{}will be returned as
{
$or: [
{Category: "Cars"}
]
}In order to not having to utilize the API of rm-authorizer directly mongo-bouncer will handle all that for you. The following paragraphs will show you how to use it.
As this is a mongoose plugin simply initialize the plugin like this. You only need the endpoint of your authorizer. That's it. Now there are two ways of handling your config
import mongoBouncer from "query-bouncer-mongoose-plugin"
mongoose.plugin(mongoBouncer, {
baseUrl: "https://your-authorizer.com"
});Mongoose will only keep the object we set in the basic setup stored and the complete config will be generated automatically on the fly. If you want to have more control and to be able to switch out components like axios we recommend you instantiate your config like this. This is also necessary if you want to use the MockAdapter
import mongoBouncer, { QbConfig } from "query-bouncer-mongoose-plugin"
const config = new QbConfig({
baseUrl: "https://your-authorizer.com"
})
mongoose.plugin(mongoBouncer, config);Now with the nature of mongoose plugins this has to be made before any schemas are initialized (which most of time will be done already). So either wrap your schemas so you make sure that the plugin gets initialized first or set the plugin for each schema you want to use (recommended)
const blogPostSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
Title: "My new Blog Post",
// ...
});
blogPostSchema.plugin(mongoBouncer, {
baseUrl: "https://your-authorizer.com"
});baseUrl: The URL the MongoBouncer that you want to connect to is hosted apiVersion: The Version of the API you want to use. Defaults to v1 axios: You can force the Plugin to use another Axios Instance. This is mainly for testing purposes and not recommended cookieName: By default the Authenticator is set up to give you a cookie named connect.sid. If however you changed that you can also adjust the cookieName here
MongoBouncer will run all the validation before your operations are being executed. As this middleware is currently not available in mongoose plugins for all methods, we currentyl support the following
- create (See Important Information about create)
- find
- findOne
- findOneAndDelete
- findOneAndRemove
- findOneAndUpdate
- findById
- findByIdAndDelete
- findByIdAndRemove
- findByIdAndUpdate
- insertMany
- remove
- update
- updateOne
- updateMany
- deleteOne
- deleteMany
This is an example on how to enalbe MongoBouncer on your model. req refers to the express Request here. The MongoBouncer property needs to be added to the Options Object of your method. Let's take a look at some of those methods
First let's set up a model.
const BlogPostSchema = new Schema({
Title: { type: String, required: true } ,
Description: { type: String },
Category: { type: String, required: true }
});
const BlogPost = mongoose.model('blogpost', BlogPostSchema);Now to create a Document with respect to the permissions you just add the MongoBouncer to the options.
As the Options Object in mongoose is only available if the Document is passed in array please make sure you that even of you just add a single Document you use it in an Array. If you use a single Object the Options Object will be empty internally and as a result Permissions will not be checked!!!
As we stated earlier our authorizer has been set up to allow the user to create BlogPosts only if the category is "Cars". So while this will work just fine.
const post = await BlogPost.create([{
Title: "MyBlogPost",
Category: "Cars",
Description: "Some cool information about my favourite car"
}], {
MongoBouncer : {
Request: req
}
});this
const post = await BlogPost.create({
Title: "MyBlogPost",
Category: "Food",
Description: "Some cool information about my favourite car"
}, {
MongoBouncer : {
Request: req
}
});will throw an Error as the user is not allowed to create Blog Posts in that Category
Let's assume we will now try to find that document again. Again as our fictive setup is that our user will only receive BlogPosts if the Category Cars in this case
BlogPost.find({ Title: "MyBlogPost" }, null, {
MongoBouncer: {
Request: req
}
});we will be returned an array with the Document we added in the Create section
If we now want to update the document we created we do it just the same way. A working update call would look like this
BlogPost.updateOne(
{ Title: "MyBlogPost", Category: "Cars" },
{ Title: "A changed Title"},
{
MongoBouncer: {
Request: req
}
}
);Internally both the Payload and the QueryRestrictions will be checked. So if we use any other Category than Cars nothing will be updated. However in this case no error will be returned but the returned Object by mongoose will just state that nothing matched our Query and nothing was updated. But if we try this e.g.
BlogPost.updateOne(
{ Title: "MyBlogPost", Category: "Cars" },
{ Title: "A changed Title", Category: "Food" },
{
MongoBouncer: {
Request: req
}
}
);an error will be thrown as a Document will be returned but we are not allowed to invoke the changes we are trying to make.
Now if you just add a Request MongoBouncer will run. To stop that from happening later down the road, even if you have already injected the Request into the options you can still disable MongoBouncer by setting the Disabled field to true. So a request like this will not run MongoBouncer
import { OperationOptionsInput } from "query-bouncer-mongoose-plugin"
const myService = (opts:OperationOptionsInput) => {
// opts is already filled with MongoBouncer: { Request }
if(someConditionApplies()){
bouncerOpts.MongoBouncer.Disable = true;
}
BlogPost.updateOne(
{ Title: "MyBlogPost", Category: "Cars" },
{ Title: "A changed Title", Category: "Food" },
opts
);
}When you test you don't want to have a query bouncer running, so you could manually switch out the axios instance with a mock. However we provide our own MockAdapter for the QueryBouncer. If you want to mock a schmema with an existing config please make sure you instantiated this config as described under advanced
my-model.ts
import { Model, Schema } from 'mongoose'
import MongoBouncer, { QbConfig } from 'query-bouncer-mongoose-plugin'
const schema = new Schema({
Title: String,
Category: String
});
// It is important that you instantiate as a new class or the tests will not work
const config = new QbConfig({
baseUrl: 'http://some-where.com/'
})
schema.plugin(MongoBouncer, config);
const model = Model('test', schema)
export default model;
export { config };my-model.spec.ts
import { MockAdapter, QbConfig, } from 'query-bouncer-mongoose-plugin';
import mymodel, { config } from './my-model.ts';
it('should do something', async () => {
// Prepare
const qBouncer = new MockAdapter(config);
qBouncer.mock({
collection: mymodel.collection.collectionName,
right: 'read',
response: {
query: { $or: { Category: 'Food' } }
}
});
// Execute
/// Your Test Code
})