The link to the website is : http://flask-alb-1207280611.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com/
Description of the functionality :
This cloud application was built on the AWS Educate Account (which is a limited access account).
The application consists of two containers : Flask-Home and Flask-Api , which run in the same EC2 instance.
The Flask-Home container can be used by just entering the url of the app as the route it is using is just "/" . The Home container connects to the RDS(Mysql) database and displays all the data in a table format.
The Flask-Api container can be used by using the route "/api/* " . The * refers to the three text processing operations that can be done by this cloud app.
- Spelling correction : The user can enter a text and also an id which can be used as tag to mark the text entered, and on submitting the text the app will correct all the spelling mistakes in it. The route for this functionality is "/api/spell" .
- Space correction : The user can enter text which can contain words without spaces, and the functionality will split the words and save the text with proper spaces. The route for this functionality is "/api/space" .
- Translation : The user can enter text in any language and the functionality will translate the text into English by using the Google Translate API . The route for this functionality is "/api/translate" .
Once the user performs any of the above mentioned actions the processed text gets saved in the database along with the original text and id appended with the date and time of the action performed. This data can be seen by visiting the home page, which uses the route "/" .
The application uses a Application Load Balancer(ALB), and the request goes to the ALB endpoint and then according to the ALB rules it gets routed to the '/ ' or the '/api/*' route .
Couldn't enable autoscaling as we don't have the access to do that in the AWS Educate account.
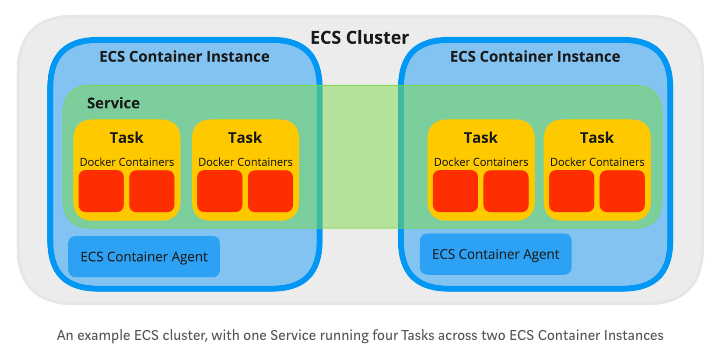
Below is an example image(not exact representation of the implementation) which shows how the cloud application is structured :
Commands used to create containers and push to ECR:
- create container image: sudo docker build -t flask-api .
- create repository in the ECR : aws ecr create-repository --repository-name ecs-flask-api
- login in the ECR : sudo $(aws ecr get-login --no-include-email --region us-east-1)
- tag the image : sudo docker tag flask-api 510068942181.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/ecs-flask-api
- push the images to the ECR (Elastic Container Repository) : sudo docker push 510068942181.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/ecs-flask-api
to login we first need to update the credentials, which can be found in the AWS account welcome page after login , in the "account details" button . The aws_access_key_id , aws_session_access_key, aws_session_token values need to be updated in the "~/.aws/credentials" file to be able to login in the ECR through the terminal.
Additional Detailed Description of the Services that I have used :
So while developing this application i started exploring the various amazon aws services and so I got inspired to use them build something, so I have used amazon ECS , ECR , RDS, EC2 , ALB and CloudWatch to build this application (couldn’t use CloudWatch for autoscaling because of access error).
Some of the services I couldn’t use because of the restricted nature of the account. Like Auto Scaling was not allowed for this account . I tried creating an amazon CloudWatch alarm and set autoscaling according to that but it showed me access error.
The Description of the various services that I have used is below (the architecture that I have implemented in the cloud can be scaled to incorporate multiple tasks on multiple EC2 instances if required) :
ECR is Elastic Container Registry where you can easily store, manage and deploy your container images . It is integrated with amazon ECS . It is even encrypted , redundant and highly available. I have used ECR to upload the container images and then if I do any changes while building the application code , I can then just rebuild the image and login into ECR from the terminal and upload the image, and ECR will tag this new image as the latest one and keep the older images in the repository as history and untag them . This way the ECR is also acting as a version control.
ECS is playing the major role in the cloud platform. It runs and manages the docker enabled applications across a logical group of amazon EC2 instances. So, basically you can instruct the ECS to launch 3 or say 5 containers of an image and the ECS automatically checks which EC2 instance it can run it in and launches the container in it.ECS also keeps track of the instances and how much resources they have and what they are running.
ECS Cluster is a logical group of EC2 instances which will be running the containers and ECS agent.
The Amazon ECS Container Agent is a component of Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS)
- responsible for managing containers and their state on behalf of Amazon ECS.
- The agent would receive requests from ECS to launch more containers and will perform this action .
- ECS uses this agent to communicate with the docker daemon on the EC2 instances
- The ECS agent gets created on its own and we don't have to manually create it.
Once we have a cluster we can create tasks that run in the cluster. A Task basically contains the metadata (configurations) required to launch a single instance of the application container as a task on a machine.
- Tasks specify the Docker image for each container
- CPU and memory requirements for each container
- Data storage
- Networking and port settings
- We can also mention the environment variables in a task
I have given the database connection settings (username,password,etc) while creating the Task. This way I don’t have to expose the password in the code and I can freely upload the code in github.
So now with these tools we can launch a container in an EC2 instance and with specific configurations mentioned in the Task . But still you will be manually running the tasks , and if the Task fails you will be manually restarting it. And you would also want to implement autoscaling.
So, to resolve this we have the capability of creating a Service,
A Service can :
- Manage long -running workflows which need to be up at all times
- Automate the RUN-TASK process
- Actively monitor running tasks
- Restart tasks if they fail
- It also has a task placement strategy where you can specify where to place the copies of your task, so for example you can mention over there to spread the tasks across availability zones to make it fault tolerant or even out the load .
ECS service keeps track of the tasks that are running and if for some reason if a task stops it will initiate a new task as replacement and will try to maintain the minimum count of tasks that we mentioned in the service. If you update anything, the service will manage stopping the old tasks and launch new tasks. Health checks ensure that new tasks are stable before launching the new tasks. And by default ECS will leave old tasks running until new tasks up and running. So if i try to roll out new task definition which somehow results in unhealthy Tasks even then my my ECS will not stop the Old Tasks so that my application keeps on running and doesn’t go offline. SO what I understand from all this is that ECS is acting like a control plane that takes your docker instances and the connected pieces and then turn them into an automated deployment platform.
I tried to implement autoscaling too, but due to the account restrictions I couldn’t, so below is the screenshot of the aws :
I am also using aws RDS which is the Relational Database Service from amazon . I have installed a MYSQL server , and this runs in a separate EC2 instance.
References :
-
Deploying Flask app to ECS : https://www.bogotobogo.com/DevOps/Docker/Docker-Flask-ALB-ECS.php
-
Learn Flask for Python : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z1RJmh_OqeA
-
AWS fundamentals : https://www.coursera.org/learn/aws-fundamentals-going-cloud-native
-
Elastic Load Balancers : https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/application/introduction.html
-
Launching RDS database instance : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzCgeRxSzy4&t=957s
-
Gentle Introduction to How AWS ECS Works with Example Tutorial : https://medium.com/boltops/gentle-introduction-to-how-aws-ecs-works-with-example-tutorial-cea3d27ce63d