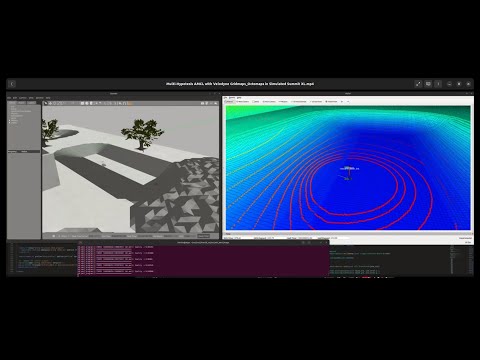
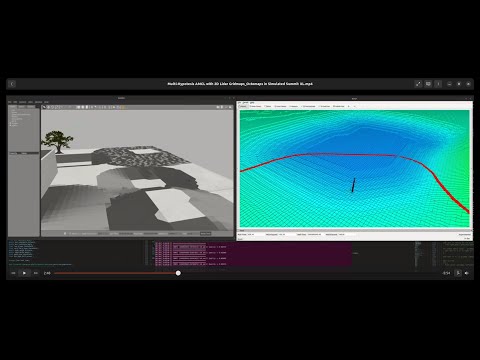
MH-AMCL is a fully functional localization algorithm implementation with Nav2. The main feature is that it maintains several hypotheses about the robot's position. The algorithm periodically generates new hypotheses on positions where the robot could be, based on the latest laser and map reading. This allows:
- Total unknown the position of the robot.
- Recover from erroneous estimates and hijacks.
The version in this repo is for non-planar environments, using the Extended Map Server
This package requires the Rolling distribution, as it is in sync with Nav2, whose main branch uses Rolling.
Just clone this repo in the workspace and build as usual:
colcon build --symlink-install
Coomin Soon
-
grid_map_map(grid_map_msgs/msg/GridMap): The environmen gridmap containig elevation and occupancy layers. -
octomap_map(octomap_msgs/msg/Octomap): The environmen octomap. -
initialpose(geometry_msgs/msg/PoseWithCovarianceStamped): Used for reset the robot's position from Rviz2. -
sensor_msgs/msg/LaserScanandsensor_msgs/msg/PointCloud2depending on the configuration
amcl_pose(geometry_msgs::msg::PoseWithCovarianceStamped): The robot's pose with the covariance associated from the best hypothesis.particle_cloud(nav2_msgs::msg::ParticleCloud): The particles from the best hypothesis.poses(visualization_msgs::msg::MarkerArray): All the particles from all the hypotheses, each one with a different color.
use_sim_time(bool, False): Use the robot's clock or the one coming from the/clocktopic.max_particles(int, 200): The maximum number of particles for each hypothesis.min_particles(int, 200): The minimum number of particles for each hypothesis.particles_step(int, 30): Particles' variation increasesparticles_stepwhen the estimation is bad and decreases when it is good.init_pos_x(double): The initial X position of the robot, if known.init_pos_y(double): The initial Y position of the robot, if known.init_pos_yaw(double): The initial Yaw position of the robot, if known.init_error_x(double): The initial X uncertainty of the robot.init_error_y(double): The initial Y uncertainty of the robot.init_error_yaw(double): The initial Yaw uncertainty of the robot.translation_noise(double, 10%): The error percentage coming from the translation component.rotation_noise(double, 10%): The error percentage from the rotational component.rotation_noise(double, 10%): The error percentage from the rotational component.distance_perception_error(double, 0.01): The error in meters of the sensor when reading distances.reseed_percentage_losers(double, 90%): The percentage of particles to be replaced when reseeding.reseed_percentage_winners(double, 3%): The percentage of particles that generate new particles when reseeding.multihypothesis(bool, true): Use multiples hypothesis, or only one - the created initially.max_hypotheses(int, 5): Maximum number of concurrent hypotheses.min_candidate_weight(float, 0.5): Minimum quality of a candidate to be considered for a new hypothesis.min_candidate_distance(double, 1.0): Minimum distance to an existing hypothesis to be considered for a new hypothesis.min_candidate_angle(double, PI/2): Minimum angle to an existing hypothesis to be considered for a new hypothesis.low_q_hypo_thereshold(float, 0.25): Under this threshold, a hypothesis is considered low quality and should be removed if there is a better candidate.very_low_q_hypo_thereshold(float, 0.10): A hypothesis is considered very low quality and should be removed under this threshold.hypo_merge_distance(double, 0.3): Distance under consideration to merge two hypotesese (angle and distance shpuld meet).hypo_merge_angle(double, 0.5): Angle to consider merging two hypotheses (angle and distance should meet).good_hypo_thereshold(double, 0.5): Threshold to consider a hypothesis to be selected as the newly selected hypothesis for the algorithm's output.min_hypo_diff_winner(double, 0.3): An hypothesis should have a qualitymin_hypo_diff_winnerbetter than the currently selected hypothesis to be the newly selected hypothesis. Low values could lead to continuing changes between the two hypotheses. High values could make it impossible to consider other hypotheses.matchers(String[], ""): List of matchers, which provides hypothesis of other prabable robot positions.type(String): type of matcher.- For type ==
matcher2d:topic(String): Topic of the perception source used
correction_sources(String[], ""): List of perception sources.type(String): Type of the corrector in [laser,pointcloud]- For type ==
laser: topic(String,/perception: Topic of the perception sourcedistance_perception_error(double, 0.05): Mean of the expected perception error.- For type ==
pointcloud: topic(String,/perception: Topic of the perception sourcedistance_perception_error(double, 0.05): Mean of the expected perception error.max_perception_distance(double, 10.0): Maximun range of the sensor.point_step(double, 1): The point step for a sensor reading. 1 means that all the readings will be used. 50 means that only one point out of 50 is used. This is used to reduce the CPU load.
Example:
mh_amcl:
ros__parameters:
use_sim_time: True
max_particles: 200
min_particles: 30
particles_step: 30
init_pos_x: 0.0
init_pos_y: 0.0
init_pos_z: 0.3
init_pos_yaw: 0.0
init_pos_pitch: 0.0
init_pos_roll: 0.0
init_error_x: 0.1
init_error_y: 0.1
init_error_z: 0.1
init_error_yaw: 0.05
init_error_pitch: 0.01
init_error_roll: 0.01
translation_noise: 0.1
rotation_noise: 0.1
reseed_percentage_losers: 0.9
reseed_percentage_winners: 0.03
multihypothesis: False
max_hypotheses: 5
min_candidate_weight: 0.5
min_candidate_distance: 1.0
min_candidate_angle: 1.57
low_q_hypo_thereshold: 0.25
very_low_q_hypo_thereshold: 0.10
hypo_merge_distance: 0.3
hypo_merge_angle: 0.5
good_hypo_thereshold: 0.5
min_hypo_diff_winner: 0.3
matchers: ['matcher_0']
matcher_0:
type: matcher2d
topic: /front_laser/scan
correction_sources: ['front_laser']
front_laser:
type: laser
topic: /front_laser/scan
distance_perception_error: 0.05
debug: true
rear_laser:
type: laser
topic: /rear_laser/scan
distance_perception_error: 0.05
pc_0:
type: pointcloud
topic: /velodyne_points
distance_perception_error: 0.1
max_perception_distance: 10.0
point_step: 50
The bottleneck is in the octomap function RayTrace. Build octomap with (OpenMPI)[https://www.open-mpi.org/] support to improve it.
@article{https://doi.org/10.1002/rob.22353,
author = {Rico, Francisco Martín and Hernández, José Miguel Guerrero and Pérez-Rodríguez, Rodrigo and Peña-Narvaez, Juan Diego and Gómez-Jacinto, Alberto García},
title = {Open source robot localization for nonplanar environments},
journal = {Journal of Field Robotics},
volume = {n/a},
number = {n/a},
pages = {},
keywords = {field robotics, localization, mobile robotics, navigation, ROS},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1002/rob.22353},
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/rob.22353},
eprint = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/rob.22353},
}