Add support for Apple's AppIntents framework to your Flutter application. For details on how to add integration with Siri, Shortcuts app, and Apple Intelligence, see Recipes.
Copy and paste the following snippet into your shell when in the target project directory.
dart pub add intelligenceTo add support for AppIntents framework, you will have to perform one-time setup which differs for different use-cases. See Recipes for more details.
Once set up, the plugin will let you act on each App Intent trigger.
E.g. while setting the selection listener in a Stateful widget:
Intelligence().selectionsStream().listen(_handleSelection);Note: the
Intelligenceclass behaves like a singleton, so you do not have to maintain the same class instance throughout the app/use-case.
List of practical applications of intelligence in your project. Click the Details dropdown to see the implementation.
Will let your app to be automated via Shortcuts workflow.
- Open the iOS project in Xcode
- Add a new Swift file and paste:
import AppIntents
import intelligence
struct OpenHeartIntent: AppIntent {
static var title: LocalizedStringResource = "Draw a Heart"
static var openAppWhenRun: Bool = true
@MainActor
func perform() async throws -> some IntentResult {
IntelligencePlugin.notifier.push("heart")
return .result()
}
}Switch out the struct's name, title, and the .pushed value to ones that match your use-case.
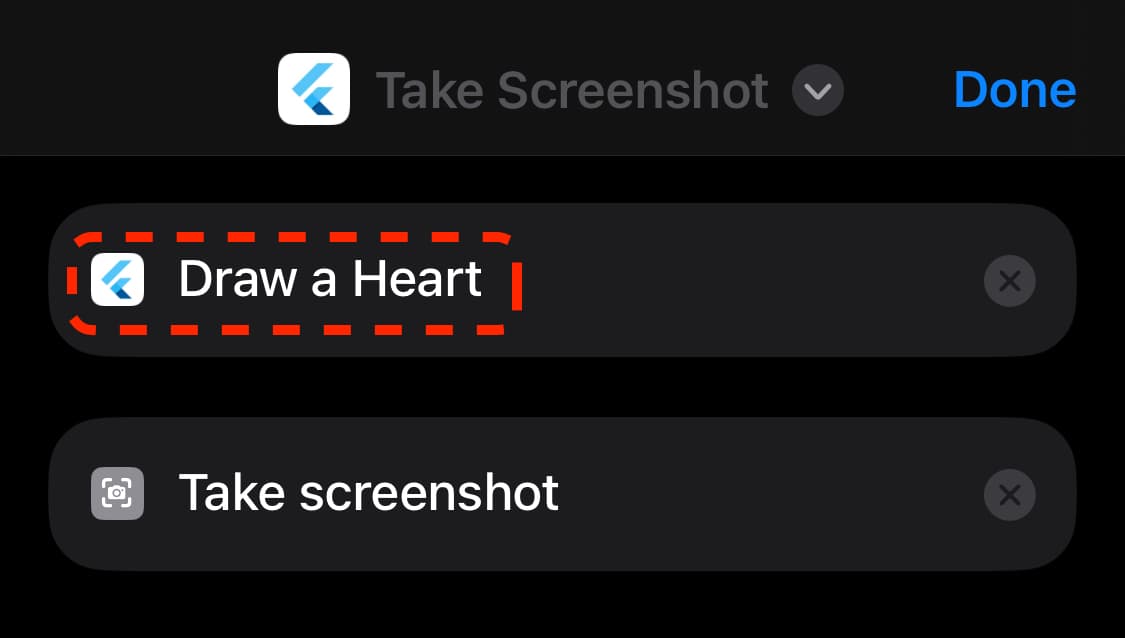
Once added, your App Intent will show up in the Shortcuts app:
To trigger the App Intent declared above by speaking a specific phrase to Siri, append:
struct OpenHeartShortcuts: AppShortcutsProvider {
static var appShortcuts: [AppShortcut] {
AppShortcut(
intent: ExampleAppIntent(),
phrases: [
"Draw my favorite shape in \(.applicationName)"
]
)
}
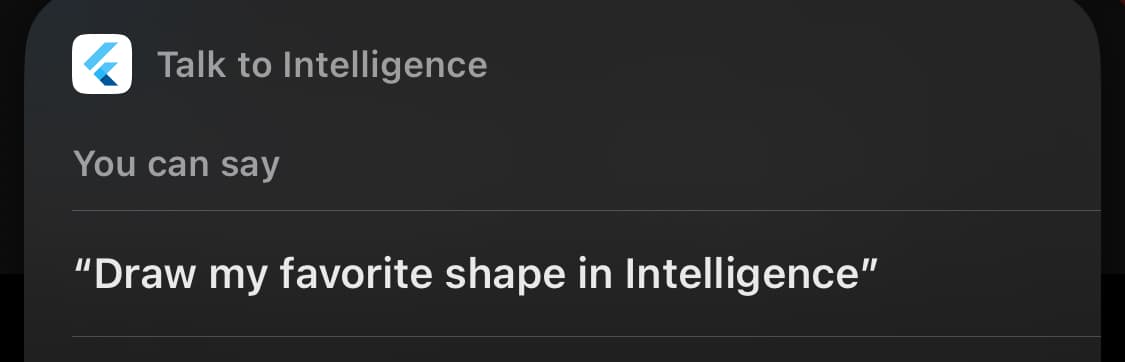
}Once deployed to the device, Siri can understand the trigger phrase and run the App Intent declared above:
Siri is capable of understanding the entities your application revolves around, letting you implement App Intents with variables.
See full implementation in the example project.
- Define an
AppEntity. It should contain a unique identifier and a text representation fields, as follows:
import CoreSpotlight
import AppIntents
struct RepresentableEntity: AppEntity {
static var defaultQuery: RepresentableQuery = RepresentableQuery()
static var typeDisplayRepresentation = TypeDisplayRepresentation(name: "Shape")
var displayRepresentation: DisplayRepresentation {
DisplayRepresentation(stringLiteral: representation)
}
let id: String
let representation: String
}
extension RepresentableEntity: IndexedEntity {
var attributeSet: CSSearchableItemAttributeSet {
let attributes = CSSearchableItemAttributeSet()
attributes.displayName = self.representation
return attributes
}
}- Create a matching
EntityQuery, like so:
import AppIntents
import intelligence
struct RepresentableQuery: EntityQuery {
func entities(for identifiers: [String]) async throws -> [RepresentableEntity] {
return IntelligencePlugin.storage.get(for: identifiers).map() { item in
return RepresentableEntity(
id: item.id,
representation: item.representation
)
}
}
func suggestedEntities() async throws -> [RepresentableEntity] {
return IntelligencePlugin.storage.get().map() { item in
return RepresentableEntity(
id: item.id,
representation: item.representation
)
}
}
}
extension RepresentableQuery: EnumerableEntityQuery {
func allEntities() async throws -> [RepresentableEntity] {
return IntelligencePlugin.storage.get().map() { item in
return RepresentableEntity(
id: item.id,
representation: item.representation
)
}
}
}- Create an
AppIntentusing the entity as a parameter.
import AppIntents
import intelligence
struct ExampleAppIntent: AppIntent {
static var title: LocalizedStringResource = "Draw shape"
static var openAppWhenRun: Bool = true
@Parameter(title: "Shape")
var target: RepresentableEntity
@MainActor
func perform() async throws -> some IntentResult {
IntelligencePlugin.notifier.push(target.id)
return .result()
}
static var parameterSummary: some ParameterSummary {
Summary("Draw \(\.$target)")
}
}
struct AppShortcuts: AppShortcutsProvider {
static var appShortcuts: [AppShortcut] {
AppShortcut(
intent: ExampleAppIntent(),
phrases: [
"Draw a \(\.$target) in \(.applicationName)"
]
)
}
}- In your
AppDelegatefile, add the following code to thedidFinishLaunchingWithOptionsmethod:
IntelligencePlugin.storage.attachListener {
AppShortcuts.updateAppShortcutParameters()
}
if #available(iOS 18.0, *) {
IntelligencePlugin.spotlightCore.attachEntityMapper() { item in
return RepresentableEntity(
id: item.id,
representation: item.representation
)
}
}- In your Dart code, use the
.populatemethod to let the operating system know about the entities available in your app:
await IntelligencePlugin().populate(const [
Representable(representation: 'Heart', id: 'heart'),
Representable(representation: 'Circle', id: 'circle'),
Representable(representation: 'Rectangle', id: 'rectangle'),
Representable(representation: 'Triangle', id: 'triangle'),
]);Note: each call to
.populateoverwrites previous entities. Call.populate([])once the entities are not accessible anymore, e.g. after a logout.
Result:


