Testing was done in Ubuntu 22.04 with ROS2 Humble and Gazebo Fortress, ymmv with different setups.
First install docker engine: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/
Then clone this repository and build the Docker image
git clone https://github.com/mazm0002/rover_sim.git
cd rover_sim
docker build -t ros_gazebo .Then install NVIDIA container toolkit in order to use a dedicated GPU within the container: https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/container-toolkit/latest/install-guide.html
Finally start the Docker container, enter the goal pose, then this should open the Gazebo GUI as well as Rviz2 with the SLAM map
Important
This command needs to be run while in the rover_sim folder
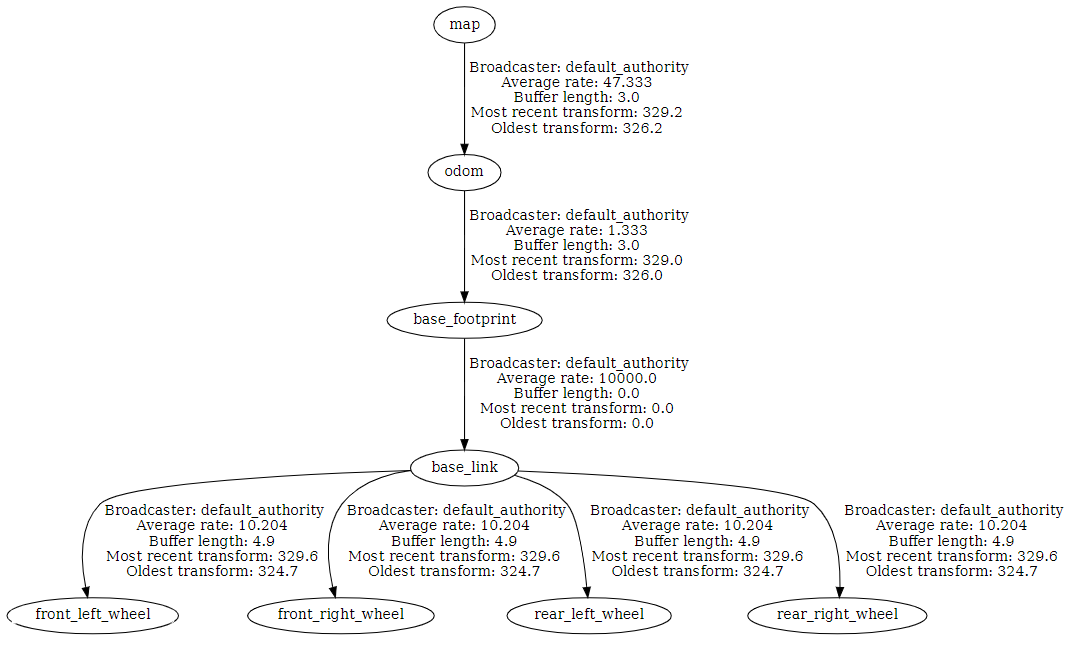
sudo docker run -it --device=/dev/dxg -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY --env="QT_X11_NO_MITSHM=1" --volume="/tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:rw" -e MESA_D3D12_DEFAULT_ADAPTER_NAME=NVIDIA --gpus all --mount src=$(pwd),target=/catkin_ws,type=bind ros_gazeboThis simulation uses the Moon World provided by AMR robots as well as the X1 Config 6 Model provided by Open Robotics. Obstacles are randomly spawned into the world around the robot. In order to simulate the sensors in the robot model (lidar and imu), the ignition::gazebo::systems::Sensors plugin was added to the sdf. Additionally, the ignition::gazebo::systems::DiffDrive plugin was added to compute odometry information as well as publish the odom->base_footprint transform that is necessary to compute the SLAM map. This information is transported from Gazebo to ROS using the ros_gz_bridge package. The robot_state_publisher package utilised the rover's sdf file to compute transforms from each wheel back to the base_link. The odometry transform as well as transforms for each link can then be used by SLAM to compute a transform to the Map fram, giving us a complete Transform tree as shown below:
 slam_toolbox in order to localise the rover's position, as well as determine it surroundings using lidar messages. The Navigation2 stack is then utilised to enable autonomous navigation to a user defined goal pose.
slam_toolbox in order to localise the rover's position, as well as determine it surroundings using lidar messages. The Navigation2 stack is then utilised to enable autonomous navigation to a user defined goal pose.
- This implementation is currently incomplete, the robot does not follow the Nav2 Goal due to issues with the timestamps in Lidar sensor measurements.
- The lidar output is currently attached to the base_link frame, but since the actual lidar is not located in that position, this can lead to inaccuracies in the SLAM output. This can be fixed by creating a new link for the lidar that sits in the correct position, as well as a joint from the lidar to base_link.
- A camera is available in the model, but not currently utilised. The appropriate gazebo plugin has to be added to the sdf, then the messages haved to be bridged to ROS in order to utilise this data.
- The ignition DiffDrive plugin is limited in comparison to ros2 control which can be added in the future to access more controllers and options, but this might require conversion from sdf to urdf.
- Testing was done in WSL with access to a dedicated GPU. If using a virtual machine ensure that your GPU is passing through.