-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 49
examples
- Invoking Workflow Examples
- Process Definitions Examples
- Service Task
- Script Task
- Conditional Flow
- Input Fields
- Multiple Start Event
- Business Rule Task
- Script Extensions
- Timer Event
- Multi-instances Tasks
- SubProcess
- Call Process
- Message Flow
- Throwing and Cathcing Messages
- Input and Output Data Handling
- Gateway
- Event Based Gateway
- Boundary Events
- UserTask Assignment
To Invoke a process from your code:
const { configuration } = require('../configuration.js');
const { BPMNServer, Logger } = require('bpmn-server');
const logger = new Logger({ toConsole: true });
const server = new BPMNServer(configuration, logger);
const api = new BPMNAPI(server));
let response=await api.engine.start('Leave Request',{type:'Vacation'},SystemUser);
const items = response.items.filter(item => {
return (item.status == 'wait');
});
items.forEach(item => {
console.log(` waiting for <${item.name}> -<${item.elementId}> id: <${item.id}> `);
});
console.log('Invoking Buy');
response = await api.engine.invoke({instanceId: response.execution.id, elementId: 'task_Buy' },
{ model: 'Thunderbird', needsRepairs: false, needsCleaning: false },SystemUser);
console.log("Ready to drive");
response = await api.engine.invoke({ instanceId: response.execution.id, elementId: 'task_Drive' },{},SsytemUser);
console.log(`that is it!, process is now complete status=<${response.execution.status}>`) const api = new BPMNAPI(new BPMNServer(configuration,new Logger({ toConsole: false}),{cron:false}));
console.log('starting serviceTask');
let response=await api.engine.start('serviceTask', { v1: 1, v2: 2 }, SystemUser, {noWait:true});
console.log('immediate response id',response.instance.id);In the above example; engine.start return immediatly, but other nodes will continue to execute
starting serviceTask
immediate response id d7df99ab-f0b5-4fdf-8ac3-2701d0bf9b79
add service start: { v1: 1, v2: 2 }
Add Service 5 3
Add Service 33 25
delaying ... 5000
delayed is done.
appDelegate service1 is now complete input: { repeat: '100', inputVar2: undefined } output: 1 item.data { v1: 1, v2: 2, result: 8, result2: 158 }
service1 end: { v1: 1, v2: 2, result: 8, result2: 158 }In Process definition (.bpmn file), use implementation attribute to define name of JavaScript/TypeScript Method to perform the Task:
<bpmn:serviceTask id="serviceTask" name="Service Task" implementation="service1">
...
</bpmn:serviceTask>class AppServices {
// for services that are not defined
async serviceCalled(item) {
}
async service1(item) {
seq++;
await delay(3000 -(seq * 100) , 'test');
item.log("SERVICE 1" + item.token.currentNode.id);
}
} <bpmn2:scriptTask id="Activity_06typtl" name="script" scriptFormat="JavaScript">
<bpmn2:script>
this.log('testing from <testing> the inside: '+data.loopKey);
</bpmn2:script>
..
</bpmn2:scriptTask> <bpmn:sequenceFlow>
<bpmn:conditionExpression xsi:type="bpmn:tFormalExpression" language="JavaScript">
$(data.needsCleaning=="Yes")
</bpmn:conditionExpression>
..
<bpmn:userTask id="task_Buy" name="Buy">
<bpmn:extensionElements>
<camunda:formData>
<camunda:formField id="needsRepairs" label="Repairs Required?" type="boolean" />
<camunda:formField id="needsCleaning" label="Cleaning Required?" type="boolean" />
</camunda:formData>
</bpmn:extensionElements>
...
</bpmn:userTask>
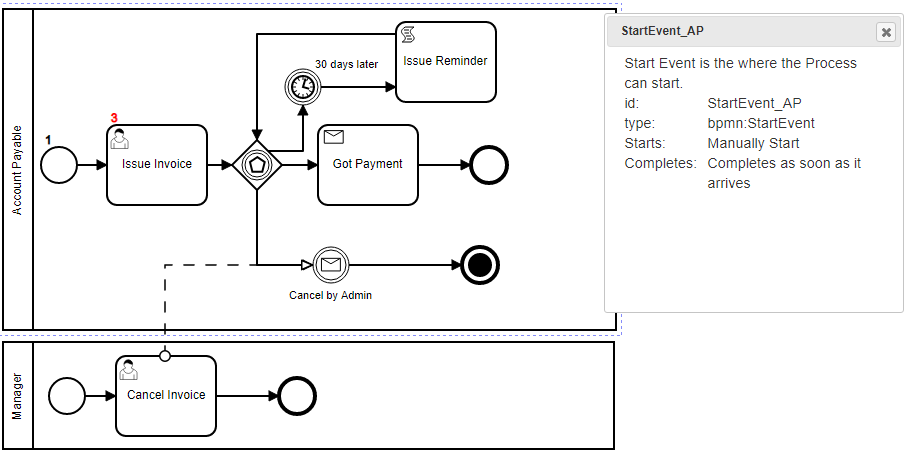
When a definition/process has multiple start node, you need to specify the start node when starting the process:
From the Web UI:
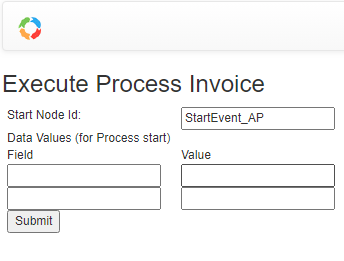
From API:
response = await api.engine.start('invoice',
{ reminderCounter: 0, caseId: caseId}, user, {startNodeId:'StartEvent_AP'});BPMN-Server supports Business Rules implemented through DMN-Engine Business Rules can be defined as a Decision Table as in this example:
Decision Table is called through
<bpmn2:businessRuleTask id="Task_1lcamp6" name="Vacation" camunda:decisionRef="Vacation">This will load the file 'Vacation.json' form the Processes folder as defined in configuration.js
Scripts can be added to listen to two events:
- Start before the Task is executed
- End after the task is executed
In this example we are adding a script to bpmn:startEvent
<bpmn2:extensionElements>
<camunda:executionListener event="start">
<camunda:script scriptFormat="JavaScript">
console.log("This is the start event");
data.records=[1,2,3];
console.log(data);
</camunda:script>
</camunda:executionListener>
<camunda:executionListener event="end">
<camunda:script scriptFormat="JavaScript">
console.log("This is the end event");
</camunda:script>
</camunda:executionListener>
</bpmn2:extensionElements>
<bpmn:intermediateCatchEvent id="Event_timer">
<bpmn:incoming>Flow_1sg7v2d</bpmn:incoming>
<bpmn:outgoing>Flow_1nku8og</bpmn:outgoing>
<bpmn:timerEventDefinition id="TimerEventDefinition_07xu06a">
<bpmn:timeDuration xsi:type="bpmn:tExpression">PT2S</bpmn:timeDuration>
</bpmn:timerEventDefinition>
</bpmn:intermediateCatchEvent>More on timers
<bpmn:scriptTask id="scriptTask" name="Script Task">
<bpmn:incoming>Flow_159xzcz</bpmn:incoming>
<bpmn:outgoing>Flow_0t7z2os</bpmn:outgoing>
<bpmn:multiInstanceLoopCharacteristics isSequential="true"
camunda:collection="$(data.records)" />
<bpmn:script><![CDATA[this.log('testing from the inside: '+data.loopKey);]]></bpmn:script>
</bpmn:scriptTask>For Multi-instance data handling see
<bpmn:callActivity id="activity_call" name="Call Task" calledElement="loop">
...
</bpmn:callActivity>
In the above example 'loop' is the name of process to be called.
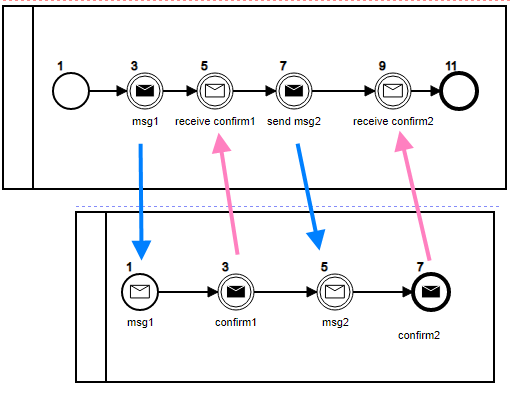
In this example, we will demonstrate how can two seperate processes communicate through "Messages"
When a process throw a message, bpmn-server checks if there is another process that can catch this message before dispatching it to AppDelegate.
<bpmn2:intermediateThrowEvent id="throw_msg1" name="msg1">
<bpmn2:messageEventDefinition id="messageEventDef1" messageRef="Msg1" />
<bpmn2:extensionElements>
<camunda:script event="start"><![CDATA[
input.caseId= data.caseId;
this.messageMatchingKey={'data.caseId': data.caseId };
]]></camunda:script>
</bpmn2:extensionElements>
...
</bpmn2:intermediateThrowEvent>The above will through a messsage as follows:
- Message Id:
Msg1 - Message Output:
caseId: <someValue>
The second process defines a start event to catch the message Msg1
<bpmn2:startEvent id="StartEvent_1w66wpl" name="msg1">
...
<bpmn2:messageEventDefinition id="messageEventDef4" messageRef="Msg1" />
</bpmn2:startEvent>
Therefore, the system will create a new instance of the second process and assign the Message output data, namely, the caseId
In addition, the second process sends a confirmation message Confirm1 to the first process
<bpmn2:intermediateThrowEvent id="throw_confirm1" name="confirm1">
<bpmn2:messageEventDefinition id="messageEventDef2" messageRef="Confirm1" />
<bpmn2:extensionElements>
<camunda:script event="transformOutput"><![CDATA[
this.output.confirm=true;
this.context.messageMatchingKey={'data.caseId': this.token.data.caseId };
]]></camunda:script>
</bpmn2:extensionElements>
...
</bpmn2:intermediateThrowEvent>Howerver, the challenge here is that make sure the message is sent to the specific instance, that is where the Matching key is used
- Message Id:
Confirm1 - Message Output:
confirm: true - Message Matching Keyt: 'data.caseId': this.token.data.caseId