-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 62
Tips
If you are using Goneovim on MacOS, you might want to use standard MacOS keyboard shortcuts such as Cmd+X to cut a highlighted region, Cmd+C to copy it, Cmd+V to paste, etc.
The easiest way to add these keymappings is to copy the vimscript file that defines these mappings for MacVim: https://github.com/macvim-dev/macvim/blob/master/runtime/macmap.vim. Then add a line like
source macmap.vimto a startup file such as $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/nvim/init.vim .
If you don't want all of the definitions in macmap.vim, you can cut and paste the ones you want into a startup file. In macmap.vim, "D-" represents the Cmd key. For example, here are the definitions that allow you to use Cmd+S to save the buffer from within various Neovim modes:
nnoremap <silent> <special> <D-s> :if expand("%") == ""<Bar>browse confirm w<Bar> else<Bar>confirm w<Bar>endif<CR>
vmap <special> <D-s> <Esc><D-s>gv
imap <special> <D-s> <C-O><D-s>
cmap <special> <D-s> <C-C><D-s>
omap <special> <D-s> <Esc><D-s>Also, if you want to change the font size using the Cmd++ or Cmd+- key, you can do so using vimscript or lua. The following is an example of lua configuration.
Note that the actual keys to be mapped depend on the keyboard language settings and layout. For example, <D-;> or <D-=> may be useful as a combination of Cmd and + key.
The following script allows you to change the fontsize without changing the window size:
vim.keymap.set("n", "<D-+>", [[:lua guifontscale(1)<CR>]], { noremap = true })
vim.keymap.set("n", "<D-->", [[:lua guifontscale(-1)<CR>]], { noremap = true })
function guifontscale(n)
if type(n) ~= "number" then
return
end
local gfa = {}
for c in vim.gsplit(vim.o.guifont, ":") do
table.insert(gfa, c)
end
local buildnewgf = ""
local h_num, w_num, ratio = nil, nil, nil
for k, v in ipairs(gfa) do
if v:find("h", 1, true) == 1 then
h_num = tonumber(v:sub(2))
h_num = h_num + n
buildnewgf = buildnewgf .. "h" .. tostring(h_num)
elseif v:find("w", 1, true) == 1 then
w_num = tonumber(v:sub(2))
if h_num then
ratio = w_num / h_num
w_num = (h_num + n) * ratio
else
w_num = w_num + n
end
buildnewgf = buildnewgf .. "w" .. string.format("%.2f", w_num)
else
v = string.gsub(v, " ", "_")
buildnewgf = buildnewgf .. v
end
if k ~= #gfa and v ~= "" then
buildnewgf = buildnewgf .. ":"
end
end
local setcmd = "set guifont=" .. buildnewgf
vim.cmd(setcmd)
return 0
endIf you also want the window size to change, so that the proportions between font size and window dimensions stays the same, use the following function along with the fontscale function above, and rename the function calls to guifontwinscale in the keymapping lines above. (This is what MacVim does by default in response to Cmd+- and Cmd+= or Cmd++.)
function guifontwinscale(n)
local lines = vim.api.nvim_get_option('lines')
local columns = vim.api.nvim_get_option('columns')
guifontscale(n)
vim.cmd('sleep 10m')
vim.cmd('winsize ' .. columns .. ' ' .. lines)
endIn MacOS, when you hold down certain Roman character keys in an editor, a little menu might pop up. It lists variants of the character with diacritical marks attached. Here are examples for "a", "e", and "L" in goneovim/nvim insert mode:
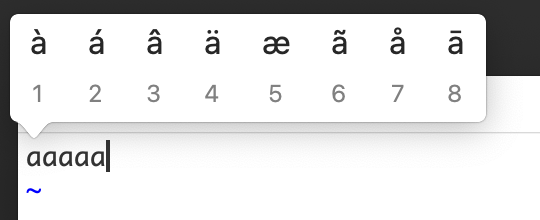
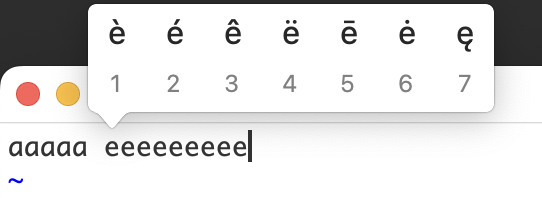
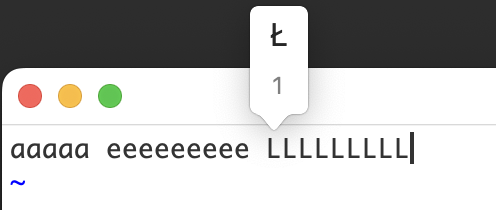
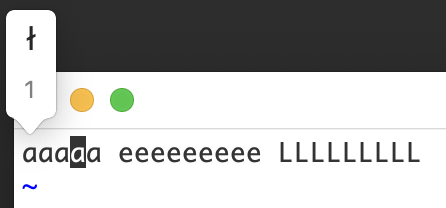
This isn't very useful in nvim, since the normal behavior of nvim is to repeat the character when you hold down a key in insert mode. A similar behavior occurs in normal mode: for example, if you hold down the "l" (lowercase "L") key to move the cursor to the right, you'll see a menu for an "l" with a slash through it:
You can ignore the popups, but if you want to get rid of them, enter the following command at a shell prompt:
defaults write -app goneovim ApplePressAndHoldEnabled -bool false
(If you want to disable to popups for all applications, see this Stackexchange answer: https://apple.stackexchange.com/questions/452748/on-macos-how-can-you-enable-repeated-keys-but-only-for-specific-apps/452755#452755 .)
If you want to enter characters with diacritical remarks in goneovim, another way to do it is with an alternative keyboard. You can enable one of these in System Preferences/Keyboard/Input Sources. There are options there to allow you to switch keyboards. Then, for example, if you use the US International - PC keyboard, typing "`" followed by "e" will enter "è".)
nvr is a neovim remote tool that allows you to control nvim processes from a shell.
https://github.com/mhinz/neovim-remote
For example, if you are running a terminal inside goneovim, the nvr command will allow you to open files on the goneovim side.
nvr /foo/baa/buzz # then, goneovim open the file /foo/bar/buzz
This is because the nvim process, which is embedded internally by goneovim, sets an environment variable called $NVIM_LISTEN_ADDRESS. nvr provides remote functionality using $NVIM_LISTEN_ADDRESS by default.
The following steps allow goneovim to be controlled by nvr as well.
export NVIM_LISTEN_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1:1234
nvim --headless &
/Applications/goneovim.app/Contents/MacOS/goneovim --server $NVIM_LISTEN_ADDRESS &
nvr --remote FILE1
nvr --remote-send 'iabc<cr><esc>'
nvr --remote-expr 'map([1,2,3], "v:val + 1")'Qt layer logging can be controlled by the following environment variables, set as follows for Windows
set QT_LOGGING_RULES=*.debug=true
set QT_MESSAGE_PATTERN=[%{time hh:mm:ss.zzz}] %{message}