Blog post explaining working here.
We will be using Rasa Stack to build our conversational A.I chatbot to answer FAQ's about Git. The reason being Rasa is open source and hence we will no longer need to send our confidential data to some alternative cloud service providers.
Apart from that Rasa offers flexibility to customize our model according to our need. By default it uses some the most popular open source libraries for Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning like SpaCy and scikit-learn with default parameters optimized for most common NLP tasks like Intent classification (understanding what user wants eg, asking question, ordering something) and Named Entity Recognition (understanding what specific keywords means eg, Bangalore-location, Google - organization)
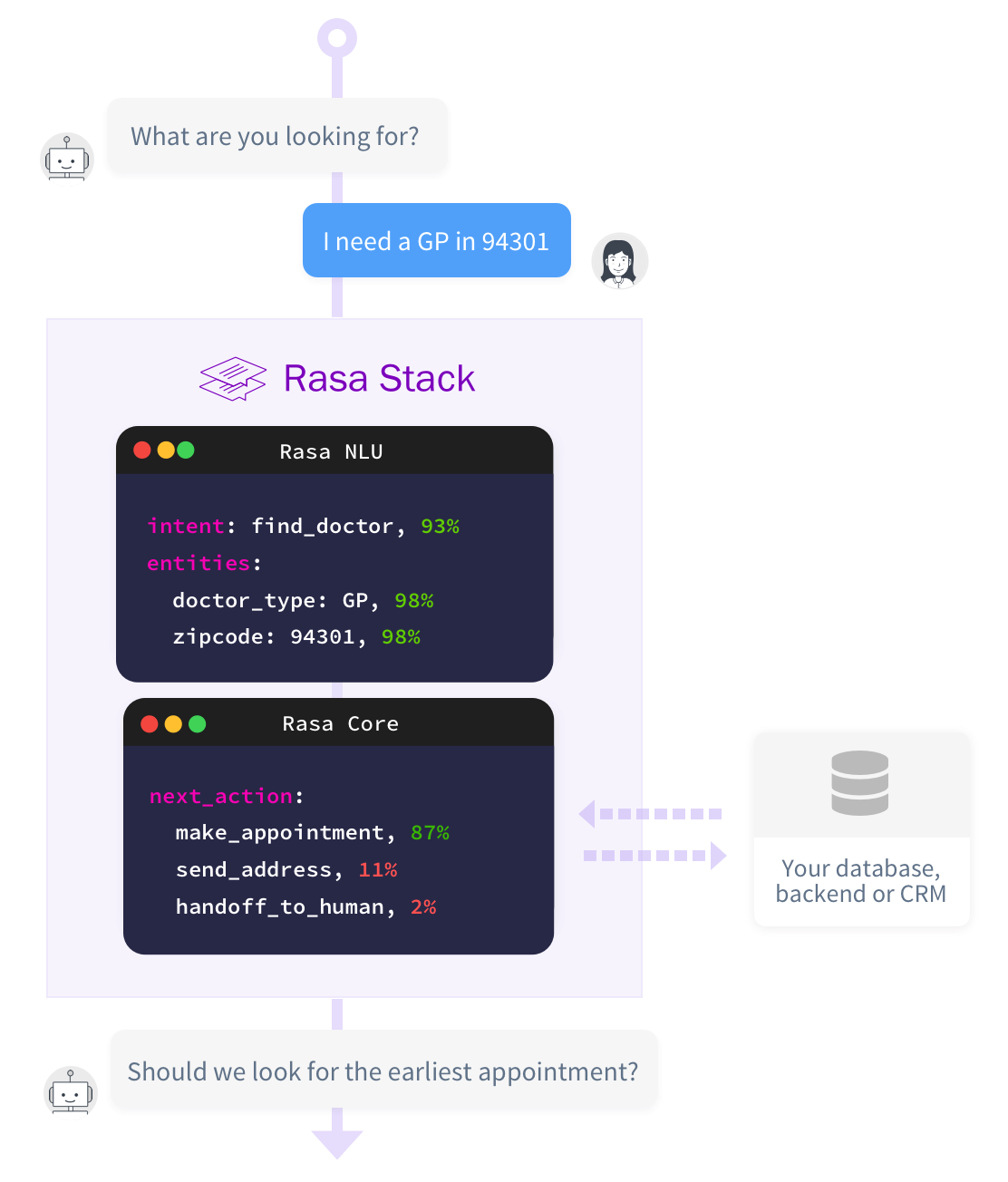
Rasa NLU handles the Natural Language Understanding (Intent clasification and N.E.R) part while Rasa Core handles the dialog management part. See below image for framework overview.
-
Install Rasa NLU: Rasa NLU Installation
-
For backend we will use spaCy + sklearn
-
Install Rasa Core (version used 9.5): Rasa Core Installation
-
fuzzywuzzy: Fuzzy string matching in Python for similar text retrieval
We will need labeled user data for training our NLU or interpreter part. While it is always better to have more data to train our ML models but in case we don't have it we can use free services such as Chatito or Tracy to synthetically generate one to suite our use case.
Data should be in json format as specified by Rasa here. An example will look like:
{
"text": "show me chinese restaurants",
"intent": "restaurant_search",
"entities": [
{
"start": 8,
"end": 15,
"value": "chinese",
"entity": "cuisine"
}
]
}Once we have our training data store it in /data in the working directory.
data
├── data.json # data for training NLU
├── faq_data.csv # CSV file containing questions and answers
└── stories.md # Sample conversations
There exits a tool called rasa-nlu-trainer which helps you visualize and edit the json data you created in the previous step. As shown below each training instance has an intent associated with it and entities highlighted (color coded for different entity type).
First install it using npm by following the instructions mentioned here and launch it by opening a terminal in your chatbot directory by typing,
$ rasa-nlu-trainerThis will open a new tab in your browser. You can even try it online without having to install anything by simply uploading your json training file.
Open a terminal in the project directory and run following command:
$ python nlu_model.pyThis will train our model to identify intent form a user using SpaCy and sk-learn backend.
Configuration for backend has been specified in the config_spacy.json file in the project directory. Below is the content of the file:
{
"pipeline":"spacy_sklearn",
"path":"./models/nlu",
"data":"./data/data.json"
}To train a dialogue model which in our case is Rasa Core python library we need to first create a stories.md file in ./data directory. First write a sample story to the newly created empty file, copy below content:
## sample story
* greet
- utter_greet
* goodbye
- utter_goodbyethen in terminal type the following command to start dialogue model training:
$ python train_init.pyOnce initial training is done this will create a dialogue folder in models directory (./models/dialogue) our dialogue management model will be stored here.
Full training to suite our use case haven't been done yet. Our model now only understands to greet and say good bye! To create stories suitable to our use case use online training recommended by Rasa Core. In terminal type the below command and follow the instructions on the screen to pose yourself as a bot and choose which actions should follow after which events.
$ python train_online.pyOnce you think your bot has started to perform reasonably well then choose option "0" shown below to export current conversion to stories.md file in the project directory. (Note there are two such files named stories.md one in project directory and other one in ./data/stories.md)
The bot wants to [action_listen]. Is this correct?
1. Yes.
2. No, the action is wrong.
0. Export current conversations as stories and quitCopy the content from project directory's stories.md file and append it to ./data/stories.md file
Once we have enough sample conversations to be suitable to our use case we can now repeat the first step to train our dialogue management model on the newly updated ./data/stories.md data by typing following command:
$ python train_init.pyYou should be now be able to run complete bot in the terminal by typing following command:
$ python dialogue_management_model.pyactions.GetAnswer has been defined in faq_domain.yml whenever bot recognizes that text sent by user is a question. See actions.py file in project directory.
I have used FuzzyWuzzy python package which does approximate string matching by computing difference based on Levenshtein distance. I have used Token Set Ration method which takes care of partial string match and when string lengths differ.
This will find the nearest matching question in the question column of ./data/faq_data.csv file and return the answer along with other details as link and page no. Possible conversation will look something like below:
USER: hello!
BOT: Hello! How can I help?
USER: pushing my changes
BOT: Here is something I found
Document: http://gitfaq.org/articles/how-do-i-push-my-changes.html
Page number: 1
Question: How do I push my changes?
Answer:
git push
git push origin branch-name
It is possible to deploy our chatbot on a http server using flask. We can either,
- Host Rasa Core services on http server by following details mentioned here or
- Use flask and requests to connect our bot to http endpoints as mentioned here.
Disadvantage of approach one is that we can only get information of which action to execute following user query and need to define rules on our end to execute that action eg, search similar question, fetching data from database etc.
This can however be avoided if followed second option.
-
I have used FuzzyWuzzy python package for string similarity which is based on Levenshtein distance and it requires both strings to contain exact or near similar words but will fail in case of semantic matching eg. in case of words like (lost, not found), (require, need) etc. To avoid this we can try to encode each question in our database and a user query by using some sentence encoder and then finding the similar pair using cosine-distance. Have a look at recently released Universal Sentence Encoder by TensorFlow.
-
Our bot implementation can only handle questions which are available in the dataset and mapped to their corresponding answers. In case of handling questions based on some ontology or some structured dataset in general we need to follow the approach of creating a knowledge graph (the info box you see on right side whenever you search for a fact on Google) first and then using an Entity-relationship model.