sSSs sSSs .S_sSSs .S_SSSs .S_sSSs .S S. sSSs .S_sSSs .S .S_sSSs sSSs .S_sSSs sSSs
d%%SP d%%SP .SS~YS%%b .SS~SSSSS .SS~YS%%b .SS SS. d%%SP .SS~YS%%b .SS .SS~YS%%b d%%SP .SS~YS%%b d%%SP
d%S' d%S' S%S `S%b S%S SSSS S%S `S%b S%S S%S d%S' S%S `S%b S%S S%S `S%b d%S' S%S `S%b d%S'
S%| S%S S%S S%S S%S S%S S%S S%S S%S S%S S%| S%S S%S S%S S%S S%S S%S S%S S%S S%|
S&S S&S S%S d*S S%S SSSS%S S%S d*S S%S S%S S&S S%S d*S S&S S%S S&S S&S S%S d*S S&S
Y&Ss S&S S&S .S*S S&S SSS%S S&S .S*S SS SS Y&Ss S&S .S*S S&S S&S S&S S&S_Ss S&S .S*S Y&Ss
`S&&S S&S S&S_sdSSS S&S S&S S&S_sdSSS S S `S&&S S&S_sdSSS S&S S&S S&S S&S~SP S&S_sdSSS `S&&S
`S*S S&S S&S~YSY%b S&S S&S S&S~YSSY SSS `S*S S&S~YSSY S&S S&S S&S S&S S&S~YSY%b `S*S
l*S S*b S*S `S%b S*S S&S S*S S*S l*S S*S S*S S*S d*S S*b S*S `S%b l*S
.S*P S*S. S*S S%S S*S S*S S*S S*S .S*P S*S S*S S*S .S*S S*S. S*S S%S .S*P
sSS*S SSSbs S*S S&S S*S S*S S*S S*S sSS*S S*S S*S S*S_sdSSS SSSbs S*S S&S sSS*S
YSS' YSSP S*S SSS SSS S*S S*S S*S YSS' S*S S*S SSS~YSSY YSSP S*S SSS YSS'
SP SP SP SP SP SP SP
Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
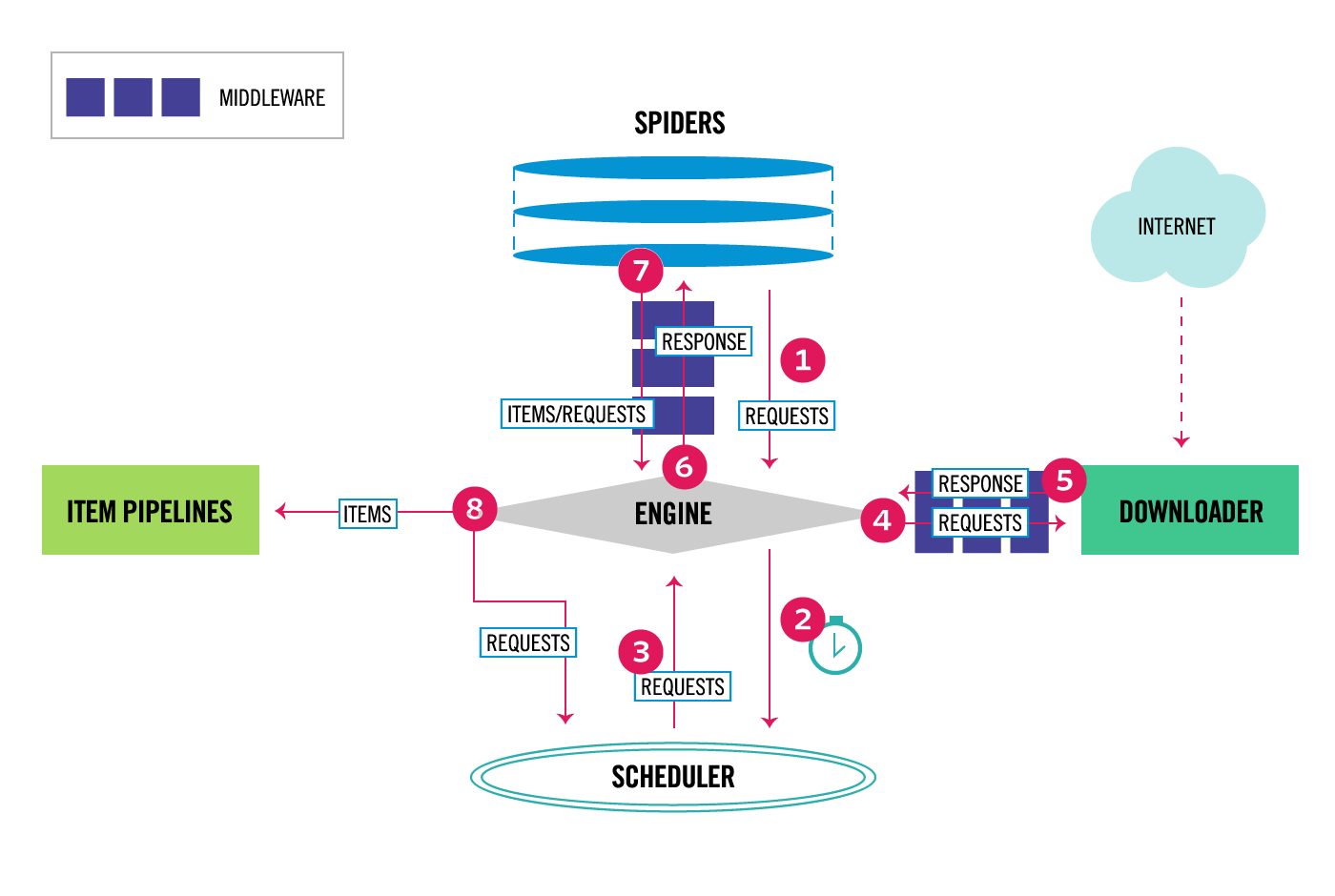
Scrapy module - Web Crawling
Scrapy is an application framework for crawling web sites and extracting structured data which can be used for a wide range of useful applications, like data mining, information processing or historical archival.
Even though Scrapy was originally designed for web scraping, it can also be used to extract data using APIs (such as Amazon Associates Web Services) or as a general purpose web crawler.
tutorial/ scrapy.cfg # deploy configuration file
tutorial/ # project's Python module, you'll import your code from here
__init__.py
items.py # project items file
pipelines.py # project pipelines file
settings.py # project settings file
spiders/ # a directory where you'll later put your spiders
__init__.py
-
Built-in support for selecting and extracting data from HTML/XML sources using extended CSS selectors and XPath expressions, with helper methods to extract using regular expressions.
-
An interactive shell console (IPython aware) for trying out the CSS and XPath expressions to scrape data, very useful when writing or debugging your spiders.
-
Built-in support for generating feed exports in multiple formats (JSON, CSV, XML) and storing them in multiple backends (FTP, S3, local filesystem)
-
Robust encoding support and auto-detection, for dealing with foreign, non-standard and broken encoding declarations.
-
Strong extensibility support, allowing you to plug in your own functionality using signals and a well-defined API (middlewares, extensions, and pipelines).
-
Wide range of built-in extensions and middlewares for handling:
- cookies and session handling
- HTTP features like compression, authentication, caching
- user-agent spoofing
- robots.txt
- crawl depth restriction
-
A Telnet console for hooking into a Python console running inside your Scrapy process, to introspect and debug your crawler Plus other goodies like reusable spiders to crawl sites from Sitemaps and XML/CSV feeds, a media pipeline for automatically downloading images (or any other media) associated with the scraped items, a caching DNS resolver, and much more
scrapy startproject project_name
scrapy crawl spider_name
scrapy crawl spider_name -o file.csv -t csv
scrapy crawl spider_name -o file.json -t json
scrapy shell "url"Using conda environments
conda env list # list all environments
conda activate Scrapy # if Scrapy is listed
conda deactivate # deactivate current environment
conda create --name Scrapy # if Scrapy is NOT listed
pip install -r requirements.txt # install dependencies
conda list # all packages in env
- Pytest sample good practices
- Travis sample travis docs