-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 282
Android Guide
This is a beginners' example to use FeatherCNN in Android Studio 3.1. We start with a blank project which checked "C++ support". Android Studio will generate a project using Gradle and CMake. For the Android.mk case, please refer to this site. In the following, we illustrate necessary steps to add models and libraries to the project.
- In the project navigator, expand the file hierarchy and find the libs folder.
- Right click or hold control key and click (macOS) on libs and open this folder in the popup window.
- Copy the compiled library to this folder. If it is compiled with source code, find your library in
build-android/install/feather. - After copy, you should be able to see the library in the navigator.
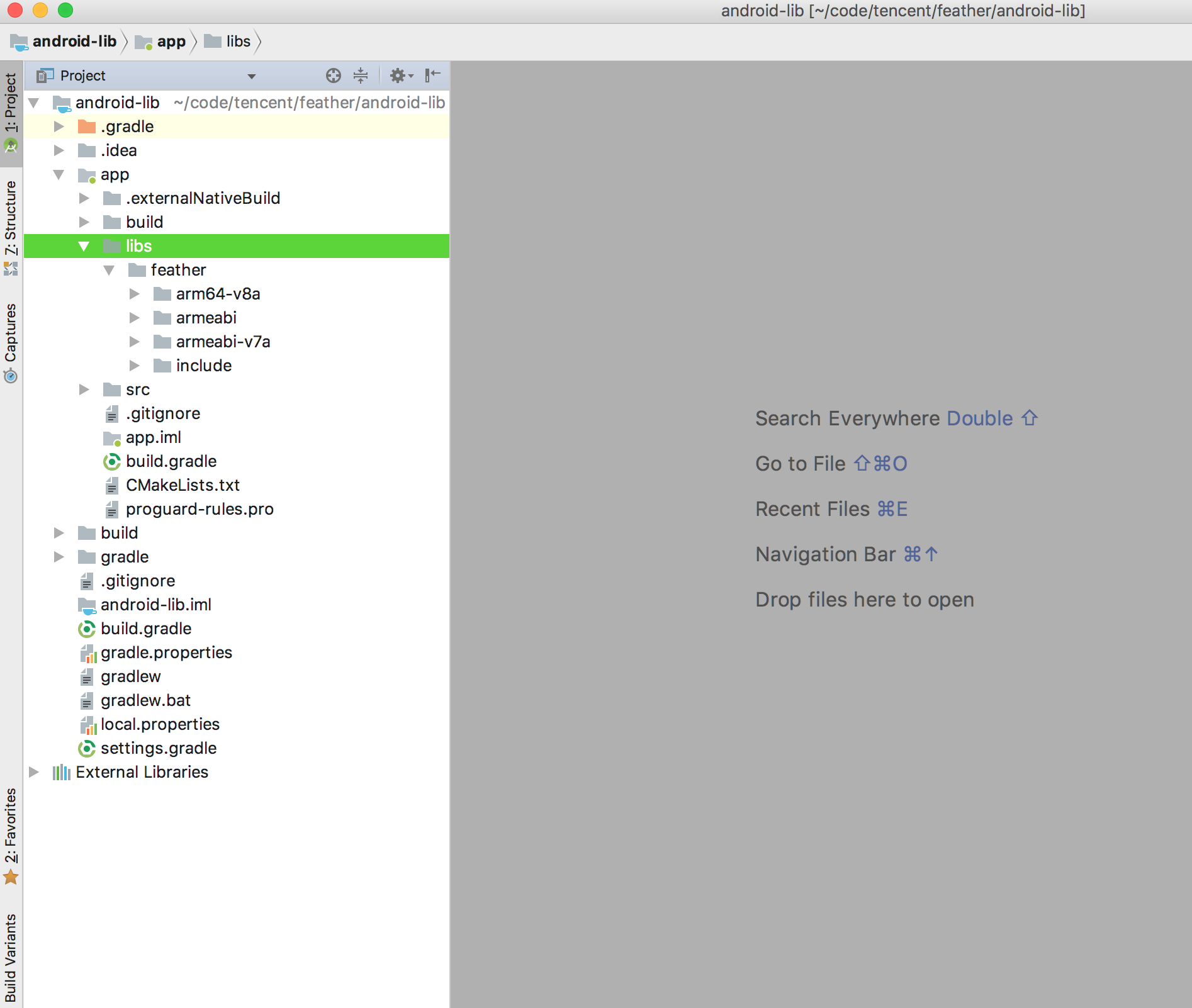
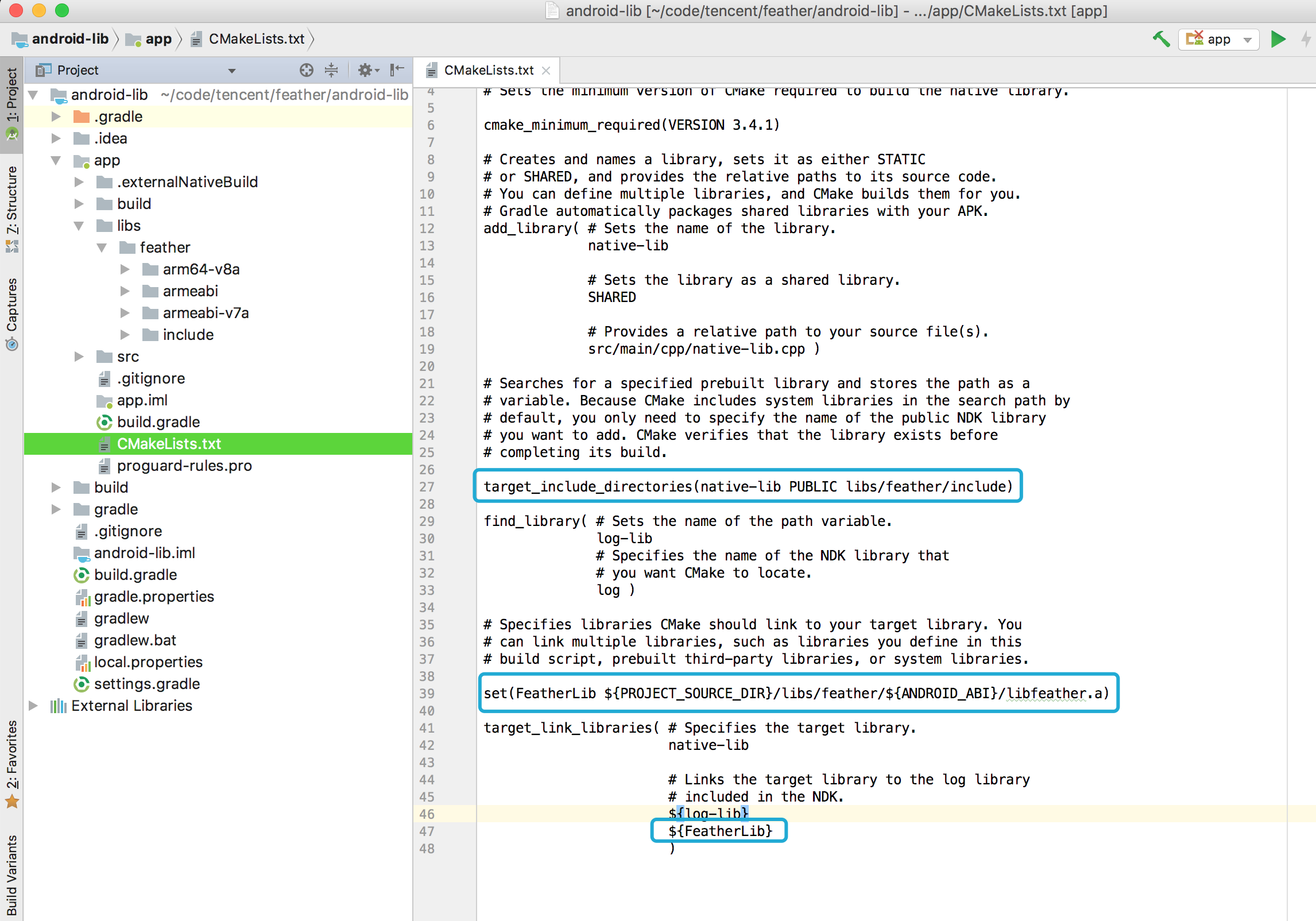
- Open CMakeLists.txt
- Edit the lines as illustrated in the figure.
- The
target_include_directoriestells cmake where to find lib headers. - The
target_link_librariespart links our library with your project.
- Open build.gradle file in the module, NOT that one for the project.
- Add
-fopenmpflag for the project in case link errors. - Add
abiFiltersto tell Android Studio only compile supported ABIs.
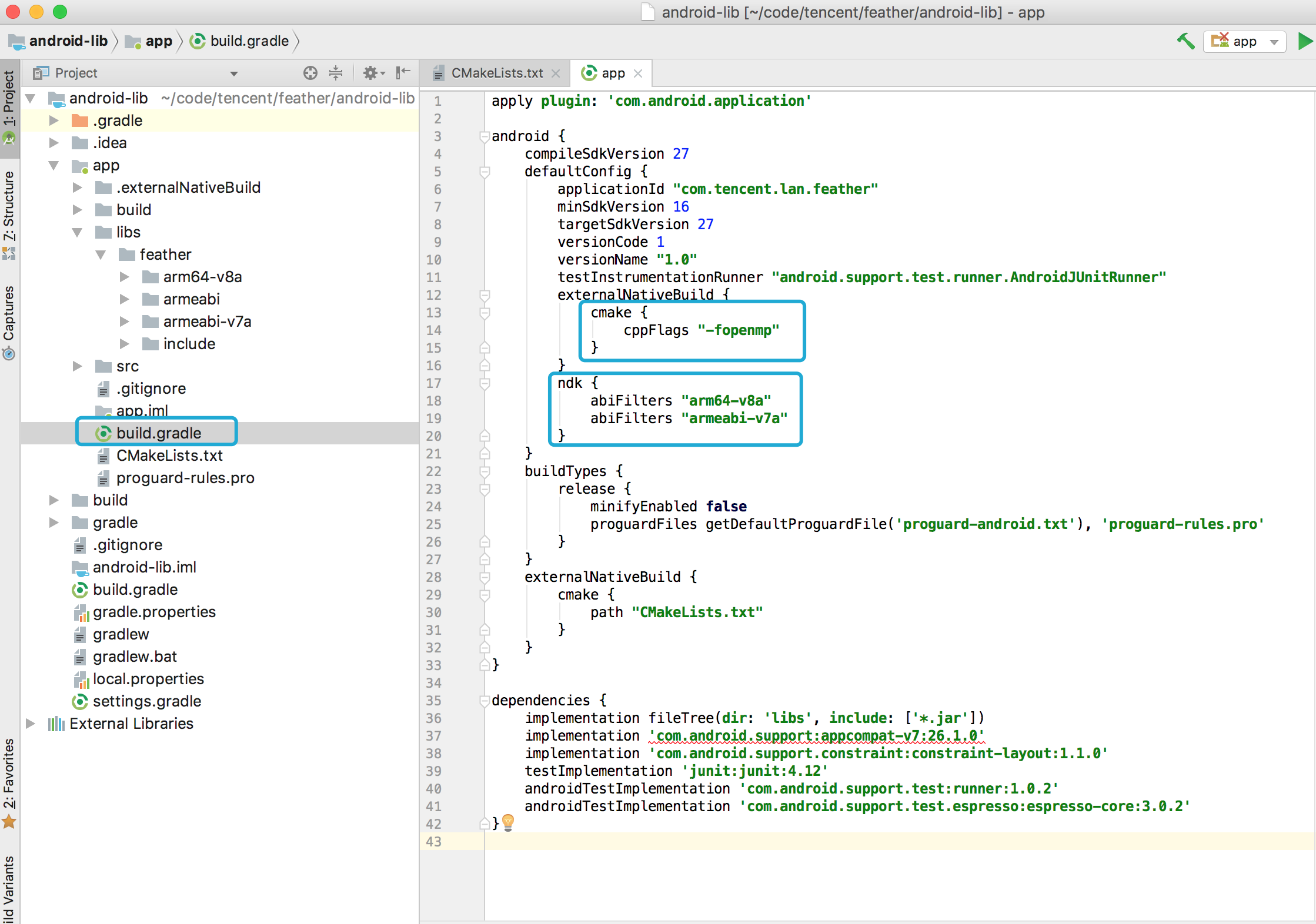
Your project should be able to build with FeatherCNN now.
We need to set up a raw folder in the resources.
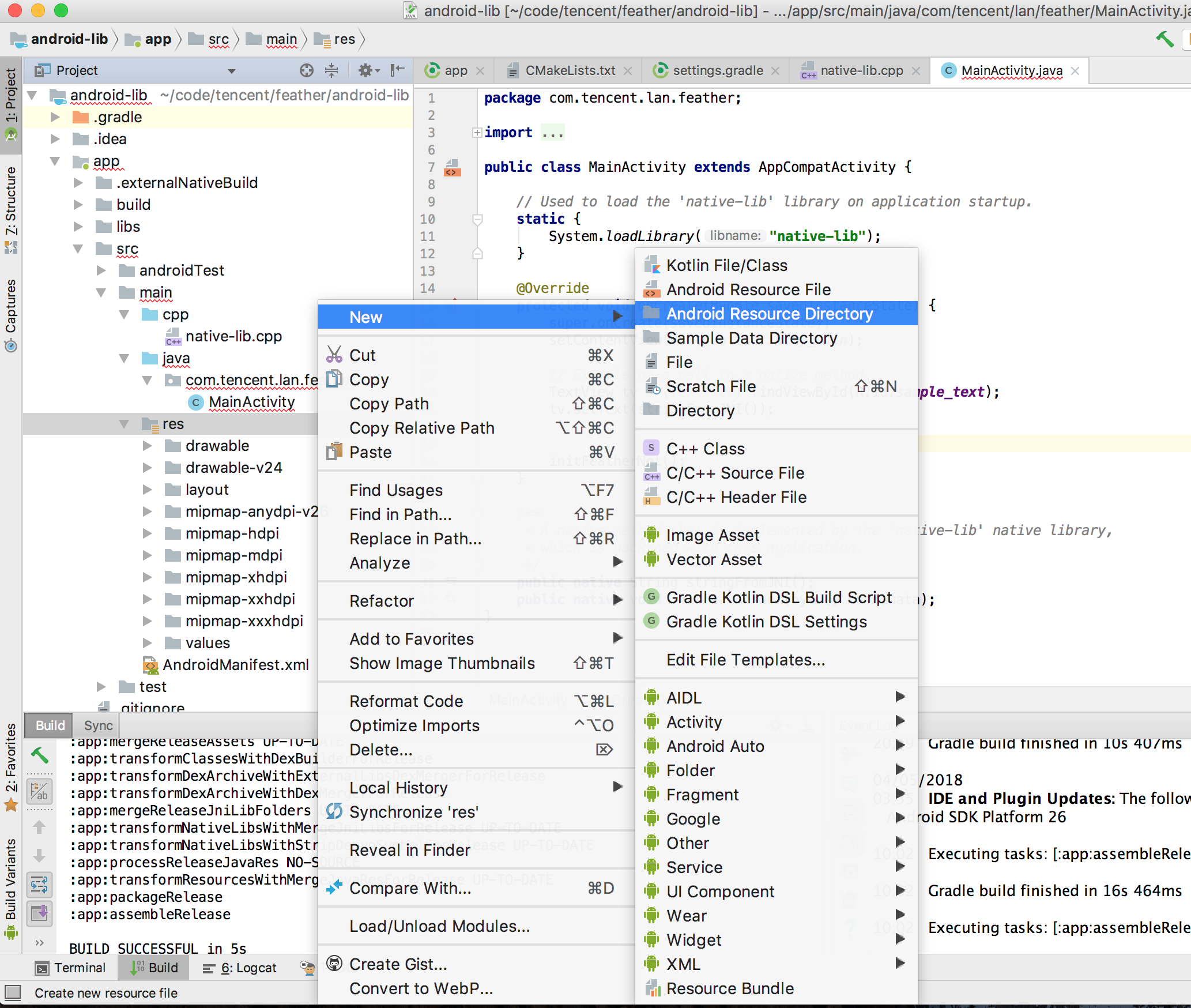
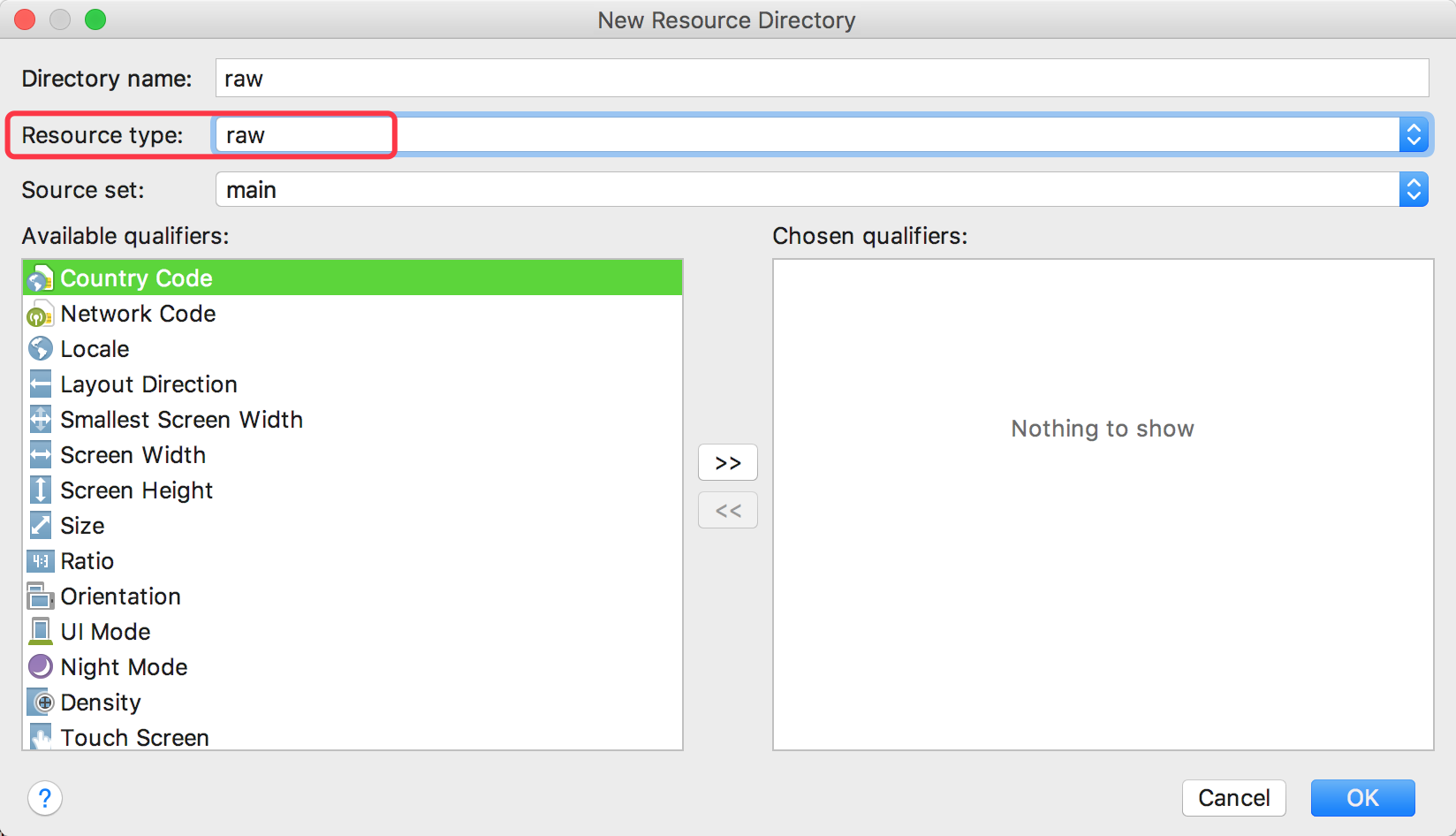
Just open the File Explorer or Finder to copy your model here.

In current Android Studio version (3.1), you can see a cpp folder with native-libs.cpp in it. Lets begin with the JNI code.
- In the C++ side, it needs to accept a
byte[]from the Java code with the feathermodel data. - We copy the data from the JNI, and initialize our net.
- Note that this code snippet put the
forward_netin a local variable. In real production situations, you should make it persistent through function calls.
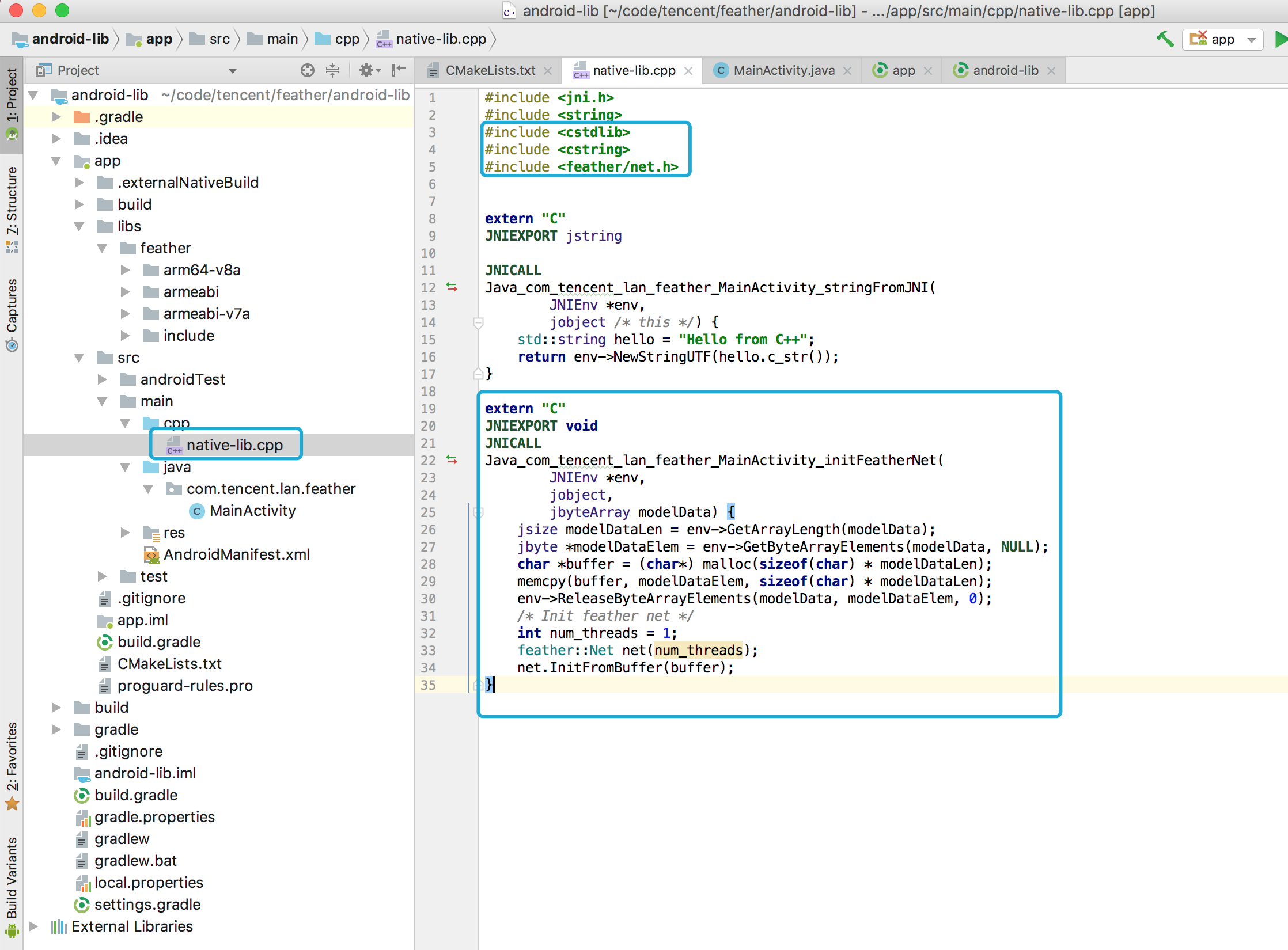
The C++ code snippet:
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT void
JNICALL
Java_com_tencent_lan_feather_MainActivity_initFeatherNet(
JNIEnv *env,
jobject,
jbyteArray modelData) {
jsize modelDataLen = env->GetArrayLength(modelData);
jbyte *modelDataElem = env->GetByteArrayElements(modelData, NULL);
char *buffer = (char*) malloc(sizeof(char) * modelDataLen);
memcpy(buffer, modelDataElem, sizeof(char) * modelDataLen);
env->ReleaseByteArrayElements(modelData, modelDataElem, 0);
/* Init feather net */
int num_threads = 1;
feather::Net net(num_threads);
net.InitFromBuffer(buffer);
}- At the Java side, we get the feathermodel from resource manager and fill that into a single byte array.
- Pass that byte array to the JNI function.
- Don't forget to declare the JNI interface.

The code snippet
InputStream is = getResources().openRawResource(R.raw.mobilenet);
try{
byte[] modelData = new byte[is.available()];
is.read(modelData);
initFeatherNet(modelData);
} catch (IOException e){
//Handle file exception here.
}Now the net is properly initialized. You can perform inference computation with the Forward method through JNI.