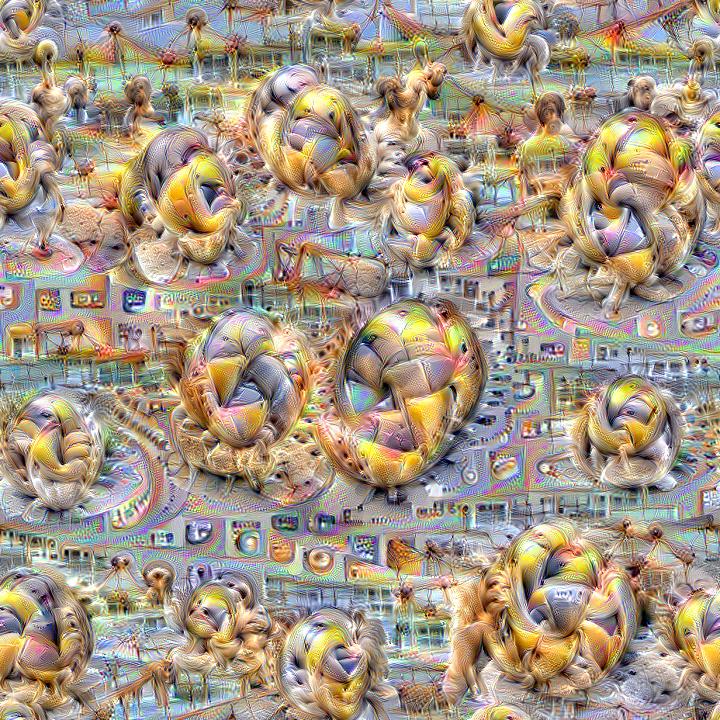
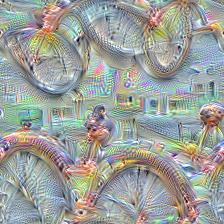
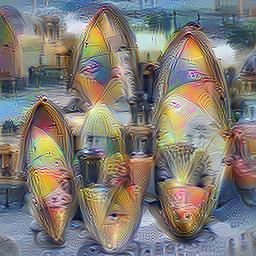This project aims to simplify the process of creating a custom DeepDream model by using pretrained GoogleNet models and custom image datasets.
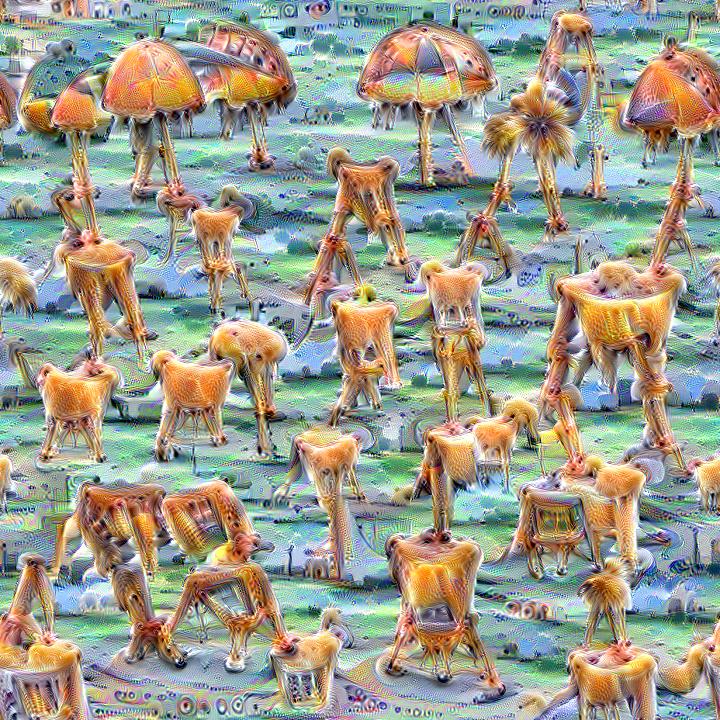
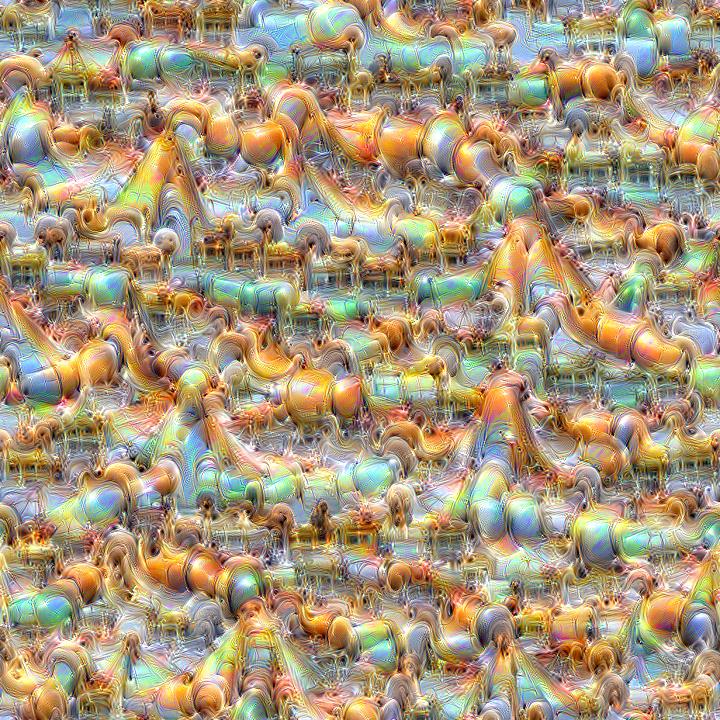
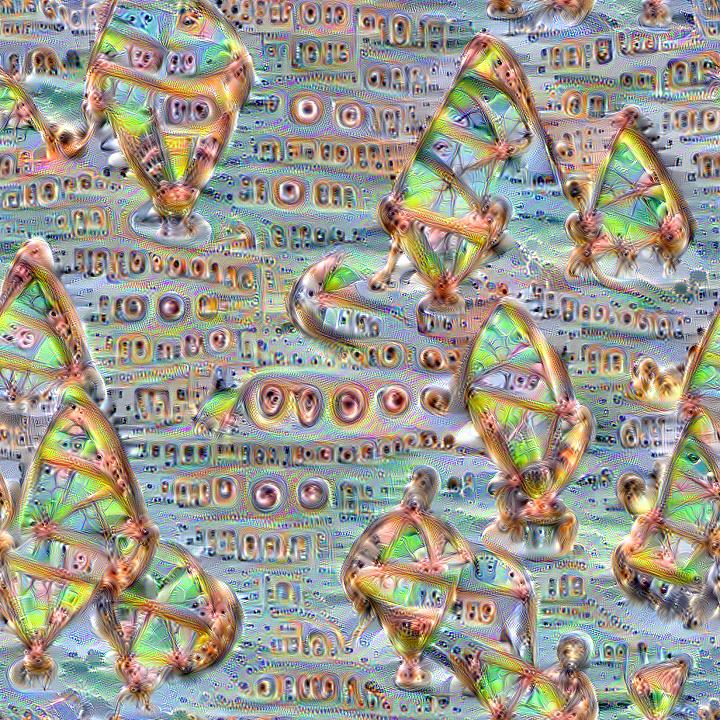
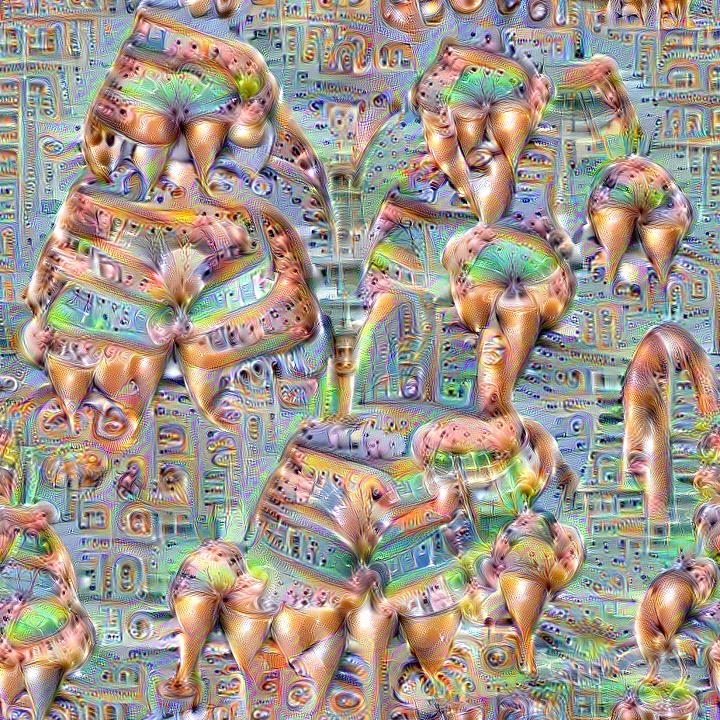
Here are some example visualizations created with custom DeepDream models trained on summer themed images:
Dependencies:
You can find detailed installation instructions for Ubuntu and Windows in the installation guide.
After making sure that PyTorch is installed, you can optionally download the Places365 GoogleNet and Inception5h (InceptionV1) pretrained models with the following command:
python models/download_models.py
If you just want to create DeepDreams with the pretrained models or you downloaded a pretrained model made by someone else with Dream-Creator, then you can skip ahead to visualizing models.
-
-
Collect Images
-
Sort images into the required format.
-
Remove any corrupt images.
-
Ensure that any duplicates are removed if you have not done so already
-
Resize the dataset to speed up training.
-
Calculate the mean and standard deviation of your dataset.
-
-
If the results are not great, then you may have to go back to step 1-2 and make some changes with what images, categories, and training parameters are used.
It can take as little as 5 epochs to create visualizations that resemble your training data using the main FC/Logits layer. In order to speed up training and create better looking results, the pretrained BVLC model used is partially frozen in order to protect the lower layers from changing.
In order to train a custom DeepDream model, you will need to create a dataset composed of images that you wish to use for training. There are a variety of ways that you can aquire images for your dataset, and you will need at least a couple hundred images for each category/class.
DeepDream is most often performed with image classification models trained on image datasets that are composed of different categories/classes. Image classification models attempt to learn the difference between different image classes and in doing so the neurons gain the ability to create dream-like hallucinations. The images you choose, the differences between them, the differences between your chosen classes, and the number of images used will greatly affect the visualizations that can be produced.
PyTorch image datasets are to be structured where the main directory/folder contains subfolders/directories for each category/class. Below an example of the required dataset structure is shown:
dataset_dir
│
└───category1
│ │ image1.jpg
│ │ image2.jpg
│ │ image3.jpg
│
└───category2
│ image1.jpg
│ image2.jpg
│ image3.jpg
Once you have created your dataset in the proper format, make sure that you remove any duplicate images if you have not done so already. There are a variety of tools that you can use for this task, including free and open source software.
If you have not done so already, you may wish to create a backup copy of your dataset.
Next you will need to verify that none of the images are corrupt in such a way that prevents PyTorch from loading them. To automatically remove any corrupt images from your dataset, use the following command:
python data_tools/remove_bad.py -delete_bad -data_path <training_data>
Next you will likely want to resize your dataset to be closer to the training image size in order to speed up training. Resizing your dataset will not prevent you from creating larger DeepDream images with the resulting model. The included resizing script will only modify images that go above the specified image size with their height or width.
To resize the images in your dataset, use the following command:
python data_tools/resize_data.py -data_path <training_data> -max_size 500
Now with your newly resized dataset, you can calculate the mean and standard deviation of your dataset for use in training, and DeepDreaming. Make sure to recalculate the mean and standard deviation again if you modify the dataset by adding or removing images.
To calculate the mean and standard deviation of your dataset, use the following command and save the output for the next step:
python data_tools/calc_ms.py -data_path <training_data>
Now you can start training your DeepDream model by running the GoogleNet training script. It's recommended that you save the model every 5-10 epochs in order to monitor the quality of the visualizations.
After training your models, you can add a color correlation matrix to them for color decorrelation with the following command:
python data_tools/calc_cm.py -data_path <training_data> -model_file <bvlc_out120>.pth
Basic training command:
python train_googlenet.py -data_path <training_data> -balance_classes -batch_size 96 -data_mean <mean> -data_sd <sd>
Input options:
-data_path: Path to the dataset directory/folder that you wish to use.-data_mean: Your precalculated list of mean values for your chosen dataset.-data_sd: Your precalculated list of standard deviation values for your chosen dataset.
Training options:
-num_epochs: The number of training epochs to use. Default is120.-batch_size: The number of training and validation images to put through the network at the same time. Default is32.-learning_rate: Learning rate to use with the ADAM or SGD optimizer. Default is1e-2.-optimizer: The optimization algorithm to use; eithersgdoradam; default issgd.-train_workers: How many workers to use for training. Default is0.-val_workers: How many workers to use for validation. Default is0.-balance_classes: Enabling this flag will balance training for each class based on class size.
Model options:
-model_file: Path to the.pthmodel file to use for the starting model. Default is the BVLC GoogleNet model.-freeze_to: Which layer to freeze the model up to; one ofnone,conv1,conv2,conv3,mixed3a,mixed3b,mixed4a,mixed4b,mixed4c,mixed4d,mixed4e,mixed5a, ormixed5b. Default ismixed3b.-freeze_aux1_to: Which layer to freeze the first auxiliary branch up to; one ofnone,loss_conv,loss_fc, orloss_classifier. Default isnone.-freeze_aux2_to: Which layer to freeze the second auxiliary branch up to; one ofnone,loss_conv,loss_fc, orloss_classifier. Default isnone.-delete_branches: If this flag is enabled, no auxiliary branches will be used in the model.
Output options:
-save_epoch: Save the model everysave_epochepochs. Default is10. Set to0to disable saving intermediate models.-output_name: Name of the output model. Default isbvlc_out.pth.-individual_acc: Enabling this flag will print the individual accuracy of each class.-save_csv: Enabling this flag will save loss and accuracy data to txt files.-csv_dir: Where to save csv files. Default is set to current working directory.
Other options:
-use_device: Zero-indexed ID of the GPU to use pluscuda:. Default iscuda:0.-seed: An integer value that you can specify for repeatable results. By default this value is random for each run.
Dataset options:
-val_percent: The percentage of images from each class to use for validation. Default is0.2.
After training a new DeepDream model, you'll need to test it's visualizations. The best visualizations are found in the main FC layer also known as the 'logits' layer. This script helps you quickly and easily visualize all of a specified layer's channels in a particular model for a particular model epoch, by generating a separate image for each channel.
Input options:
-model_file: Path to the pretrained GoogleNet model that you wish to use.-learning_rate: Learning rate to use with the ADAM or L-BFGS optimizer. Default is1.5.-optimizer: The optimization algorithm to use; eitherlbfgsoradam; default isadam.-num_iterations: Default is500.-layer: The specific layer you wish to use. Default is set tofc.-extract_neuron: If this flag is enabled, the center neuron will be extracted from each channel.-image_size: A comma separated list of<height>,<width>to use for the output image. Default is set to224,224.-jitter: The amount of image jitter to use for preprocessing. Default is16.-fft_decorrelation: Whether or not to use FFT spatial decorrelation. If enabled, a lower learning rate should be used.-color_decorrelation: Whether or not to use color decorrelation. Optionally provide a comma separated list of values for the color correlation matrix. If no values are provided, an attempt to load a color correlation matrix from the model file will be made before defaulting to the ImageNet color correlation matrix.-random_scale: Whether or not to use random scaling. Optionally provide a comma separated list of values for scales to be randomly selected from. If no values are provided, then scales will be randomly selected from the following list:1, 0.975, 1.025, 0.95, 1.05.-random_rotation: Whether or not to use random rotations. Optionally provide a comma separated list of degree values for rotations to be randomly selected from or a single value to use for randomly selecting degrees from[-value, value]. If no values are provided, then a range of[-5, 5]wil be used.-padding: The amount of padding to use before random scaling and random rotations to prevent edge artifacts. The padding is then removed after the transforms. Default is set to0to disable it.
Processing options:
-batch_size: How many channel visualization images to create in each batch. Default is10.-start_channel: What channel to start creating visualization images at. Default is0.-end_channel: What channel to stop creating visualization images at. Default is set to-1for all channels.
Only Required If Model Doesn't Contain Them, Options:
-model_epoch: The training epoch that the model was saved from, to use for the output image names. Default is120.-data_mean: Your precalculated list of mean values that was used to train the model, if they weren't saved inside the model.-num_classes: The number of classes that the model was trained on. Default is120.
Output options:
-output_dir: Where to save output images. Default is set to the current working directory.-print_iter: Print progress everyprint_iteriterations. Set to0to disable printing.-save_iter: Save the images everysave_iteriterations. Default is to0to disable saving intermediate results.
Other options:
-use_device: Zero-indexed ID of the GPU to use pluscuda:. Default iscuda:0.-seed: An integer value that you can specify for repeatable results. By default this value is random for each run.
Basic FC (logits) layer visualization:
python vis_multi.py -model_file <bvlc_out120>.pth
Advanced FC (logits) layer visualization:
python vis_multi.py -model_file <bvlc_out120>.pth -layer fc -color_decorrelation -fft_decorrelation -random_scale -random_rotation -lr 0.4 -output_dir <output_dir> -padding 16 -jitter 16,8
This script lets you create DeepDream hallucinations with trained GoogleNet models.
Input options:
-model_file: Path to the pretrained GoogleNet model that you wish to use.-learning_rate: Learning rate to use with the ADAM or L-BFGS optimizer. Default is1.5.-optimizer: The optimization algorithm to use; eitherlbfgsoradam; default isadam.-num_iterations: Default is500.-content_image: Path to your input image. If no input image is specified, random noise is used instead.-layer: The specific layer you wish to use. Default is set tomixed5a.-channel: The specific layer channel you wish to use. Default is set to-1to disable specific channel selection.-extract_neuron: If this flag is enabled, the center neuron will be extracted from the channel selected by the-channelparameter.-image_size: A comma separated list of<height>,<width>to use for the output image. If a single value for maximum side length is provided along with a content image, then the minimum side length will be calculated automatically. Default is set to224,224.-jitter: The amount of image jitter to use for preprocessing. Default is16.-fft_decorrelation: Whether or not to use FFT spatial decorrelation. If enabled, a lower learning rate should be used.-color_decorrelation: Whether or not to use color decorrelation. Optionally provide a comma separated list of values for the color correlation matrix. If no values are provided, an attempt to load a color correlation matrix from the model file will be made before defaulting to the ImageNet color correlation matrix.-random_scale: Whether or not to use random scaling. Optionally provide a comma separated list of values for scales to be randomly selected from. If no values are provided, then scales will be randomly selected from the following list:1, 0.975, 1.025, 0.95, 1.05.-random_rotation: Whether or not to use random rotations. Optionally provide a comma separated list of degree values for rotations to be randomly selected from or a single value to use for randomly selecting degrees from[-value, value]. If no values are provided, then a range of[-5, 5]wil be used.-padding: The amount of padding to use before random scaling and random rotations to prevent edge artifacts. The padding is then removed after the transforms. Default is set to0to disable it.-layer_vis: Whether to use DeepDream or direction visualization when not visualizing specific layer channels. One ofdeepdreamordirection; default isdeepdream.
Only Required If Model Doesn't Contain Them, Options:
-data_mean: Your precalculated list of mean values that was used to train the model, if they weren't saved inside the model.-num_classes: The number of classes that the model was trained on, if it wasn't saved inside the model.
Output options:
-output_image: Name of the output image. Default isout.png.-print_iter: Print progress everyprint_iteriterations. Set to0to disable printing.-save_iter: Save the images everysave_iteriterations. Default is to0to disable saving intermediate results.
Tiling options:
-tile_size: The desired tile size to use. Either a comma separated list of<height>,<width>or a single value to use for both tile height and width. Default is set to0to disable tiling.-tile_overlap: The percentage of overlap to use for the tiles. Default is25for 25% overlap. Overlap percentages over 50% will result in problems.-tile_iter: Default is50.
Other options:
-use_device: Zero-indexed ID of the GPU to use pluscuda:. Default iscuda:0.-seed: An integer value that you can specify for repeatable results. By default this value is random for each run.
Basic DeepDream:
python vis.py -model_file <bvlc_out120>.pth -layer mixed5a
Advanced DeepDream:
python vis.py -model_file <bvlc_out120>.pth -layer mixed5a/conv_5x5_relu -channel 9 -color_decorrelation -fft_decorrelation -random_scale -random_rotation -lr 0.4 -padding 16 -jitter 16,8
See here for more information on all the included scripts/tools relating to dataset creation, cleaning, and preparation.