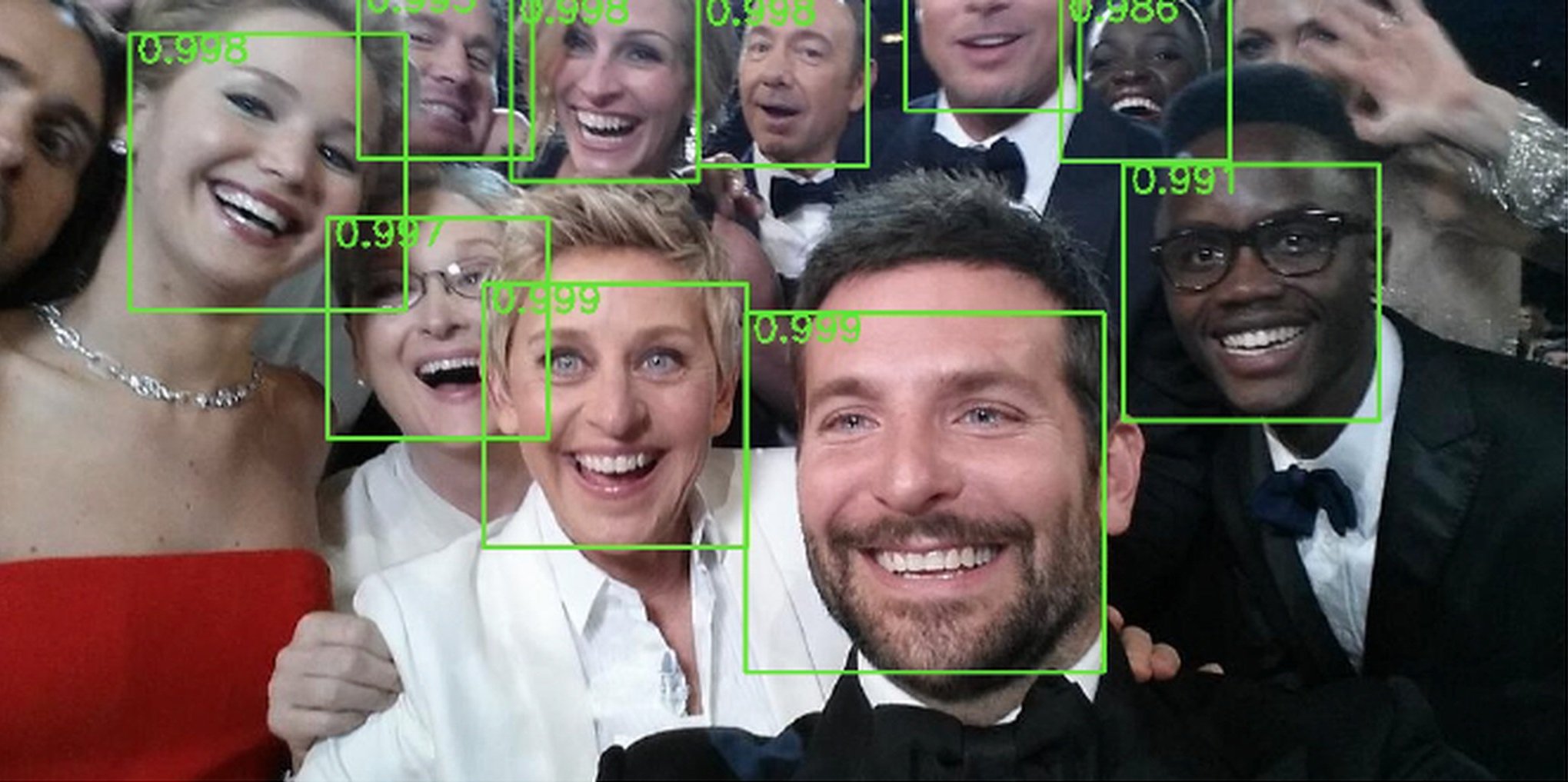
YOLOV3 is a state-of-the-art object recognition algorithm which can be trained on any kind of data and it will detect that particular object precisely wherever it might be. With the combination of yolo and deep learning module in OpenCV we have achieved a more precise face detection model. When an image is passed to the model, this will try to find the images and draws a kind of bounding box around them, which might be easier for users to understand, along with the bounding boxes, this will also display how confident the model is in predicting the persons face.
YOLOv3 is an abbreviation word for You look only once, where this algorithm has shaken most of the developers all around the world in the past 5 years, due to its immense ability to quickly learn and remember any object we have trained or labelled it. There is a unique method to work with yolo models where we require the images to be labelled firstly using specific tools available online or installing it in your local machine. (Labelling software’s links are provided below). the labelling process might take a long time depending upon on your dataset. The images are labelled according to the specification made by the user, whether we'd like to detect multiple objects in an image are single object, depending on it, the text file is created with following parameters,
- The class of the objects, starting from 0,1,2.
- The coordinates of the bounding box drawn.
Sample Label File
The Label file consists of following items.
- The class of the object
- Top_left coordinate of the bounsing box
- Top_right coordinate of the bounding box
- Bottom_left coordinate of the bounding box
- Bottom_right coordinate of the bounding box
References
- https://viso.ai/deep-learning/yolov3-overview/
- https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3
- https://in.mathworks.com/discovery/deep-learning.html
If you guys ever feel like bored and wanna spend your time for something good, you can sit idle and label images, which might really help people around you to do some crazy things.(Whatever im saying it is done in python)
- Download the labelimg.zip file from the below link provided. https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg
- Open your anaconda prompt and create a new environment in the location where you have unzipped your labelling files.
- After that, past the following line of code in your terminal and press enter. pyrcc5 -o libs/resources.py resources’
- pip install lxml
- Run python labeling.py, it will open the window, where you can start labelling.
- Run python labeling.py [image_path_folder] [pre_defined_class_file], here pre_defined_class_file represents the number of classes you need to your data, so you need to change it before starting to label your images, you can find that file in data folder.
- Make sure to change the format to yolo on the left-hand side, where by default it might be in pascal file format.
- Finally, click on create bounding box icon and start drawing and make sure to provide class to your bounding box every time you draw a box in an image.
- Click on the mentioned official GitHub repository of yolov5 and either fork it or open it in google colab or you can even run it in your local machine by downloading the files if you have a good system specification. https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
- Scroll down and open the file in google colab.
- Make sure your labelled dataset is your drive and ready to be connected with the yolov5 model.
- Run the first cell and see the magic at the left-hand side of the colab screen.
- Click on data folder, double click on coco128.yaml file and replace the path of the dataset with your dataset files saved in the drive and also make sure to change the number of classes, the class names should be in same order as you have given while labelling.
- Locate down to training cell and alter the code accordingly, such as number of epochs depending on the accuracy you are getting and also batch size. !python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 3 --data coco128.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --cache
- Finally, the model will be saved in weights folder, which will be created separate folder runs along with the results and evaluation metrics.
So, before execution we have some pre-requisites that we need to download or install i.e., anaconda environment, python and a code editor. Anaconda: Anaconda is like a package of libraries and offers a great deal of information which allows a data engineer to create multiple environments and install required libraries easy and neat.
Download link:
Python: Python is a most popular interpreter programming language, which is used in almost every field. Its syntax is very similar to English language and even children and learning it nowadays, due to its readability and easy syntax and large community of users to help you whenever you face any issues.
Download link:
https://www.python.org/downloads/
Code editor: Code editor is like a notepad for a programming language which allows user to write, run and execute program which we have written. Along with these some code editors also allows us to debug, which usually allows users to execute the code line by line and allows them to see where and how to solve the errors. But I personally feel visual code is very good to work with any programming language and makes a great deal of attachment with user.
Download links:
Let us define an environment and why we need different environments. An environment is a collection of libraries that are required to run our project. When we already have an environment with the necessary libraries, why do we need a new environment? To avoid version mismatches, we create a new environment for each project. For example, in your previous project, you used "tf env" with tensorflow 2.4 and keras 2.4, but in your current project, you must use tensorflow 2.6 and keras 2.6. If you continue your project in the "tf env" environment, there will be a version mismatch and you will need to update tensorflow and keras, but this will cause problems with the previous project's execution. To avoid this, we create a new environment with tensorflow 2.6 and keras 2.6 and resume our project.
Let us now see how to create an environment in anaconda.
- Type “conda create –n <<name_of_your_env>>” example: conda create -n env
- It will ask to proceed with the environment location, type ‘y’ and press enter.
- When you press ‘y’, the environment will be created. To activate your environment type conda activate <<your_env_name>> . E.g., conda activate myenv.
- You can see that the environment got changed after conda activate myenv line. It changed from “base” to “myenv” which means you are now working in “myenv” environment.
- To install a library in your virtual environment type pip install <library_name>. e.g., pip install pandas
- Instead of installing libraries one by one you can even install by bunch, i.e., we have a txt file called requirements.tx which consists of all the libraries required to proceed with the project, so we can use it.
- so, before installing requirements.txt, make sure you are in the specific path where your requirements.txt is located, basically this file is located in the folder where our executable files are located, so we need to move to that directory by following command. cd C:\folder_name
- Here C -> drive, folder name -> path where your executable file is saved
- I go to that file path in anaconda using cd command
- Go to drive where your project file is.
- Go to the path of your project using cd
- Type pip install –r requirements.txt
- And all your required libraries will be downloaded and you can start your project.
- But if you want to use jupyter notebook on the new environment you have to set it up for the new environment.
- After you have installed all the libraries and created an environment, you need an editor to run the code, that is starting jupyter notebook, as soon as you enter jupyter notebook in the terminal you will definitely get this error. “Jupiter” is not recognized as an internal or external command. So, to solve it it we have 2 commands.
- conda install –c conda-forge jupyterlab
- conda install –c anaconda python Now you are ready to use jupyter on this environment and start with your project!
Note: Make sure you have added path while installing the software’s.
- Install the prerequisites/software’s required to execute the code from reading the above blog which is provided in the link above.
- Press windows key and type in anaconda prompt a terminal opens up.
- Before executing the code, we need to create a specific environment which allows us to install the required libraries necessary for our project. • Type conda create -name “env_name”, e.g.: conda create -name project_1 • Type conda activate “env_name, e.g.: conda activate project_1
- Make sure you are in the correct path in your terminal, where you have saved your executable file/folder. E.g.: cd C:\USERS\PERSONAL\YOLO\project_name, then press enter.
- Install necessary libraries from requirements.txt file provided.
- Run pip install -r requirements.txt or conda install requirements.txt (Requirements.txt is a text file consisting of all the necessary libraries required for executing this python file. If it gives any error while installing libraries, you might need to install them individually.)
- Run yolo_face.py in your anaconda terminal and make sure to change the path where your executable files are located. Example: python yoloface.py --image samples/demo.jpg --output-dir outputs/ Please follow the above links on how to install and set up anaconda environment to execute files.
The Datafile which was used in this project was some yolov3 configuration files, A configuration or .cfg file is nothing but a detailed explanation about the number of parameters being used in the model. A typical .cfg files consists of all the parameters required for training and test our model. Some of the parameters such as, Learning rate, convolutional filters, mask, number of classes etc.
- We might face an issue while installing specific libraries.
- Make sure you have the latest version of python, since sometimes it might cause version mismatch.
- Adding path to environment variables in order to run python files and anaconda environment in code editor, specifically in visual studio code.
- Loading an understanding the transfer learning concept might be tricky at the start. Please refer to the algorithm description to learn more about transfer learning.
Note: All the required data hasn't been provided over here i.e the model weigths are not provided over here. Please feel free to contact me for any issues.