-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 23
Home
Execute Serverless Functions with Image Recognition
Classify images as soon as you upload them in a database with serverless functions
Cloud
Developers can accelerate development and build applications that executes actions based on events. This developer pattern leverages Cloudant events that triggers a Cloud Function to classify the images uploaded.
Anthony Amanse
- link to demo video
The application demonstrates an IBM Cloud Functions (based on Apache OpenWhisk) that gets an image from the Cloudant database and classifies it through Watson Visual Recognition. The use case demonstrates how actions work with data services and execute logic in response to Cloudant events.
One function, or action, is triggered by changes (in this use case, an upload of a document) in a Cloudant database. These documents are piped to another action that submits the image to Watson Visual recognition and upload a new document in Cloudant with the classifiers produced by Watson.
When the reader has completed this Code Pattern, they will understand how to:
- Create and Deploy Cloud Functions
- Trigger Cloud Functions with Cloudant changes
- Use Watson Image Recognition with Cloud Functions
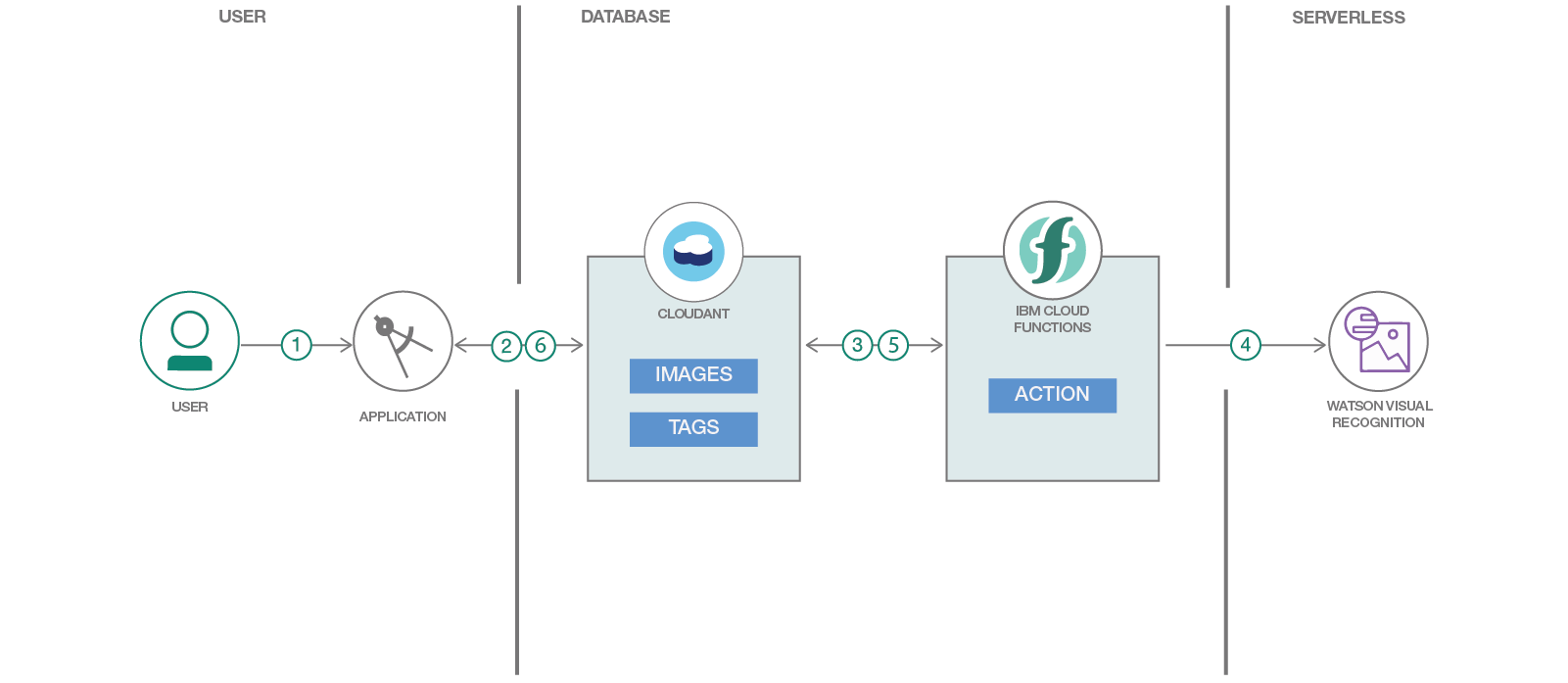
- User chooses a picture from the gallery.
- The image is stored in the Cloudant database.
- Cloud Function is triggered when there's a new image in the database.
- Cloud Function gets the image and uses Watson Visual Recognition to process the image.
- Cloud Function stores the results (classes with scores) from Visual Recognition in the database.
- The user can see the new tags or classes in the image they uploaded.
- IBM Cloud Functions (powered by Apache OpenWhisk): Execute code on demand in a highly scalable, serverless environment.
- Cloudant: A fully managed data layer designed for modern web and mobile applications that leverages a flexible JSON schema.
- Watson Visual Recognition: Visual Recognition understands the contents of images - visual concepts tag the image, find human faces, approximate age and gender, and find similar images in a collection.
- Serverless: An event-action platform that allows you to execute code in response to an event.
There are times where setting up your application's server will take more than a reasonable amount of time in your development cycle. With serverless computing, you can get away with setting up servers and just run your code. This way, you can spend more time programming your application and less time with managing your server. Serverless, despite the name, is actually still using servers to execute your functions. Where it stands out is you only get charged for how much time it took your code to run and not worry about paying for idle time. Your functions are only executed by events or directly through REST APIs.
IBM Cloud Functions which is based on OpenWhisk can help you get started on building your application leveraging the cost-efficiency and scalability of serverless computing. A simple use case of Cloud Function is executing an action when a user uploads something on a database. The developer pattern Serverless Image Recognition uses a Cloudant database and triggers an action based on changes in the database. The developer pattern is using a web app to showcase the serverless implementation. When a user uploads an image, the executed action gets the image and classifies it using Watson Visual Recognition then tags the image based on the classifiers it got from the service.
Based on my personal experience with serverless, the time saved in not configuring an application's backend infrastructure is always beneficial to developers. I get to spend more time focusing on the code rather than managing the infrastructure. One drawback I saw in serverless is a cold start for functions. This can be seen the first time you run your function or when your function hasn't been executed for a long time. Although this can be remedied by having a cron job to warm-up your serverless functions, there are also times that you may want to consider using a server for your application.
- Apache OpenWhisk: Open source cloud platform that executes functions in response to events at any scale.
- Node.js Cloudant: Official Cloudant library for Node.js.
- Watson APIs Node.js SDK: Node.js client library to use the Watson APIs.