-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 287
Vector Clock
In computer science, a "vector clock" is an algorithm that partially orders events by their
causality (by happened-before relation). Its use is similar to Lamport timestamp. Unlike Lamport timestamp, vector clock is accurate and has no false positive errors.
A vector clock is a vector of sequence numbers of highest observed events from each validator.
If there's no fork, the length of vector clock is always equal to the number
of validators in current epoch.
In Lachesis, the vector clock is used not only to determine event causality, but to
compute forklessCause relation. In order to do this, two vector clocks with
opposite directions are required:
- x.HighestBefore[v] is a vector of sequence numbers of
"highest observed by
x event" events from eachvalidator v. - x.LowestAfter[v] is a vector of sequence numbers of
"lowest which observe
x event" events from eachvalidator v.
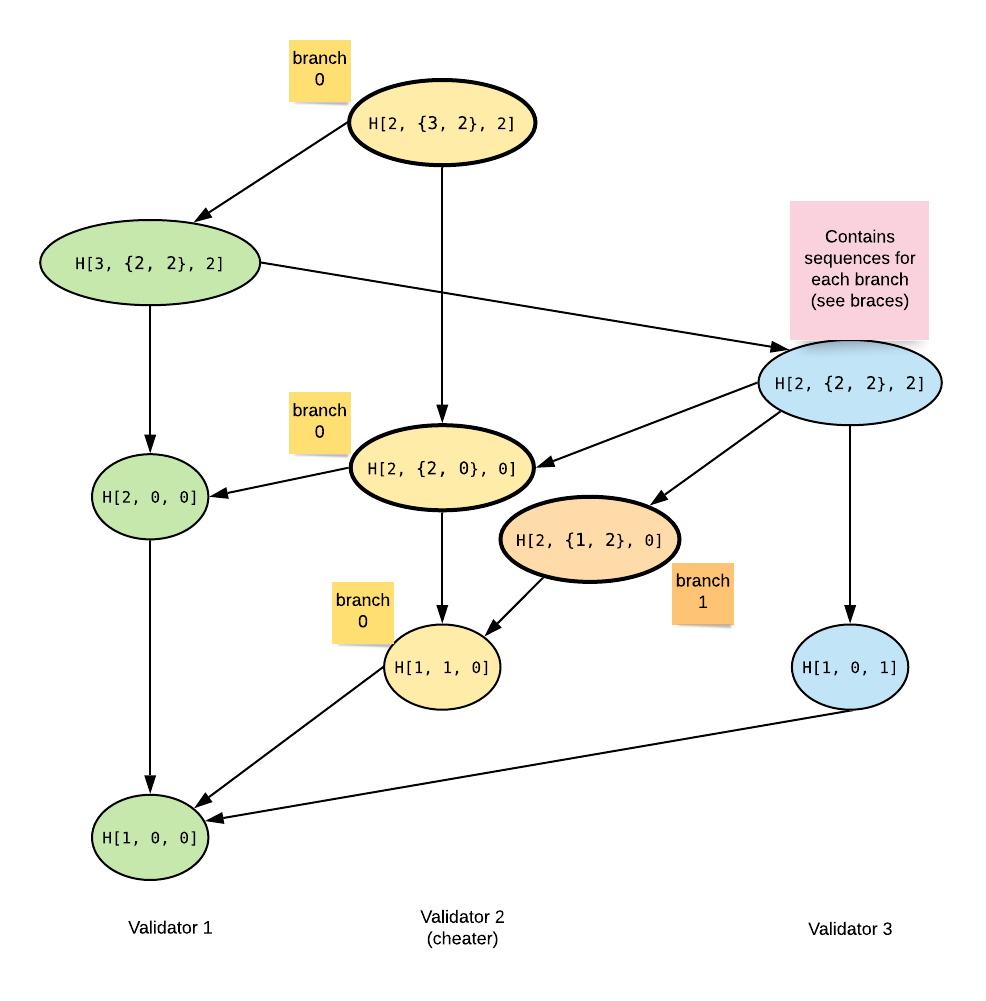
If a validator is a cheater, then both vectors will store
sequences for each validator's branch and will contain more elements than the number of validators.
The current implementation of these calculations may be found in the vector package.
The HighestBefore depends only on event's subgraph. Thus, it doesn't change once it's calculated.
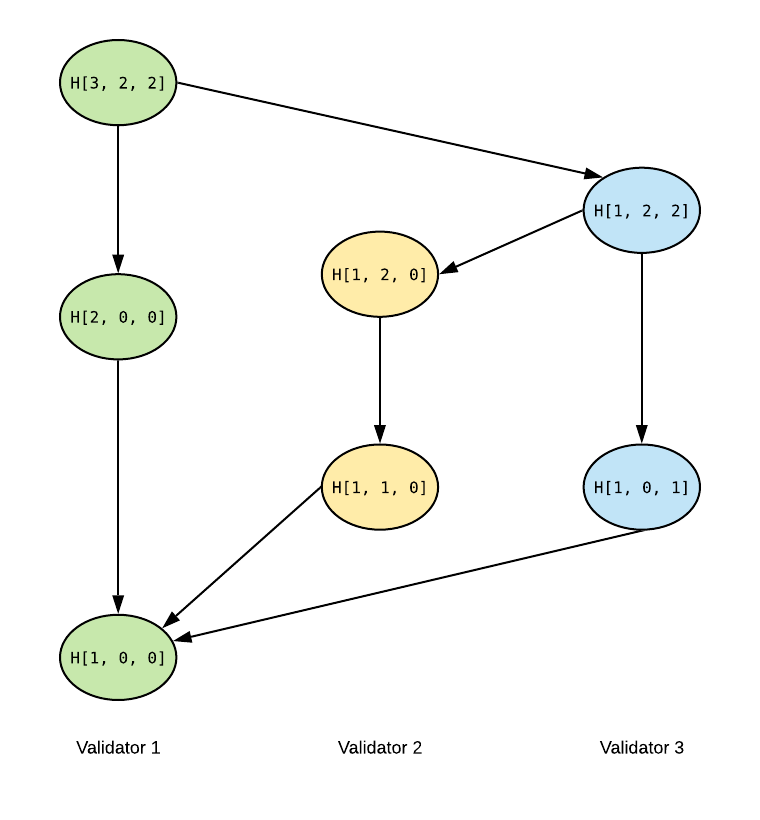
Unlike HighestBefore vector, LowestAfter vector of a past event may get updated after connection of the present event. As an illustration of LowestAfter, we show how LowestAfter vector is computed after each new connection of each event.
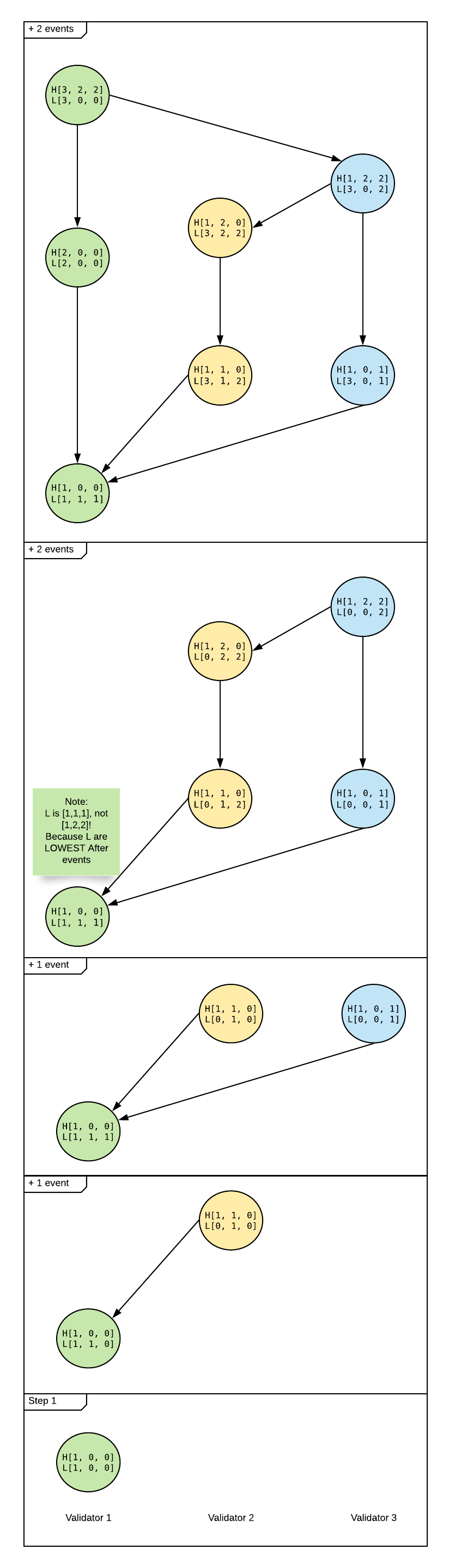
The definition of forklessCause may be found in consensus.
To calculate the forklessCause relation, the following algorithm is used:
function forklessCause(eventA, eventB)
counter = 0
if eventA observes a fork from eventB creator
return false
for v in validators
a = eventA.HighestBefore[v]
b = eventB.LowestAfter[v]
if b <= a AND b != 0 AND not(eventA observes a fork from v)
counter += validator.Stake
return counter >= {QUORUM}The main idea of the above function is that
eventB.LowestAfter[v]<=eventA.HighestBefore[v] if and only if
highest observed event by eventA, from the validator v, observes eventB.
When there exists a fork, the calculation will be more complex, which may be found
in the vector package.
When a fork event occurs, the related validator virtually splits into 2 honest validators (branches).
The full algorithms may be found in vector package.