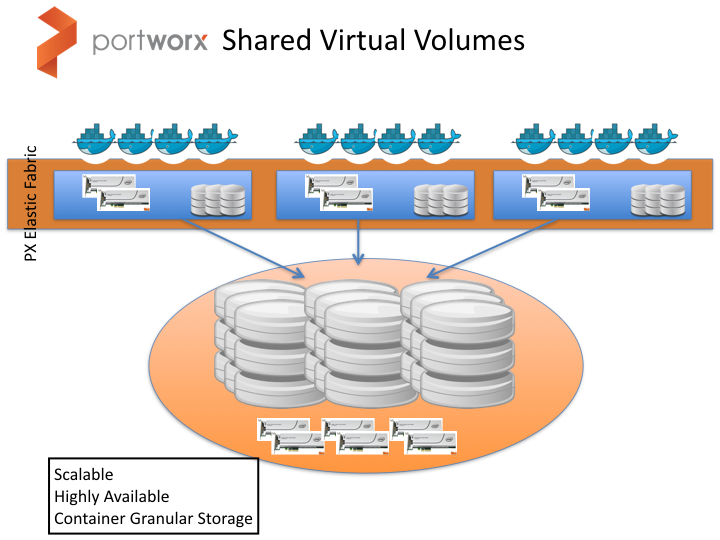
Through shared volumes (also known as a global namespace), a single volume's filesystem is concurrently available to multiple containers running on multiple hosts.
A typical pattern is for a single container to have one or more volumes. Conversely, many scenarios would benefit from multiple containers being able to access the same volume, possibly from different hosts. Accordingly, the shared volume feature enables a single volume to be read/write accessible by multiple containers. Example use cases include:
- a techincal computing workload sourcing its input and writing its output to a shared volume
- scaling the number of Wordpress containers based on load while managing a single shared volume.
The shared volumes feature is only available in px-dev version 0.5.4 and above.
To create a Portworx shared volume, use the pxctl command. (Future releases will enable shared volumes through "docker volume create".)
# pxctl volume create my_shared_vol --shared --size=5 --repl=3
# pxctl volume list
ID NAME SIZE HA SHARED STATUS
944424689751331159 my_shared_vol 5.0 GiB 3 yes up - detached
Note the "SHARED" status of the volume, in the above output.
Shared volumes are accessed in the same way any volume would be used in Docker. For example:
host1# docker run -it --name box1 -v my_shared_vol:/data --volume-driver=pxd busybox sh
A shared volume can be accessed by containers on different hosts. Any host in the cluster can access a shared volume by name. For example:
host2# docker run -it --name box1 -v my_shared_vol:/data --volume-driver=pxd busybox sh
All writes and modifications to files and directories will be immediately available to consumers of the shared volume. Concurrency of files is handled by the volume's filesystem.
Any nodes outside of the Portworx cluster can access a shared volume through NFS with the following format:
mount -o nolock HOSTNAME:/var/lib/osd/pxns/my_shared_vol /local_mnt
The "-o nolock" is a temporary restriction, as is the requirement HOSTNAME must correspond to the host where the volume is attached.