Yaml Extension provides deeper integration with YAML (YAML Ain't Markup Language), including linting yaml documents and validating against known JSON schemas, including Kubernetes resources.
Yaml Extension requires some additional tools to be installed on your Mac:
- Node.js 16 and NPM 7 or newer
- Node.js is used to run redhat-developer/yaml-language-server
- NPM is used to install the server during extension installation
- Older versions of Node.js and NPM should still work, but newer versions are advised.
To install the current stable version of Node, click the "Recommended for Most Users" button to begin the download. When that's done, double-click the .pkg installer to begin installation.
Node version managers — If you use something like nvm or fnm, make sure it is configured inside your profile file (.zprofile or .bash_profile) instead of your "rc" file (.zshrc or .bashrc). See Environment Variables for more. You may also have to restart Nova for any changes to take effect.
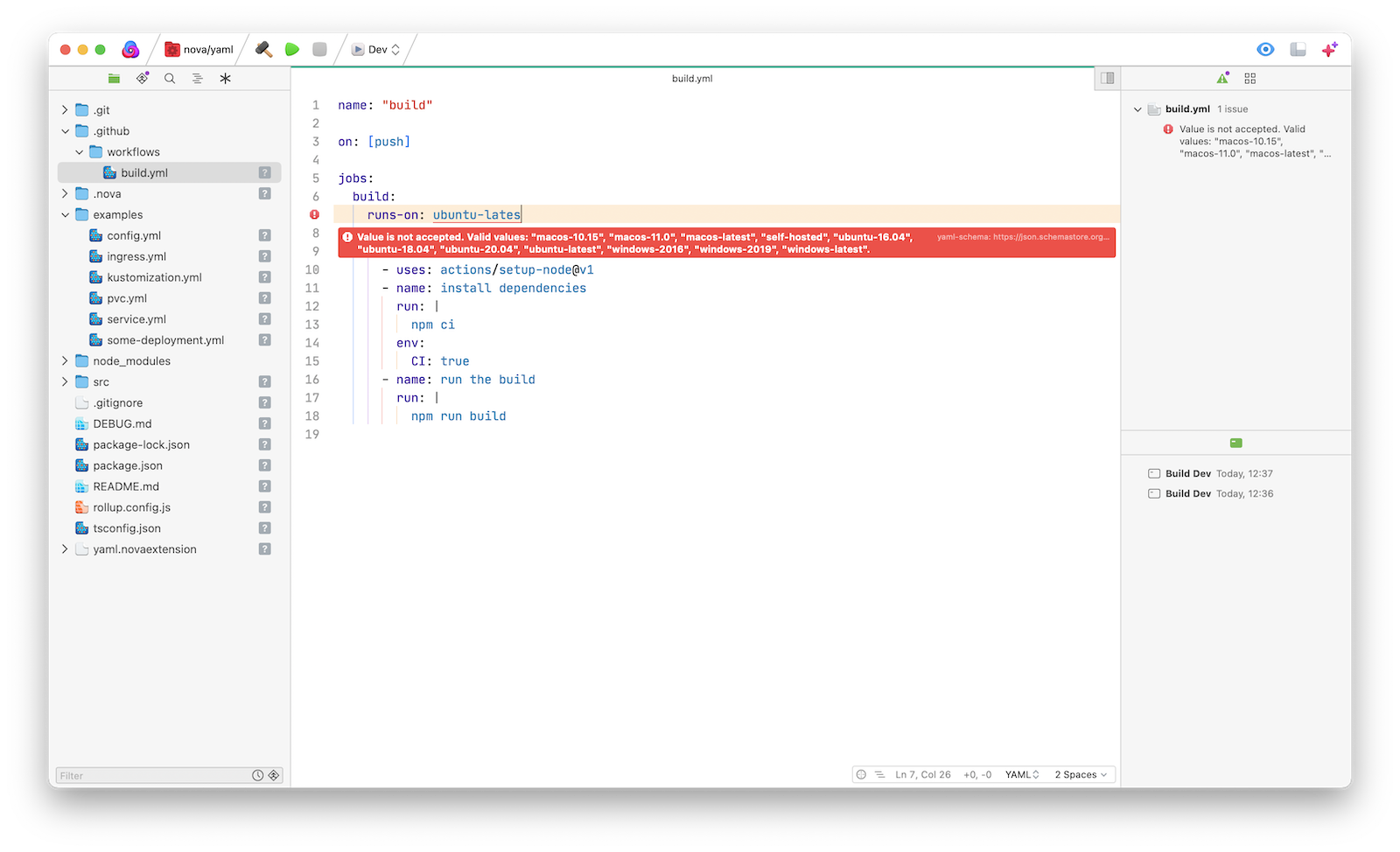
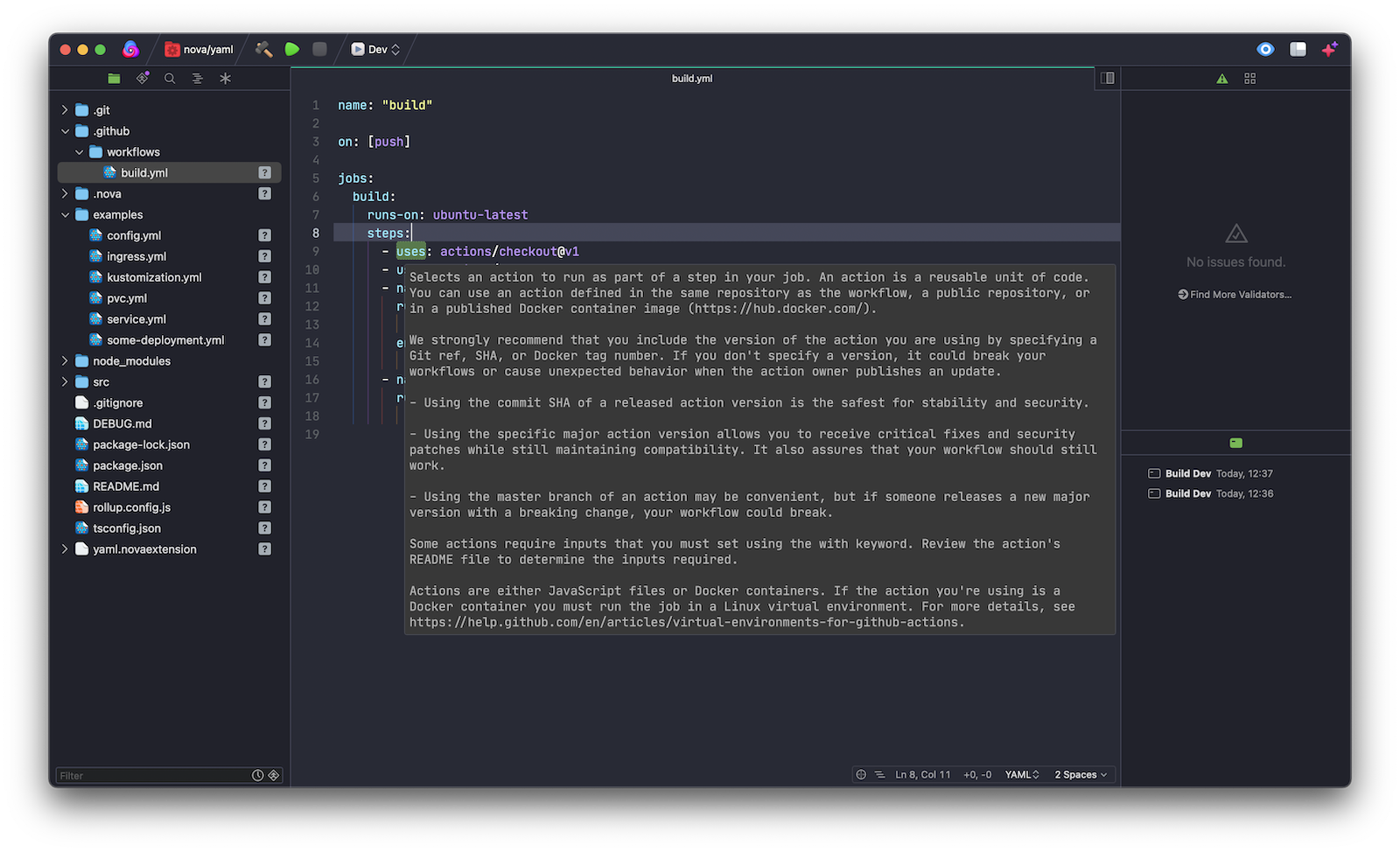
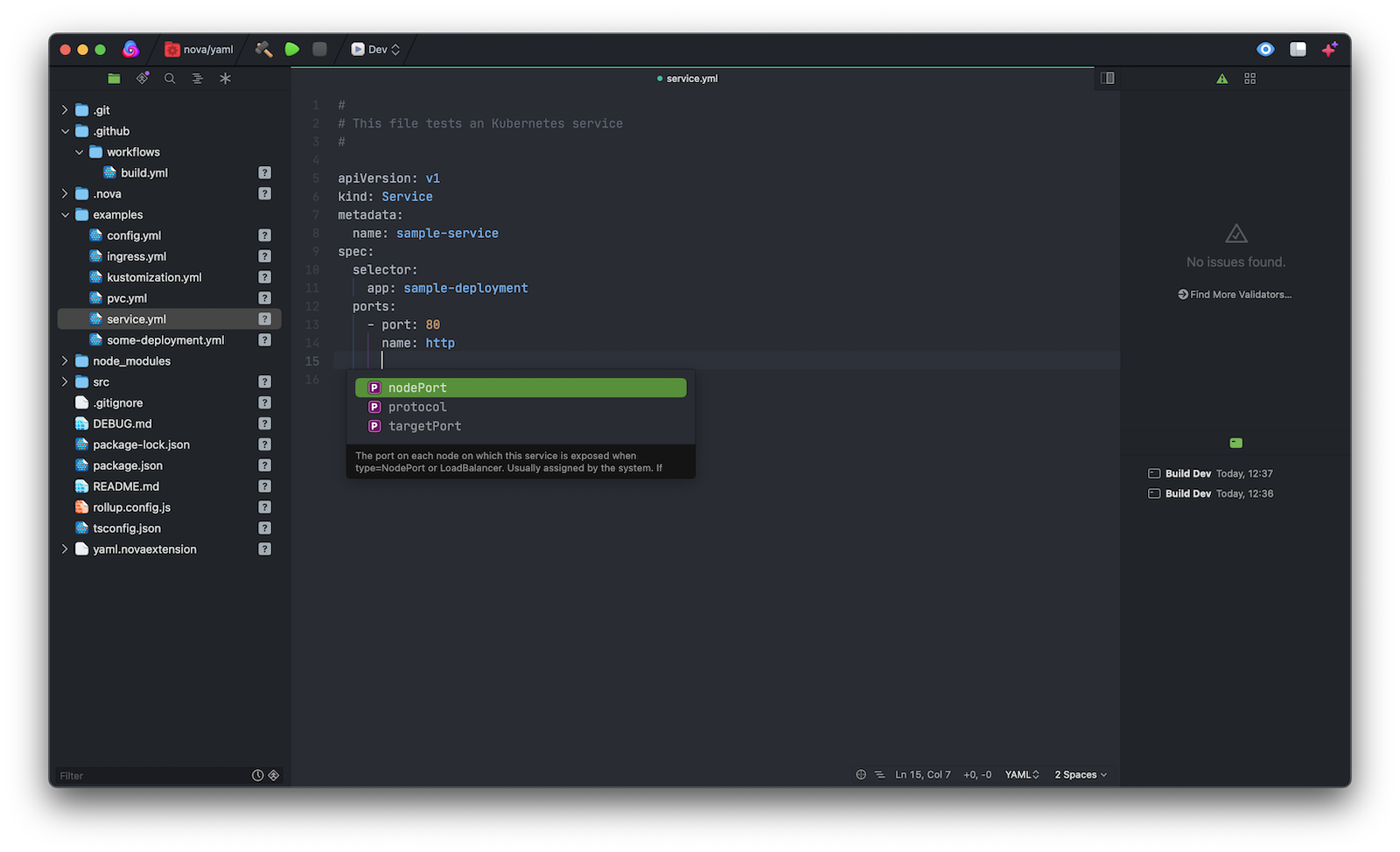
Yaml Extension runs any time you open a local project with YAML files in it, it automatically lints all open files, then reports errors and warnings in Nova's Issues sidebar and the editor gutter:
This extension works by associating YAML files with JSON schemas based on well-known names
and open-source schemas that are available online.
For example, .circleci/config.yml or .github/workflows/**.yml have known schemas which we can validate those files against.
To see all available schemas, visit www.schemastore.org/json/.
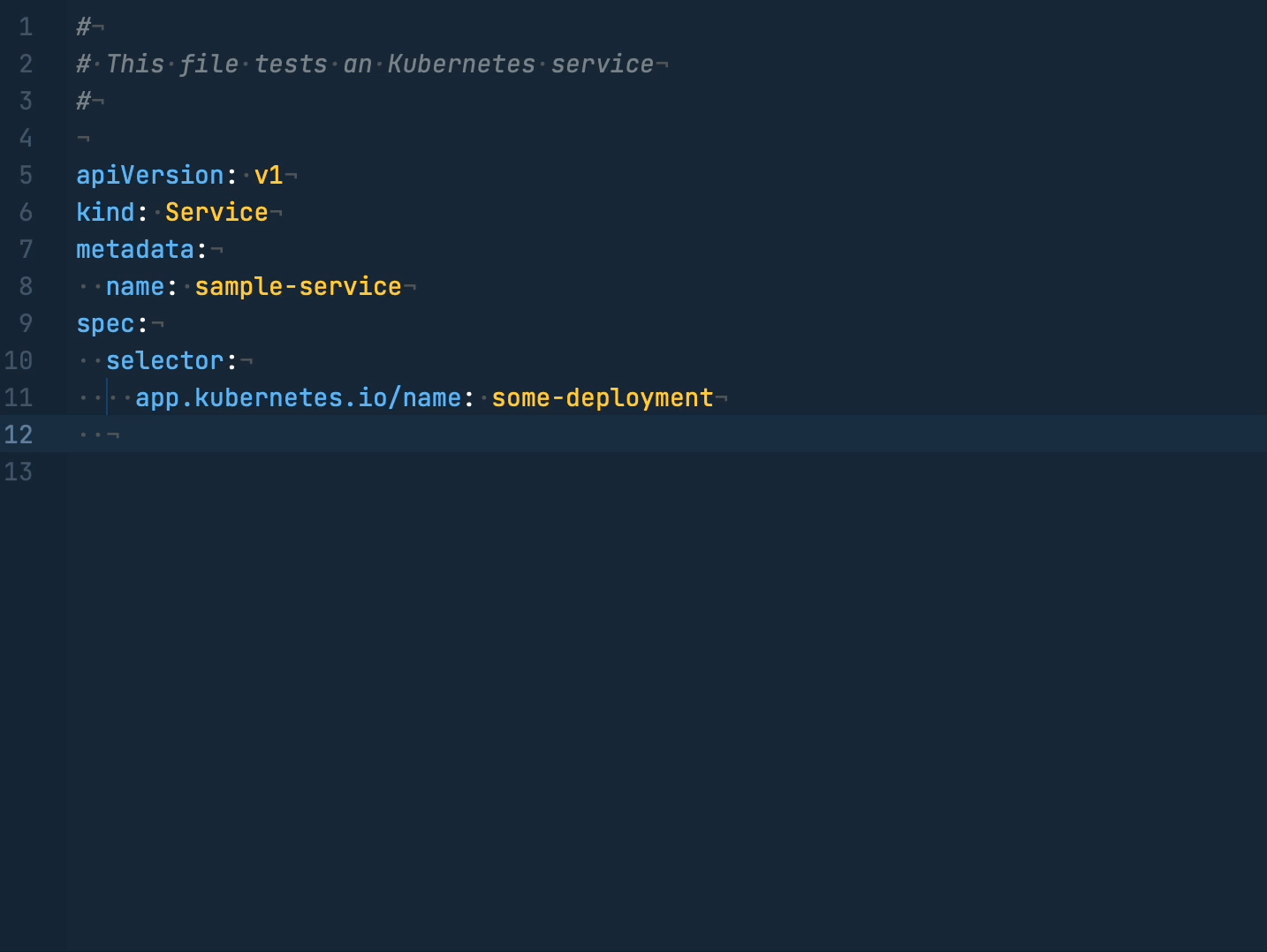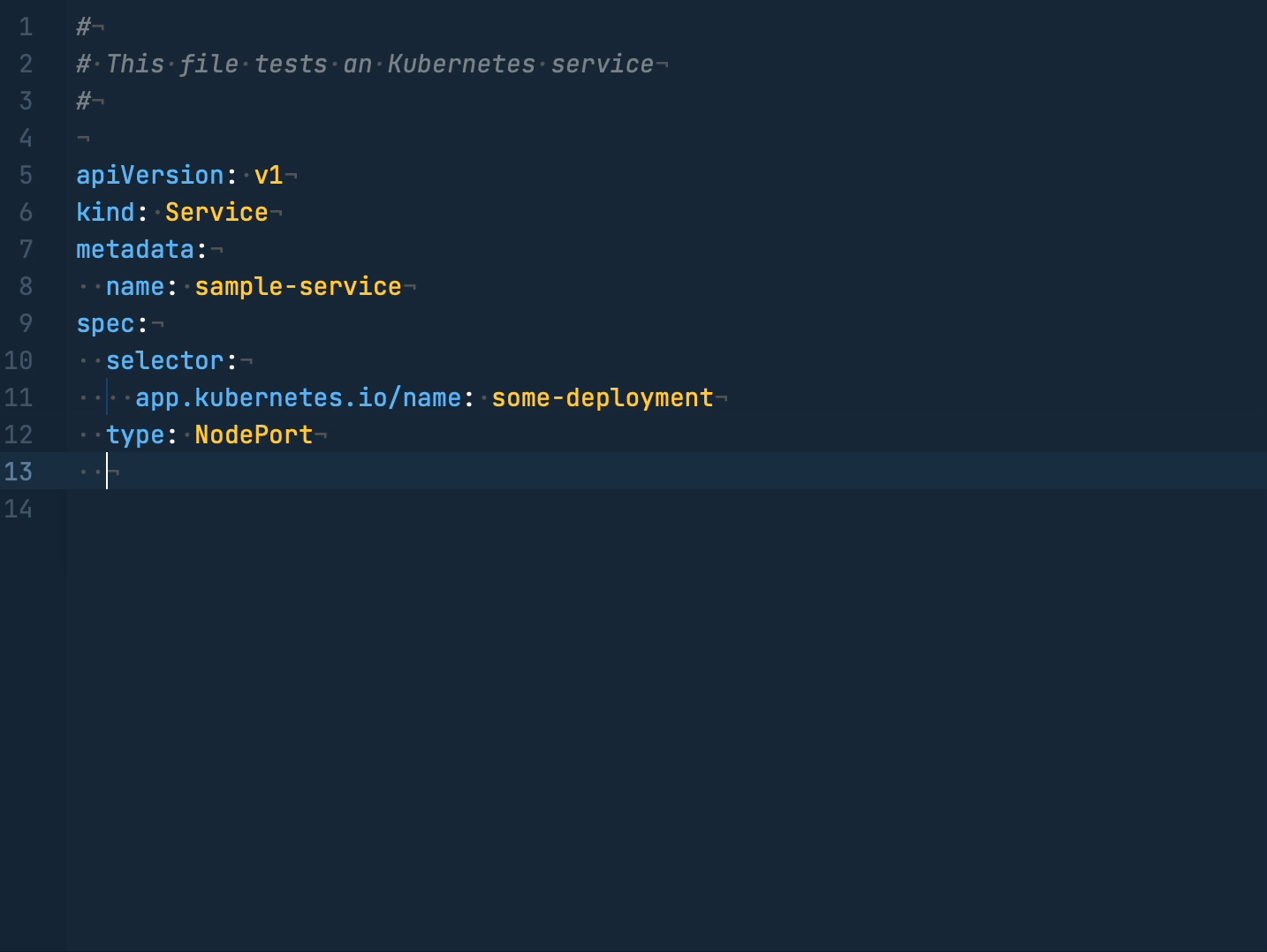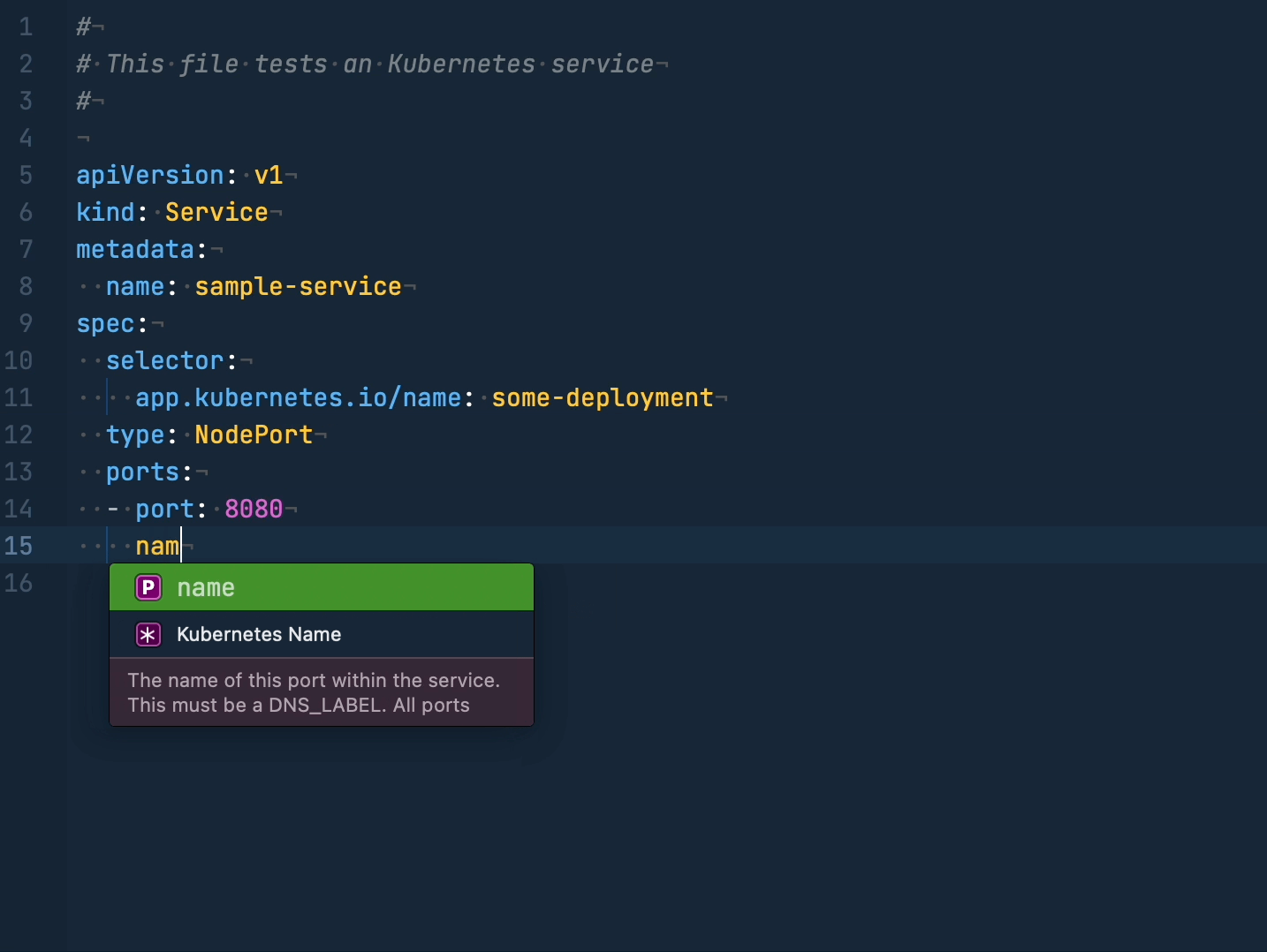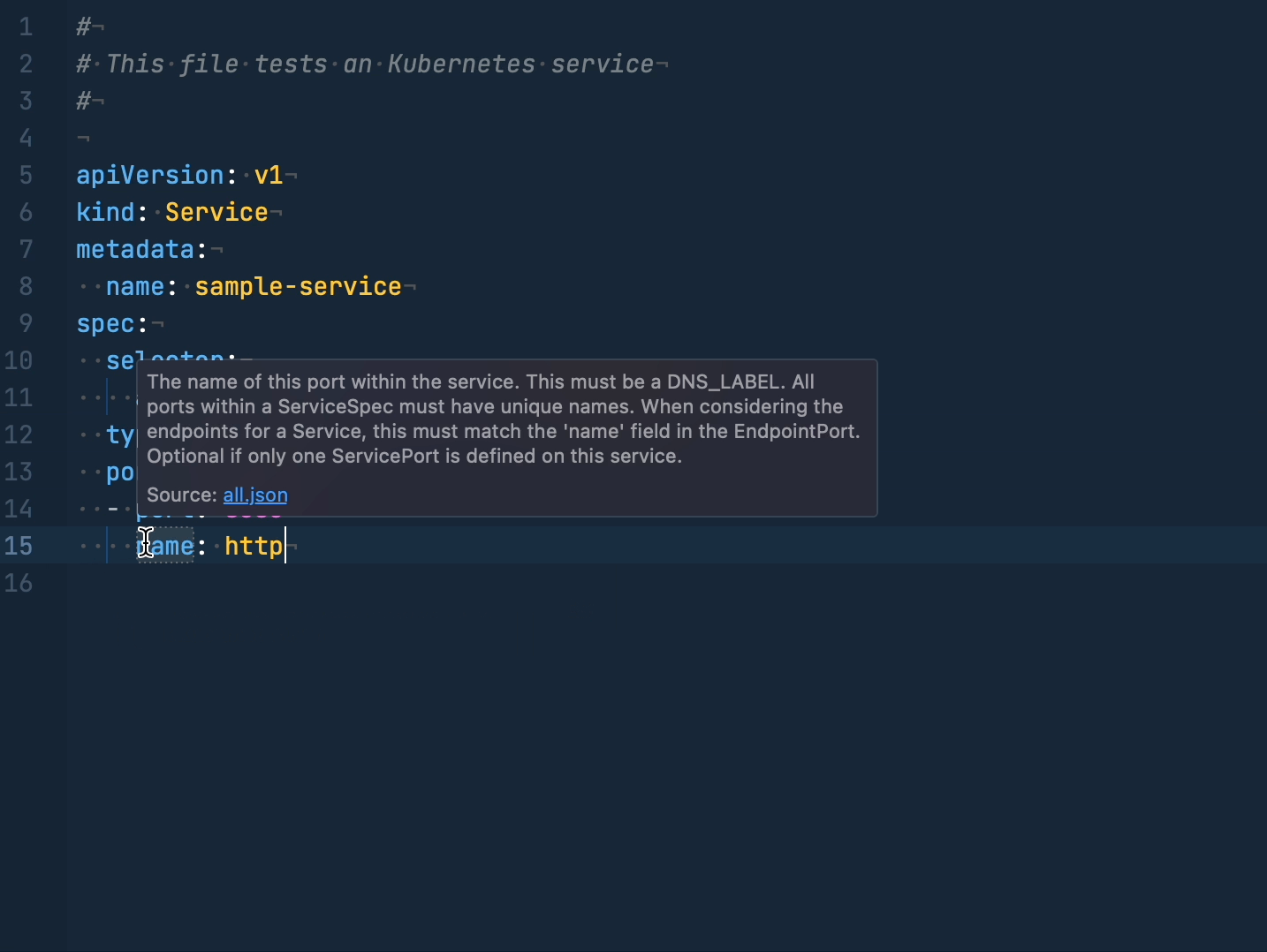
You can also configure custom schema mappings in .nova/Configuration.json manually, e.g.
{
"yaml.schemas": {
"https://json.schemastore.org/lerna.json": "my-custom-lerna.yaml"
"https://json.schemastore.org/github-action.json": ["*-action.yml"],
"../some/relative/path.json": [
"app-config.yml",
"app-config.*.yml"
]
}
}Where the key is a URL or path to the your JSON schema, and the value is a glob pattern or array of patterns of files to match against.
Currently, Nova doesn't support this type of configuration so it cannot be done in the Project → Project Settings... UI.
You can add this special comment at the top of your schema file to tell the Yaml Extension which schema to use:
# yaml-language-server: $schema=<urlToTheSchema>or with a relative path:
# yaml-language-server: $schema=../relative/path/to/schemaor with an absolute path:
# yaml-language-server: $schema=/absolute/path/to/schemaYAML tags let you programatically control the parsing of values in YAML files. For example, a tag could be used to unpack a secret:
passwordKey: !secret database.passwordYaml Extension needs to know about these tags so it can help with suggestions and error messages. You can define these globally or per-project inside of Nova.
Note: global and per-project custom tags are not merged. If you have global tags you will need to duplicate them if you want to use per-project tags.
Each line of the configuration should be a separate tag you want to add. It can optionally have a type, which Yaml Extension will check the value of.
The type can be either scalar, mapping or sequence,
for more information, look here.
To set global custom-tags, go to Extensions → Extension Library.... Then navigate to YAML and then to the Preferences tab.
To set per-project, navigate to your project settings by clicking your project name in the top left. Then go to YAML in the side bar and configure Custom tags there.
!secret scalar
!automobile mapping
!peopleList sequence
Yaml Extension runs the redhat-developer/yaml-language-server
Language Server which pulls down associations from https://www.schemastore.org/api/json/catalog.json
and filters out the ones that aren't YAML.
When you open a YAML file,
it sees if it is associated with a schema and if it is,
it downloads the schema to do hover/validation/completions.
You can opt-in to Kubernetes support on a per-project basis.
You need to manually configure your project's settings in .nova/Configuration.json to
tell the Yaml Language Server which files you want it to consider to be Kubernetes ones.
To help with this, there is the Extensions → YAML → Setup Kubernetes Schemas command to bootstrap the process.
It will open your local .nova/Configuration.json and attempt to add a placeholder
schema mapping towards the latest supported Kubernetes JSON schema.
Warning This command covers lots of cases for your existing (or non-existing project configuration) but it will erase any previous
yaml.schemasthat you may have set. If you have custom schemas setup, I'd recommend running the command in a blank project and manually merging the JSON back together again.
The placeholder is setup to match suffixes based on the kubectl api-resources output,
but you can customise this as much as you'd like.
You can re-run the command to reset back to the placeholder.
Under the hood there is one generic Kubernetes schema which decides the structure based on what
apiVersionandkindare set to. So you don't need to worry about mapping different schemas to different files.This schema is from yannh/kubernetes-json-schema and the command picks the highest version that is known to work with the Language Server.
The placeholder will match files like:
deployment.ymlmy-special-service.yamlingress.ymlapp-cm.yaml- The test examples
Hopefully a future version of this extension will parse out the
apiVersionandkindvalues and validate files dynamically based on them, but this currently isn't possible. This is being tracked here.
The underlying Language Server provides more configuration which you can use by editing the .nova/Configuration.json file in your project. Details of these options can be found here.
Yaml Extension requires these Nova permissions:
network:
- to associate YAML files with json schemas
- to download individual json schemas to validate against
- to download the language server when you first install or subsequently update the extension.
process:
- to determine where Node.js is installed
- to install the language server with NPM
- to run the language server which provides most of the features
filesystem:
- to read in YAML files so they can be validated
- to write back to files when applying completions
- to install the language server in extension storage (
~/Library/Application Support/Nova/Extensions/robb-j.yaml) - when using the Setup Kubernetes Schemas command
This information is based on my experience setting up the language server (which I didn't write). If you find it is doing something not described above please fill out an Issue, I want this information to be as accurate and informative as possible.
- Select the Extensions → Extension Library... menu item
- Search for
"Yaml" - Click the Install Button
If believe something isn't working, you can try restarting the yaml server. Select the Extensions → YAML → Restart Server menu item
If things seem really wrong, check the extension console to find out more information.
Select the Extensions → Show Extension Console menu item, then pick the Yaml source.
If you see any errors in that log that aren't like Error: Invalid parameter: registrations,
or the stack trace below that, please fill out an Issue.
- Indentation on completions can be incorrect
This repo does not provide the YAML syntax highlighting in Nova, those are provided by Panic.