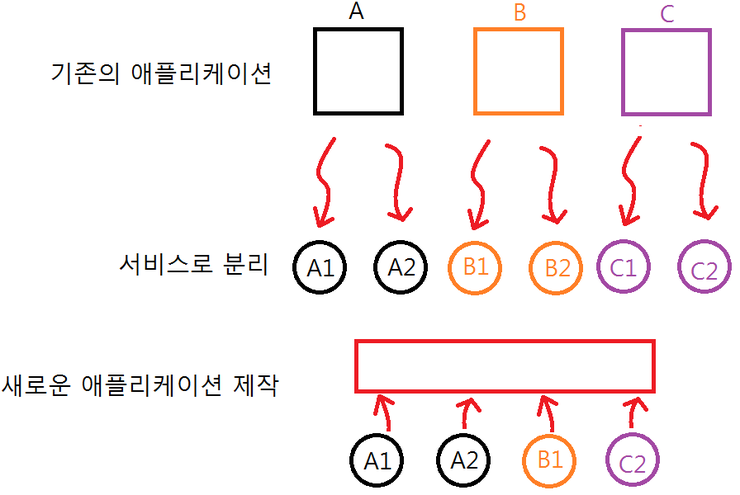
API의 구조를 이야기할 때, 대표적으로 SOAP과 REST가 흔히 비교된다. SOAP은 프로토콜이며, REST는 아키텍쳐 스타일이기 때문이다.
-
SOAP는 분산 컴퓨팅 환경을 위해 설계되었으며 REST는 지점 간 환경을 위해 설계되었다.
-
WADL을 사용하여 REST 서비스에 대한 인터페이스를 정의 할 수 있다.
SOAP(Simple Object Access Protocol)은 일반적으로 널리 알려진 HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP 등을 통해 XML 기반의 메시지를 컴퓨터 **네트워크 상에서 교환하는 프로토콜**이다. -위키피디아-
SOAP는 SOA를 따르는 웹서비스 디자인 표준이며, WSDL(Web Services Description Language)을 이용해 정의한다. XML을 기반으로 헤더와 바디를 조합하는 디자인패턴으로 설계된다.
- 플랫폼과 프로그래밍에 독립적이다.
- 분산컴퓨팅 환경에서 사용하기 위한 디자인이다.(요청과 응답이 매우 체계적으로 구성되고 DTD를 사용할 수 있다)
- 웹서비스를 위해 널리 사용하는 표준이며, 확장성이 뛰어나다.
- 어렵고, 무겁고, 느리다.
즉, 의사 소통과 같은 엄격한 계약을 체결해야하는 경우에 유용 하다.
SOA란 대규모 컴퓨터 시스템을 구축할 때의 개념으로 업무상의 일 처리에 해당하는 소프트웨어 기능을 서비스로 판단하여 그 서비스를 네트워크상에 연동하여 시스템 전체를 구축해 나가는 방법론이다. 위키피디아
즉, 비즈니스 소프트웨어를 독립적인 서비스로 분리하여 시스템을 구축하며, 이로 인해 각 서비스들을 다른 방식으로 묶어 새로운 서비스를 만들어 낼 수 있다. 공급업체와 협력업체 및 고객들과 연결하는 새로운 방법을 확보할 수 있고 변화 요구에서 신속히 반응할 수 있다는 것이다.
WSDL은 웹 서비스 기술언어 또는 기술된 정의 파일의 총칭으로 XML로 기술된다. 웹 서비스의 구체적 내용이 기술되어 있어 서비스 제공 장소, 서비스 메시지 포맷, 프로토콜 등이 기술된다. - 위키피디아 -
WSDL은 SOAP과 XML 스키마를 결합해 인터넷 상에 웹 서비스를 제공하기 위해 사용하며, 아래와 같은 정보를 담고 있다.
- 웹 서비스의 name, URL 정보
- SOAP 메세지의 인코딩 규칙
- SOAP 메세지 전송을 위한 프로토콜 정보
- 웹서비스를 이용하는데 필요한 인터페이스 정보(type, including name, operations, parameter, data)
<description>
<types></types>
<interface></interface>
<binding></binding>
<service></service>
</description>2.0버전은 위의 형태로 구현되어 있으며, 아래는 예시이다.
- types(types,message)
- 메세지나 프로시저에 대한 데이터 타입 설정
- 메세지 전송과 관련된 데이터 포맷 정의
- interface(portType)
- WSDL문서는 이와 같이 구체적으로 물리적인 부분(데이터 타입)에서 추상적이고 논리적인 부분(인터페이스)까지 모두 포괄해 참조 가능
- binding
- 논리적 모델과 물리적 모델 사이의 연결을 제공
- 이미 정의한 추상적인 포트타입에 있는 SOAP를 어떻게 전송할 것인지 구체적으로 기술한 실제 포트에 연결
- SOAP에 HTTP와 SMTP같은 프로토콜을 사용하면 프록시나 방화벽은 통과할 수 있지만, 보안성에 있어서는 취약
- service
- 포트 타입과 바인딩을 이용해서 서비스에 대한 웹 주소 또는 URL 지정
- SOAP 서버를 설정한 위치를 지정하는 것이 일반적인 방법
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<description xmlns="http://www.w3.org/ns/wsdl"
xmlns:tns="http://www.example.com/wsdl20sample"
xmlns:whttp="http://www.w3.org/ns/wsdl/http"
xmlns:wsoap="http://www.w3.org/ns/wsdl/soap"
targetNamespace="http://www.example.com/wsdl20sample">
<!-- Abstract types(데이터 타입/method의 인자와 리턴 값 선언) -->
<types>
<xs:schema xmlns="http://www.example.com/wsdl20sample"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://www.example.com/wsdl20sample">
<xs:element name="request">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="header" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="xs:string">
<xs:attribute name="name" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="body" type="xs:anyType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="method" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="uri" type="xs:anyURI" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="response">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="header" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="xs:string">
<xs:attribute name="name" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="body" type="xs:anyType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="status-code" type="xs:anySimpleType" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="response-phrase" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
</types>
<!-- Abstract interfaces : 인터페이스 정의 -->
<interface name="RESTfulInterface">
<fault name="ClientError" element="tns:response"/>
<fault name="ServerError" element="tns:response"/>
<fault name="Redirection" element="tns:response"/>
<operation name="Get" pattern="http://www.w3.org/ns/wsdl/in-out">
<input messageLabel="GetMsg" element="tns:request"/>
<output messageLabel="SuccessfulMsg" element="tns:response"/>
</operation>
<operation name="Post" pattern="http://www.w3.org/ns/wsdl/in-out">
<input messageLabel="PostMsg" element="tns:request"/>
<output messageLabel="SuccessfulMsg" element="tns:response"/>
</operation>
<operation name="Put" pattern="http://www.w3.org/ns/wsdl/in-out">
<input messageLabel="PutMsg" element="tns:request"/>
<output messageLabel="SuccessfulMsg" element="tns:response"/>
</operation>
<operation name="Delete" pattern="http://www.w3.org/ns/wsdl/in-out">
<input messageLabel="DeleteMsg" element="tns:request"/>
<output messageLabel="SuccessfulMsg" element="tns:response"/>
</operation>
</interface>
<!--binding : 실제 네트워크 protocol과 protType 매핑 즉, 어떻게 주고 받을지-->
<!-- Concrete Binding Over HTTP -->
<binding name="RESTfulInterfaceHttpBinding" interface="tns:RESTfulInterface"
type="http://www.w3.org/ns/wsdl/http">
<operation ref="tns:Get" whttp:method="GET"/>
<operation ref="tns:Post" whttp:method="POST"
whttp:inputSerialization="application/x-www-form-urlencoded"/>
<operation ref="tns:Put" whttp:method="PUT"
whttp:inputSerialization="application/x-www-form-urlencoded"/>
<operation ref="tns:Delete" whttp:method="DELETE"/>
</binding>
<!-- Concrete Binding with SOAP-->
<binding name="RESTfulInterfaceSoapBinding" interface="tns:RESTfulInterface"
type="http://www.w3.org/ns/wsdl/soap"
wsoap:protocol="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindings/HTTP/"
wsoap:mepDefault="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/mep/request-response">
<operation ref="tns:Get" />
<operation ref="tns:Post" />
<operation ref="tns:Put" />
<operation ref="tns:Delete" />
</binding>
<!-- Web Service offering endpoints for both the bindings-->
<service name="RESTfulService" interface="tns:RESTfulInterface">
<endpoint name="RESTfulServiceRestEndpoint"
binding="tns:RESTfulInterfaceHttpBinding"
address="http://www.example.com/rest/"/>
<endpoint name="RESTfulServiceSoapEndpoint"
binding="tns:RESTfulInterfaceSoapBinding"
address="http://www.example.com/soap/"/>
</service>
</description>REST(Representational State Transfer)는 표준을 정의하지 않는 아키텍처 스타일이다. 일반적으로 JSON이 많이 사용되지만, XML, YAML등 protocol을 강제하지 않는다.
- 플랫폼, 프로그래밍에 독립적이다.
- 가볍고 빠르고 쉽다.
- 형식에 구애받지 않는다.(XML, JSON, HTML 등 무엇이든 사용 가능)
- HTTP 프로토콜에서만 사용가능하다.
- 분산환경에 비적합하다.(point to point 통신 모델 가정)
- 보안, 정책 등에 표준이 없다.
- https://deepwelloper.tistory.com/89
- https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/SOAP
- https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EC%84%9C%EB%B9%84%EC%8A%A4_%EC%A7%80%ED%96%A5_%EC%95%84%ED%82%A4%ED%85%8D%EC%B2%98
- https://m.blog.naver.com/PostView.nhn?blogId=wndrlf2003&logNo=220526883782&proxyReferer=https:%2F%2Fwww.google.com%2F
- http://egloos.zum.com/tequiero35/v/941680
- https://jeong-pro.tistory.com/153
- https://www.it-swarm-ko.tech/ko/web-services/wsdl-vs-rest-%ec%9e%a5%eb%8b%a8%ec%a0%90/957543713/