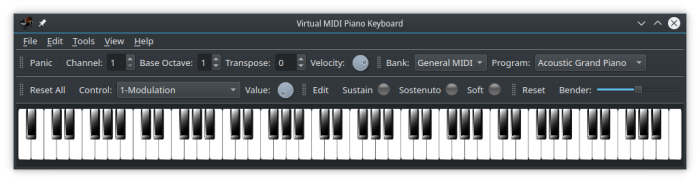
This program is a MIDI events generator/receiver. It doesn't produce any sound by itself, but can be used to drive a MIDI synthesizer (either hardware or software, internal or external). You can use the computer's keyboard to play MIDI notes, and also the mouse. You can use the Virtual MIDI Piano Keyboard to display the played MIDI notes from another instrument or MIDI file player. To do so, connect the other MIDI port to the input port of VMPK.
VMPK has been tested in Linux, Windows and Mac, but maybe you can build it also on other operating systems. If you can compile and test the program, please drop a mail to the author.
The Virtual Keyboard by Takashi Iway vkeybd has been the inspiration for this one. It is a wonderful piece of software and has served us well for many years. Thanks!
VMPK uses a modern GUI framework: Qt, that gives excellent features and performance. Drumstick-RT provides MIDI input/output features. Both frameworks are free and platform independent, available for Linux, Windows and Mac OSX.
The alphanumeric keyboard mapping can be configured from inside the program using the GUI interface, and the settings are stored in XML files. Some maps for Spanish, German and French keyboard layouts are provided, translated from the ones provided by VKeybd. Raw keyboard mappings can also be defined translating X11, Windows or Mac keycodes to MIDI notes.
VMPK can send program changes and controllers to a MIDI synth. The definitions for different standards and devices can be provided as .INS files, the same format used by QTractor and TSE3. It was developed by Cakewalk and used also in Sonar.
This software is far from being complete. See the TODO file for a list of pending features. Please feel free to contact the author to ask questions, report bugs, and propose new features.
See https://vmpk.sourceforge.io for more details.
Latest release is available in Sourceforge:
https://sourceforge.net/projects/vmpk/files
You need Qt 6.2 or newer (Qt5 >= 5.9 is also supported). Install the -devel package for your system, or download the open source edition:
https://www.qt.io/download
Drumstick 2.10 is required in all platforms. It uses the ALSA sequencer in Linux, WinMM in Windows and CoreMIDI in Mac OSX, which are the native MIDI systems in all the supported platforms.
https://drumstick.sourceforge.net
The build system is based on CMake (>= 3.16). You can download it from:
https://www.cmake.org
You need also a C++17 compiler.
https://gcc.gnu.org/
https://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw/
Optionally, you can build a Windows setup program using NSIS.
https://nsis.sourceforge.io/
Download the sources from https://sourceforge.net/projects/vmpk/files Unpack the sources in your home directory, and change to the unpacked dir.
$ tar xvf vmpk-x.y.z.tar.gz
$ mkdir vmpk-x.y.z-build
You can choose between CMake and Qmake to prepare the build system, but qmake is intended only for testing and development.
$ cmake -S vmpk-x.y.z -B vmpk-x.y.z-build
or
$ ccmake -S vmpk-x.y.z -B vmpk-x.y.z-build
or
$ cmake-gui -S vmpk-x.y.z -B vmpk-x.y.z-build
After that, compile the program:
$ cmake --build vmpk-x.y.z-build
if the program has been compiled successfully, you can install it:
$ cmake --install vmpk-x.y.z-build
There are more targets available:
$ cmake --build vmpk-x.y.z-build --target uninstall
$ cmake --build vmpk-x.y.z-build --target clean
You can get some compiler optimisation when building the program, but don't expect too much improvement. There are two ways. First, using a predefined configuration type:
$ cmake -S vmpk-x.y.z -B vmpk-x.y.z-build -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
The CMake "Release" type uses the compiler flags: -O3 -DNDEBUG. Other predefined build types are Debug, RelWithDebInfo, and MinSizeRel.
The second way is to choose the compiler flags yourself:
$ export CXXFLAGS="-O2 -march=native -mtune=native -DNDEBUG"
$ cmake -S vmpk-x.y.z -B vmpk-x.y.z-build
You need to find the best CXXFLAGS for your own system.
If you want to install the program at some place other than the default (/usr/local) use the following CMake option:
$ cmake -S vmpk-x.y.z -B vmpk-x.y.z-build -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr
Other optional configuration options are:
- ENABLE_DBUS: activates the DBus interface, enabled on Linux by default.
- EMBED_TRANSLATIONS: include translations inside the executable as resources. This option is OFF by default. Useful for portable builds.
- BUILD_DOCS: create the man page from XML sources (ON by default). If OFF, then a pre-built man page included in the source tarball is installed.
- USE_QT5: Prefer building with Qt5 instead of Qt6. Off by default.
example:
$ cmake -S vmpk-x.y.z -B vmpk-x.y.z-build -DENABLE_DBUS=No
A man page is included in the source package, ready to be installed and used. But if you prefer to generate the man page yourself, the build system can do it if you have installed in your system the following packages:
- xsltproc program.
- docbook XSLT stylesheets.
The package names depend on the Linux distribution. For Debian they are: xsltproc, docbook-xsl and docbook-xml. For openSUSE: libxslt, docbook_4, and docbook-xsl-stylesheets.
To compile the sources in Windows, you need to download either the .bz2 or .gz archive and uncompress it using any utility that supports the format, like 7-Zip.
To configure the sources, you need qmake (from Qt) or CMake. You need to set the PATH including the directories for Qt binaries, MinGW binaries, and also CMake binaries. The program cmake-gui is the graphic version of CMake.
To use the program in Windows, you need some MIDI synth. It is possible to use the "Microsoft GS Wavetable SW Synth" that cames with Windows, but for better performance and quality, the FluidSynth library is included. Another option is Virtual MIDI Synth.
Of course, an external MIDI hardware synth would be an even better approach.
To connect VMPK to/from other MIDI programs, you need some virtual MIDI cable software, like MIDI Yoke, LoopBe1 or Tobias Erichsen's LoopMIDI.
http://www.midiox.com/myoke.htm
https://www.nerds.de/en/loopbe1.html
https://www.tobias-erichsen.de/software/loopmidi.html
The build system is configured to create an app bundle. You need the Apple development tools and frameworks, as well as the Qt SDK. Note that VMPK >= 0.6 requires the Cocoa framework, with the corresponding Cocoa version of Qt.
To compile VMPK using Makefiles, generated by qmake:
$ qmake vmpk.pro -spec macx-g++
$ make
$ macdeployqt build/vmpk.app
To compile using Makefiles, generated by CMake:
$ cmake -G "Unix Makefiles" -S vmpk-x.y.z -B vmpk-x.y.z-build
$ make
To create Xcode project files:
$ qmake vmpk.pro -spec macx-xcode
or
$ cmake -G Xcode -S vmpk-x.y.z -B vmpk-x.y.z-build
You can use the MIDI synth library that is included in Mac OSX, with or without an external program like SimpleSynth. Also from the same author is MIDI Patchbay.
In addition to the aforementioned tools, VMPK uses work from the following open source projects.
-
from Qtractor, by Rui Nuno Capela https://qtractor.sourceforge.io Instrument definition data classes, Shortcuts editor dialog
-
Icon and logo by Theresa Knott https://openclipart.org/detail/366/piano-by-theresaknott
See AUTHORS for a complete list of acknowledgments
Thank you very much.