DRL-agent using the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) method
This projects goal is to utilize Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to train an agent to control 4 joints of a "robotic reach-arm" in order to reach a defined position with its hand.
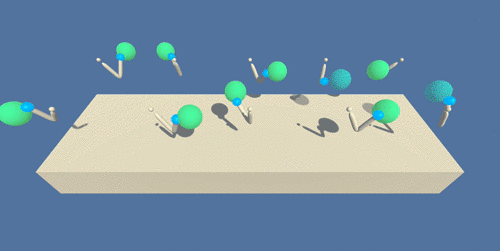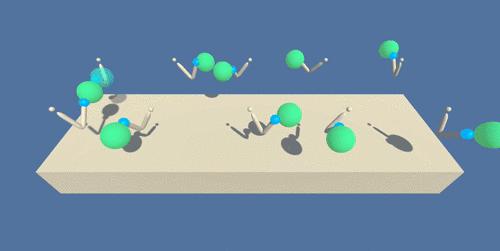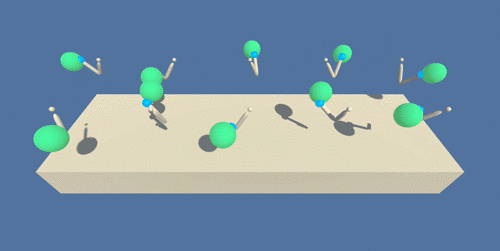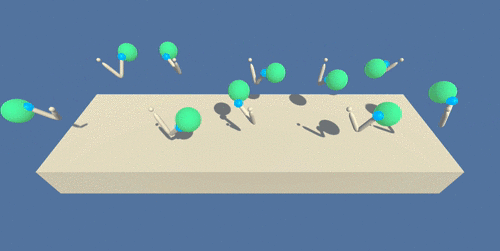
A trained agent will can be seen in below animation, in which the defined position is marked with a green sphere:
(source: https://s3.amazonaws.com/video.udacity-data.com/topher/2018/June/5b1ea778_reacher/reacher.gif)
In RL the environment defines what the agent will learn. In this case the environment allows the agent to choose the magnitude of 4 dimensionsof its action in each timesequence. The action space is continuous, which poses the essence, as well as the challenge in this project. Every action dimension must be in range -1 to 1.
Also the state space is not discrete, but continuous and is perceived by the agent in 33 dimensions. (33 continuous input features)
The rewards of the environment, which serve as reinforcement for the agent to learn, are assigned when its rules are fullfilled:
A reward of +0.1 is provided each timestep the hand of the reacher is placed in the target sphere. 0 reward if it is not placed inside the target sphere.
The task is episodic. To solve the problem the average score must exceed +30 for at least 100 consecutive episodes.
In order to reduce the probability that we end up with an agent that chooses to take actions, that do not lead to fast learning, we 20 run agents simultaneously and average the scores.
The following system prerequisites are required to get it running with my instructions:
- Windows 10 64-Bit.
- Anaconda for Windows.
- GPU with CUDA support(this will not run on CPU only, as its explicitly disabled). Cudatoolkit version 9.0.
- Set up conda environment with Python >=3.6
- Conda create –name <env_name> python=3.6
- Install Jupyter Kernel for this new environment.
- python -m ipykernel install --user --name <Kernel_name> --display-name "<kernel_name>".
- Download ML-Agents Toolkit beta 0.4.0a.
- install it by running following command, with activated conda environment in the directory of ml-agents, that contains the setup.py.
- pip install -e . .
- install PyTorch.
- conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=9.0 -c pytorch.
- Get Unity Environment designed for this project.
- Windows (64-bit): click here.
- Place the file in the DRLND GitHub repository, in the
p2_continuous_control/folder, and unzip (or decompress) the file.
Follow the instructions in the Jupyter notebook file Continuous_control.ipynb to train the agent! For explanations, please see the attached Report.pdf and the comments in the code of model.py and ddpg_agent.py.
After approximately 100 training episodes the agent will reach the average score of +30 for 100 consecutive episodes, which defines this environment as solved.
In this project an "actor-critic" DDPG, as defined in Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning by Timothy P. Lillicrap et al. was implemented.
To improve exploration of this agent stochastic Ornstein-Uhlenbeck was added to the selected action, which lead to an improved learning curve.
In order to make the DRL agent more stable in regards to auto-correlation of weights adjustments, the "Fixed Q-Targets" method was utilized combined with a "Replay Buffer". We update the target neural networks (NN) wiht a "soft-update" method after each training step. Thereby the target network (see "Fixed Q-targets" ) is iteratively updated with the weights of the trained "regular" NN.