Back to Projects List
Automatic multi-anatomical skull structure segmentation of cone-beam computed tomography scans using 3D UNETR
- Luc Anchling (UoM)
- Nathan Hutin (UoM)
- Maxime Gillot (UoM)
- Baptiste Baquero (UoM)
- Celia Le (UoM)
- Romain Deleat-Besson (UoM)
- Jonas Bianchi (UoM, UoP)
- Antonio Ruellas (UoM)
- Marcela Gurgel (UoM)
- Marilia Yatabe (UoM)
- Najla Al Turkestani (UoM)
- Kayvan Najarian (UoM)
- Reza Soroushmehr (UoM)
- Steve Pieper (ISOMICS)
- Ron Kikinis (Harvard Medical School)
- Beatriz Paniagua (Kitware)
- Jonathan Gryak (UoM)
- Marcos Ioshida (UoM)
- Camila Massaro (UoM)
- Liliane Gomes (UoM)
- Heesoo Oh (UoP)
- Karine Evangelista (UoM)
- Cauby Chaves Jr
- Daniela Garib
- F ́abio Costa (UoM)
- Erika Benavides (UoM)
- Fabiana Soki (UoM)
- Jean-Christophe Fillion-Robin (Kitware)
- Hina Joshi (UoNC)
- Lucia Cevidanes (UoM)
- Juan Prieto (UoNC)
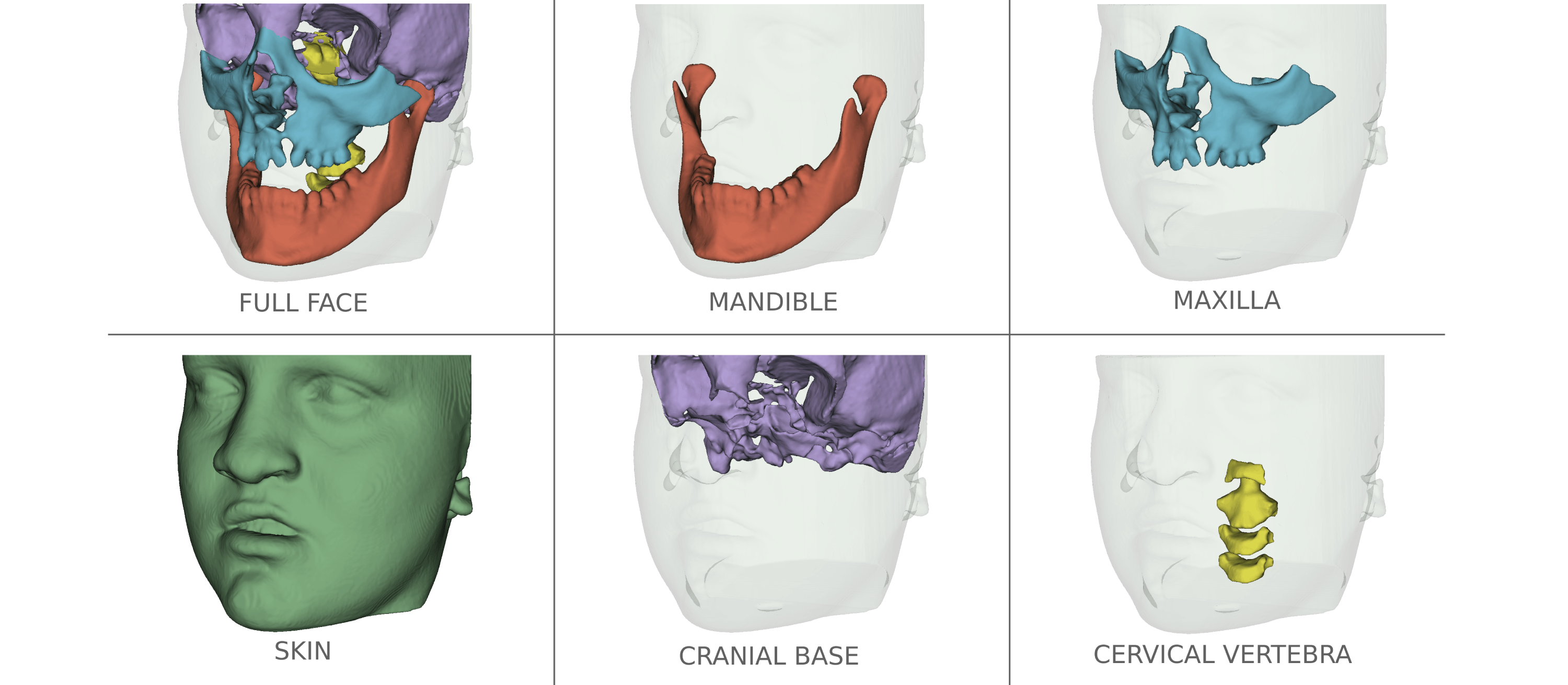
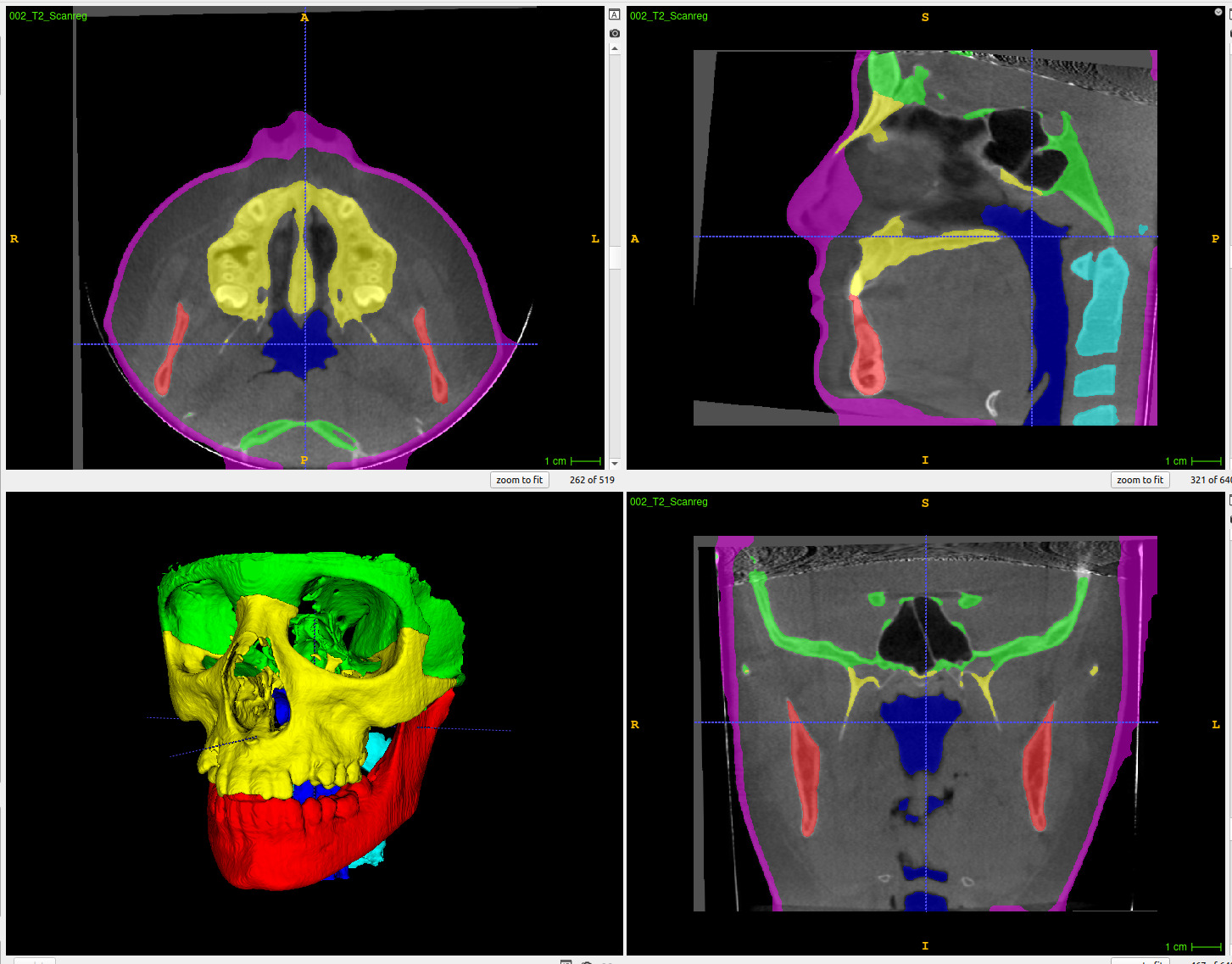
The segmentation of medical and dental images is a fundamental step in automated clinical decision support systems. It supports the entire clinical workflow from diagnosis, therapy planning, intervention, and follow-up. In this paper, we propose a novel tool to accurately process a full-face segmentation in about 5 minutes that would otherwise require an average of 7h of manual work by experienced clinicians. This work focuses on the integration of the state-of-the-art UNEt TRansformers (UNETR) of the Medical Open Network for Artificial Intelligence (MONAI) framework. We trained and tested our models using 618 de-identified Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) volumetric images of the head acquired with several parameters from different centers for a generalized clinical application. Our results on a 5-fold cross-validation showed high accuracy and robustness with an Dice up to 0.962 pm 0.02.
- Do some maintenance to the previously made code
- Train new segmentations of stable regions of reference for image registration models (Cranial Base, Mandible, Maxilla)
- Use the previously made code to train a model for the segmentation of the masks structures
- New segmentation models have been trained and tested
- An extension has been added to this module to take segmentation files as input to generate vtk files
- Train models to detect bone defects and patients with alveolar and palatal cleft
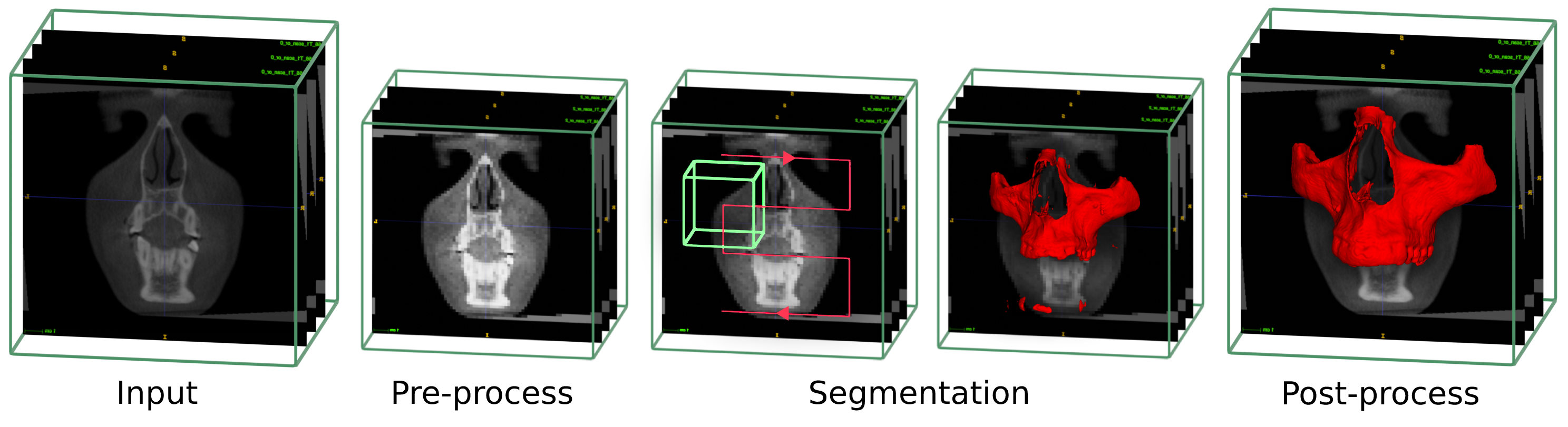
- Dicom File can be used as input
- Contrast correction and rescaling to the trained model spacing
- Use the UNETR classifier network through the scan to perform a first raw segmentation
- Post process steps to clean and smooth the segmentation
- Upscale to the original images size
-
Selection of the different parameters and which structure to segment
-
Use of a dialog progress bar to show/cancel the progress of the segmentation in real time (top right end corner).
-
One the 3D view, result of one of the segmentation with the generated VTK files
-
A prediction takes from 120s to 300s for one patient depending on the local computer GPU capacity ( 15GB down to 3GB)
- The scan intensity in the pink region ( mainely nose, lips and eyes ) will be set to 0 to make it impossible to identify the patient
- The bones segmentations are used to make sure we dont remove important informations during the process