{%= include("install-npm", {save: true}) %}
var Prompt = require('{%= name %}');
var prompt = new Prompt({
name: 'colors',
message: 'What are your favorite colors?',
choices: [
'red',
'blue',
'yellow'
]
});
// promises
prompt.run()
.then(function(answers) {
console.log(answers)
})
.catch(function(err) {
console.log(err)
})
// async
prompt.ask(function(answers) {
console.log(answers)
});Features you won't find with other prompts!
Define choices as a function. This allows you to dynamically generate the choices when the question is asked.
var prompt = new Prompt({
name: 'colors',
message: 'What are your favorite colors?',
choices: function() {
// dynamically build choices
return ['red', 'blue', 'green'];
}
});Easy to configure!
Just pass an object of arrays on choices, and each key in the object will be used as the group "toggle":
var Prompt = require('{%= name %}');
var prompt = new Prompt({
name: 'install',
message: 'Which packages do you want to install?',
choices: {
dependencies: ['generate', 'micromatch'],
devDependencies: ['mocha', 'kind-of']
}
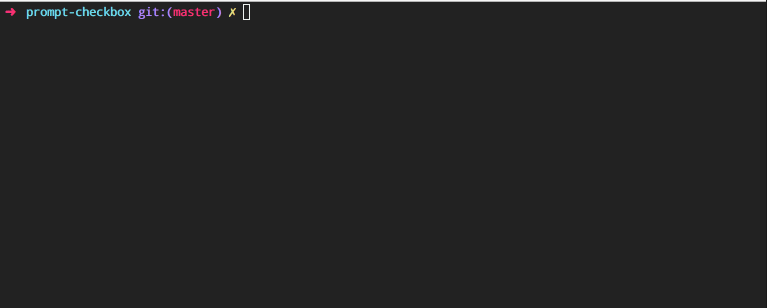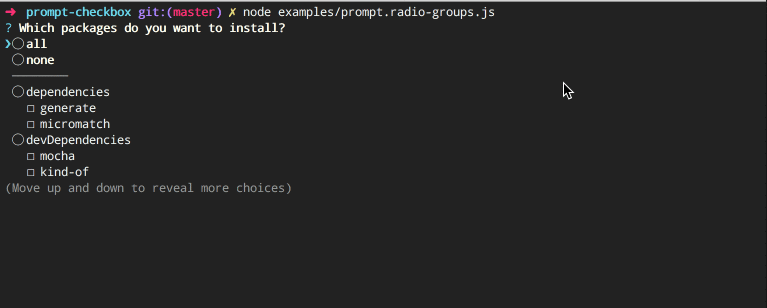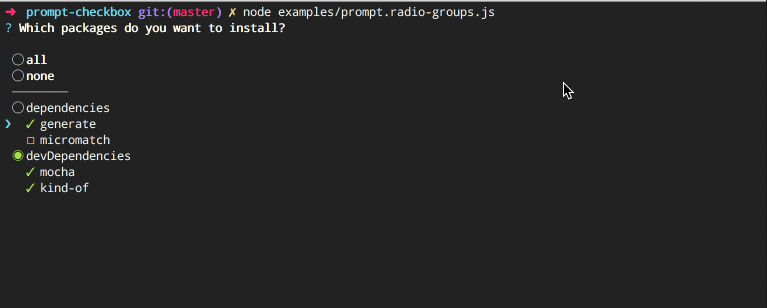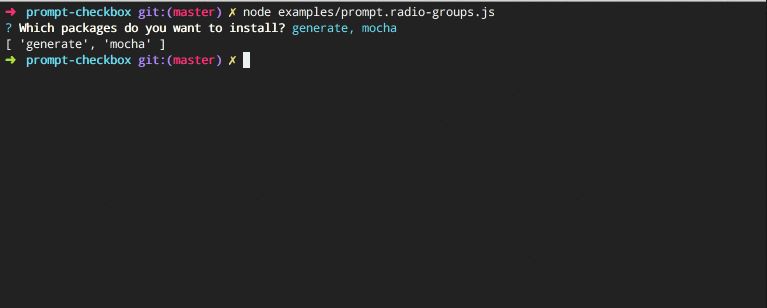
});Adds all and none choices, which select or deselect all choices, respectively. Named "radio choices" since it acts like a hybrid between checkboxes and radio buttons.
Code example
var Prompt = require('{%= name %}');
var prompt = new Prompt({
name: 'install',
message: 'Which packages do you want to install?',
radio: true,
choices: ['foo', 'bar', 'baz']
});Use "radio" choices with choice groups.
var Prompt = require('{%= name %}');
var prompt = new Prompt({
name: 'install',
message: 'Which packages do you want to install?',
radio: true,
choices: {
dependencies: ['generate', 'micromatch'],
devDependencies: ['mocha', 'kind-of']
}
});The following options are either specific to prompt-checkbox, or have behavior that differs in some way from the built-in options from [prompt-base][]. (Any other options from [prompt-base][] may be used as well.)
Type: string|number|array
Default: undefined
Specify the "default" choices to check when the prompt is initialized. Default can be a choice name (string), index (number), or an array of choice names or indices.
Examples
Specify default as a string (choice name):
var prompt = new Prompt({
name: 'colors',
message: 'Best flavor?',
default: 'chocolate',
choices: ['chocolate'] // <= hmm, I wonder what they'll choose?
});Specify an array of defaults (choice names or indices):
var prompt = new Prompt({
name: 'colors',
message: 'Favorite colors?',
default: [1, 'blue'],
choices: ['red', 'blue', 'yellow']
});Type: boolean
Default: undefined
Enable hybrid radio-checkbox support, which adds all and none radio options for toggling all options on and off.
var Prompt = require('{%= name %}');
var prompt = new Prompt({
name: 'colors',
message: 'What are your favorite colors?',
radio: true,
choices: [
'red',
'blue',
'yellow'
]
});Type: function
Default: undefined
Modify answer values before they're returned.
Example
Use options.transform and the prompt.choices.get() method to convert answers (checked choices) to an array of objects (versus of an array of strings).
var Prompt = require('{%= name %}');
var prompt = new Prompt({
name: 'colors',
message: 'What are your favorite colors?',
choices: ['red', 'blue', 'yellow'],
transform: function(answer) {
// - "this" is the prompt instance
// - "this.choices.get()" returns the choice object for each choice
return answer ? answer.map(this.choices.get.bind(this.choices)) : [];
}
});In addition to the keypresses that are supported by [prompt-base][], the following keypress offer different behavior that is specific to checklists:
- down - move the pointer (cursor) down one row for each keypress
- up - move the pointer (cursor) up one row for each keypress
- i - toggle all choices to the opposite of their current state.
- a - enable or disable all choices
- space - toggle a choice
- number - toggle the choice at the given index (starting at 1)
Register the prompt with enquirer:
var Enquirer = require('enquirer');
var enquirer = new Enquirer();
enquirer.register('checkbox', require('{%= name %}'));For formatting questions, [enquirer][] supports either:
- declarative, inquirer-style question format
- functional format using the
.questionmethod.
Inquirer-style questions
Declarative questions format, similar to inquirer.
var questions = [
{
name: 'color',
message: 'What is your favorite color?',
type: 'checkbox',
default: 'blue',
choices: ['red', 'yellow', 'blue']
}
];
enquirer.prompt(questions)
.then(function(answers) {
console.log(answers)
});Or:
enquirer.prompt({
name: 'color',
message: 'What is your favorite color?',
type: 'checkbox',
default: 'blue',
choices: ['red', 'yellow', 'blue']
})
.then(function(answers) {
console.log(answers)
});Functional-style questions
Use the .question method to pre-register questions, so they can be called later. Also, the message may be passed as the second argument, or as a property on the question options.
enquirer.question('letter', 'What are your favorite letters?', {
type: 'checkbox', //<= specify the prompt type
choices: ['a', 'b', 'c']
});
enquirer.question('numbers', {
type: 'checkbox', //<= specify the prompt type
message: 'What are your favorite numbers?',
choices: ['1', '2', '3']
});
// pass the name(s) or questions to ask
enquirer.prompt(['letters', 'numbers'])
.then(function(answers) {
console.log(answers)
});