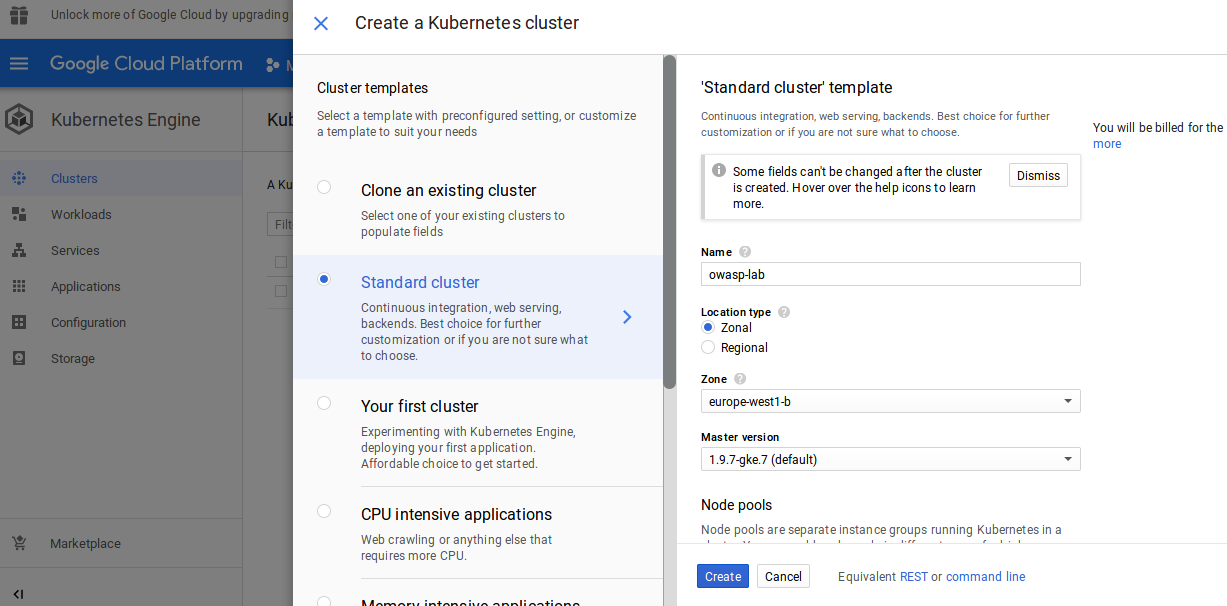
You find here thw options on how to create a kubernetes cluster.
-
Option A : Kubernetes Engine
- A Google Cloud Platform Account
- Enable the Kubernetes Engine
See the following resources to learn more:
-
Option B: Create a Kubernetes Cluster on Ubuntu
You can follow the steps on this page or try this quickstart as a Google Cloud Training lab.
New users of Google Cloud Platform are eligible for a $300 free trial.
Take the following steps to enable the Kubernetes Engine API:
- Visit the Kubernetes Engine page) in the Google Cloud Platform Console).
- Create or select a project.
- Wait for the API and related services to be enabled. This can take several minutes.
- Make sure that billing is enabled for your project. HOW TO ENABLE BILLING
To complete this quickstart, you can use either Google Cloud Shell or your local shell.
Before getting started, you should use gcloud to configure two default settings: your default project and compute zone.
Your project has a project ID, which is its unique identifier. When you first create a project, you can use the automatically-generated project ID or you can create your own.
Your compute zone is an approximate regional location in which your clusters and their resources live. For example, us-west1-a is a zone in the us-west region
gcloud config set project [PROJECT_ID]gcloud config set compute/zone [COMPUTE_ZONE]where [COMPUTE_ZONE] is the desired geographical compute zone, such as
us-west1-a.
Once connected to the cloud shell, you should see that you are already authenticated and that the project is already set to your PROJECT_ID
gcloud auth listCommand output
Credentialed accounts:
- <myaccount>@<mydomain>.com (active)NOTE : Full documentation iof how to use
gcloudis available from https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud.
Create a new Google Cloud Platform project: https://console.developers.google.com/project
We will start with creating three Ubuntu 16.04 servers. This will give you three servers to configure. To get this three member cluster up and running, you will need to select Ubuntu 16.04, 4GM RAM servers and enable Private Networking.
You can download ubuntu server from here.
Create 3 hosts and call them node-master, node-1 and node-2.
Set your hostnames for your servers as follows:
| Server | Hostname | Role |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | node-master | Master |
| 2 | node-1 | Node |
| 3 | node-2 | Node |
On each of the three Ubuntu 16.04 servers run the following commands as root:
apt-get update && apt-get install -y apt-transport-https
curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | apt-key add -
cat <<EOF >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
deb http://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main
EOF
apt-get update
apt-get install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl docker.ioTo create the docker group and add your user:
1 Create the docker group.
$ sudo groupadd docker2 Add your user to the docker group.
$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USERroot@node-master:~# kubeadm init
[init] using Kubernetes version: v1.12.2
[preflight] running pre-flight checks
[preflight/images] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight/images] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight/images] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[kubelet] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[preflight] Activating the kubelet service
[certificates] Generated ca certificate and key.
[certificates] Generated apiserver-kubelet-client certificate and key.
[certificates] Generated apiserver certificate and key.
[certificates] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [node-master kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 10.132.0.4]
[certificates] Generated etcd/ca certificate and key.
[certificates] Generated apiserver-etcd-client certificate and key.
[certificates] Generated etcd/server certificate and key.
[certificates] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [node-master localhost] and IPs [127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certificates] Generated etcd/peer certificate and key.
[certificates] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [node-master localhost] and IPs [10.132.0.4 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certificates] Generated etcd/healthcheck-client certificate and key.
[certificates] Generated front-proxy-ca certificate and key.
[certificates] Generated front-proxy-client certificate and key.
[certificates] valid certificates and keys now exist in "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certificates] Generated sa key and public key.
[kubeconfig] Wrote KubeConfig file to disk: "/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf"
[kubeconfig] Wrote KubeConfig file to disk: "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf"
[kubeconfig] Wrote KubeConfig file to disk: "/etc/kubernetes/controller-manager.conf"
[kubeconfig] Wrote KubeConfig file to disk: "/etc/kubernetes/scheduler.conf"
[controlplane] wrote Static Pod manifest for component kube-apiserver to "/etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml"
[controlplane] wrote Static Pod manifest for component kube-controller-manager to "/etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml"
[controlplane] wrote Static Pod manifest for component kube-scheduler to "/etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-scheduler.yaml"
[etcd] Wrote Static Pod manifest for a local etcd instance to "/etc/kubernetes/manifests/etcd.yaml"
[init] waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as Static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[init] this might take a minute or longer if the control plane images have to be pulled
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 26.505711 seconds
[uploadconfig] storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.12" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[markmaster] Marking the node node-master as master by adding the label "node-role.kubernetes.io/master=''"
[markmaster] Marking the node node-master as master by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[patchnode] Uploading the CRI Socket information "/var/run/dockershim.sock" to the Node API object "node-master" as an annotation
[bootstraptoken] using token: jzmnwk.hr7rdlr922pzu2d4
[bootstraptoken] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstraptoken] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstraptoken] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstraptoken] creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes master has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of machines by running the following on each node
as root:
kubeadm join 10.132.0.4:6443 --token jzmnwk.hr7rdlr922pzu2d4 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f7bd8e35bb89ada8734f9305e7e4cc1d8ebe553cdc165d245dcb1bc4d5b75d28
root@node-master:~# exityou need to run the following as a regular user:
$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
$ sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
$ sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/configYou can now join any number of machines by running the kubeadm join command on each node as root. This command will be created for you as displayed in your terminal for you to copy and run.
kubeadm join 10.132.0.4:6443 --token jzmnwk.hr7rdlr922pzu2d4 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f7bd8e35bb89ada8734f9305e7e4cc1d8ebe553cdc165d245dcb1bc4d5b75d28To check that all nodes are now joined to the master run the following command on the Kubernetes master node-master:
#kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node-1 Ready <none> 3m37s v1.12.2
node-2 Ready <none> 3m8s v1.12.2
node-master Ready master 5m13s v1.12.2You must get that all the nodes are ready, if it is nt the case do the following step
Get the Weave Net yaml:
curl -o weave.yaml https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/v1.8/net.yamlInspect the yaml contents:
cat weave.yamlOn the node-master Kubernetes master node run the following commands:
kubectl apply -f weave.yamlchck again
kubectl get nodes