Easy to use Google Maps in your Flask application
- Jinja
- Flask
- A google api key get here
To contribute with the project, clone it, create a virtualenv and install all of you need to dev, see below:
git clone https://github.com/flask-extensions/Flask-GoogleMaps.git
cd Flask-GoogleMaps
poetry use env 3.8 # just to create virtualenv at the first time
poetry shell # activate virtualenv
poetry install # to install all for devTo use in your project just use your dependency manager to install it, with pip is like this:
pip install flask-googlemapsFlask-GoogleMaps includes some global functions and template filters in your Jinja environment, also it allows you to use the Map in views if needed.
in your app
from flask import Flask
from flask_googlemaps import GoogleMaps
app = Flask(__name__)
# you can set key as config
app.config['GOOGLEMAPS_KEY'] = "8JZ7i18MjFuM35dJHq70n3Hx4"
# Initialize the extension
GoogleMaps(app)
# you can also pass the key here if you prefer
GoogleMaps(app, key="8JZ7i18MjFuM35dJHq70n3Hx4")In template
{{googlemap("my_awesome_map", lat=0.23234234, lng=-0.234234234, markers=[(0.12,
-0.45345), ...])}}That's it! now you have some template filters and functions to use, more details in examples and screenshot below.
- You can create the map in the view and then send to the template context
- you can use the template functions and filters directly
from flask import Flask, render_template
from flask_googlemaps import GoogleMaps
from flask_googlemaps import Map
app = Flask(__name__, template_folder=".")
GoogleMaps(app)
@app.route("/")
def mapview():
# creating a map in the view
mymap = Map(
identifier="view-side",
lat=37.4419,
lng=-122.1419,
markers=[(37.4419, -122.1419)]
)
sndmap = Map(
identifier="sndmap",
lat=37.4419,
lng=-122.1419,
markers=[
{
'icon': 'http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/ms/icons/green-dot.png',
'lat': 37.4419,
'lng': -122.1419,
'infobox': "<b>Hello World</b>"
},
{
'icon': 'http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/ms/icons/blue-dot.png',
'lat': 37.4300,
'lng': -122.1400,
'infobox': "<b>Hello World from other place</b>"
}
]
)
return render_template('example.html', mymap=mymap, sndmap=sndmap)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)- lat: The latitude coordinate for centering the map.
- lng: The longitutde coordinate for centering the map.
- zoom: The zoom level. Defaults to
13. - maptype: The map type -
ROADMAP,SATELLITE,HYBRID,TERRAIN. Defaults toROADMAP. - markers: Markers array of tuples having (lat, lng, infobox, icon). Defaults to
None. - or markers: a list of dicts containing icon, lat, lng, infobox.
- or markers: Markers dictionary with icon urls as keys and markers array as values.
- varname: The instance variable name.
- style: A string containing CSS styles. Defaults to
"height:300px;width:300px;margin:0;". - identifier: The CSS ID selector name.
- cls: The CSS Class selector name. Defaults to
"map". - language: The map language. Defaults to
"en". - region: The map region. Defaults to
"US".
Also controls True or False:
- zoom_control
- maptype_control
- scale_control
- scale_control
- streetview_control
- rotate_control
- fullscreen_control
- scroll_wheel
- collapsible (map collapses by click on varname_collapse button)
- mapdisplay (show a collapsible map by default or not)
- center_on_user_location (using HTML5 Geolocation)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
{{"decoupled-map"|googlemap_js(37.4419, -122.1419, markers=[(37.4419,
-122.1419)])}} {{mymap.js}} {{sndmap.js}}
</head>
<body>
<h1>Flask Google Maps Example</h1>
<h2>Template function centered, no marker</h2>
{{googlemap("simple-map", 37.4419, -122.1419)}}
<h2>Template filter decoupled with single marker</h2>
{{"decoupled-map"|googlemap_html(37.4419, -122.1419)}}
<h2>Template function with multiple markers</h2>
{% with map=googlemap_obj("another-map", 37.4419, -122.1419,
markers=[(37.4419, -122.1419), (37.4300, -122.1400)]) %} {{map.html}}
{{map.js}} {% endwith %}
<h2>First map generated in view</h2>
{{mymap.html}}
<h2>Second map generated in view</h2>
<h3>Example for different icons in multiple markers with infoboxes</h3>
{{sndmap.html}}
</body>
</html>Here's an example snippet of code:
Map(
identifier="catsmap",
lat=37.4419,
lng=-122.1419,
markers=[
{
'icon': 'http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/ms/icons/green-dot.png',
'lat': 37.4419,
'lng': -122.1419,
'infobox': "<img src='cat1.jpg' />"
},
{
'icon': 'http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/ms/icons/blue-dot.png',
'lat': 37.4300,
'lng': -122.1400,
'infobox': "<img src='cat2.jpg' />"
},
{
'icon': 'http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/ms/icons/yellow-dot.png',
'lat': 37.4500,
'lng': -122.1350,
'infobox': "<img src='cat3.jpg' />"
}
]
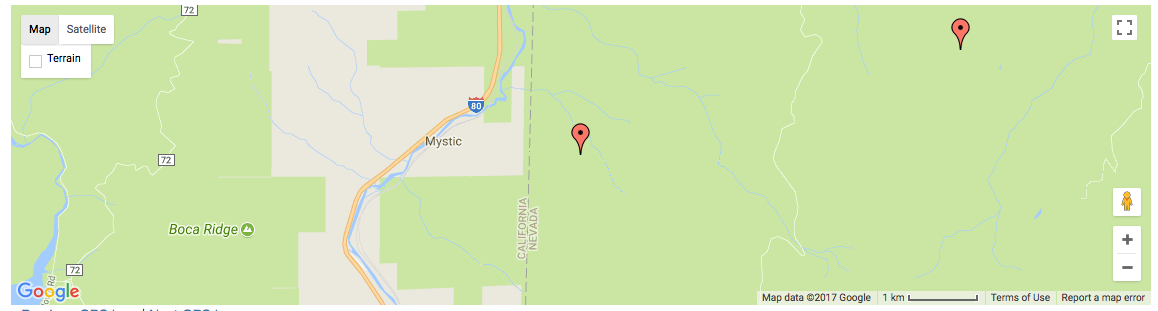
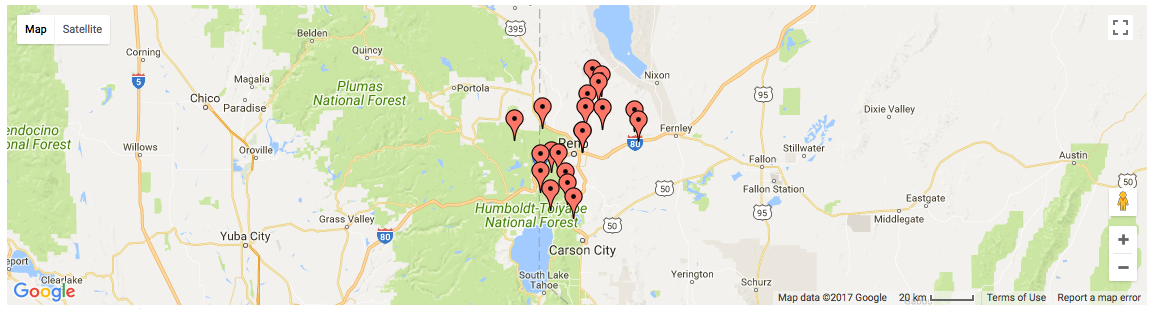
)Which results in something like the following map:

Allow users to easily fit all markers within view on page load
@app.route('/map-unbounded/')
def map_unbounded():
"""Create map with markers out of bounds."""
locations = [] # long list of coordinates
map = Map(
lat=locations[0].latitude,
lng=locations[0].longitude,
markers=[(loc.latitude, loc.longitude) for loc in locations]
)
return render_template('map.html', map=map)@app.route('/map-bounded/')
def map_bounded():
"""Create map with all markers within bounds."""
locations = [] # long list of coordinates
map = Map(
lat=locations[0].latitude,
lng=locations[0].longitude,
markers=[(loc.latitude, loc.longitude) for loc in locations],
fit_markers_to_bounds = True
)
return render_template('map.html', map=map)from flask_googlemaps import get_address, get_coordinates
API_KEY = 'YOUR API KEY'
#Reverse Geocoding: getting detailed address from coordinates of a location
print(get_address(API_KEY,22.4761596,88.4149326))
#output: {'zip': '700150', 'country': 'India', 'state': 'West Bengal', 'city': 'Kolkata', 'locality': 'Kolkata', 'road': 'Techno City', 'formatted_address': 'Sirin Rd, Mauza Ranabhutia, Techno City, Kolkata, West Bengal 700150, India'}
#Geocoding: getting coordinates from address text
print(get_coordinates(API_KEY,'Netaji Subhash Engineering College Kolkata'))
#output: {'lat': 22.4761596, 'lng': 88.4149326}$ git clone https://github.com/flask-extensions/Flask-GoogleMaps
$ cd Flask-GoogleMaps/If you have Poetry
$ poetry installwithout poetry
$ pip install --upgrade pip
$ pip install -e .
$ pip install -r requirements.txtRun it.
$ FLASK_GOOGLEMAPS_KEY="YourKeyHERE" FLASK_APP=examples/example.py flask run
running on localhost:5000 .....Access: http://localhost:5000/ and http://localhost:5000/fullmap
Please see this page developers.google.com/maps/documentation/javascript/tutorial and contribute!