NetDB Network tracking database (NetDB) utilises the LAMP (Linux, Apache, MariaDB and Perl) stack for scraping and storing your network infomration in a centralised location. Details are available on the Wiki.
All credit goes to Jonathan Yantis.
This fork adds a configurable parameter for additional SSH options. Reason for this is that some older cisco devices only support SHA1 ciphers, so a ssh connection can't be established. If your device doesn't support newer ciphers you will get an error like "no matching key exchange method found. Their offer: diffie-hellman-group1-sha1" when trying to connect via openssh.
To install NetDB on a vanilla Red Hat based distribution run the following commands
- Clone the NetDB
git clone https://github.com/EarlRamirez/netdb.git - Run the installation script
sudo sh <path_to_netdb>/netdb_install.sh - Enter the database passwords
- Enter NetDB UI password
When the installation script is completed, point your browser to the IP address of the server.
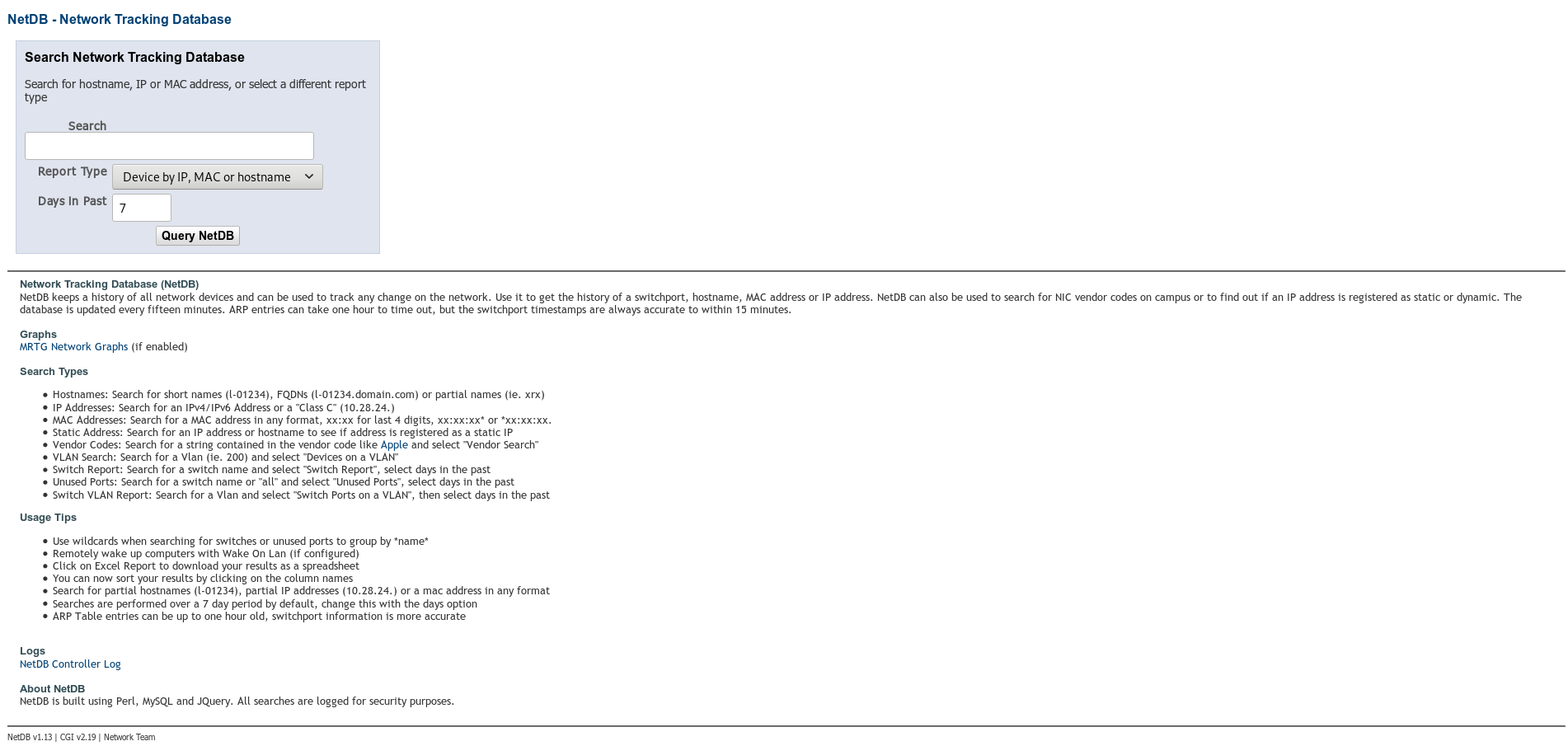
- NetDB main page
- NetDB Results
There are a few things that was not done by the installation script; therefore, a few modifications are required for NetDB to start scraping your networking equipment, for example, Cisco switches and routers.
If there isn't any DNS for your devices, its recommended that you update your hosts file with the IP and the host name of your devices
- Using your favourite editor update the hosts file,
vim /etc/hosts10.0.0.1 device1 10.0.0.2 device2
NetDB will only scarp the devices that are in the devicelist.csv which is located in /opt/netdb/data/devicelist.csv. The devicelist.csv supports both ARP and VRF, for example, device1 supports has VRF and device1 does not the configuration file will look like this
- Add devices to the devicelist.csv
vim /opt/netdb/data/devicelist.csvdevice1,arp,vrf-one,vrf-two device2,arp
The final step is to update the netdb.conf with the credentials of your networking devices
- Edit the confoguration file
vim /etc/netdb.confand update the following linesdevuser = your_switch_user # Level 5 cisco user (show commands only) devpass = your_passwd
All commands below are executed as netdb
-
Try to scrape devices for data for the first time, add a -debug value if there are problems
netdbctl -ud -v
-
Import data in to database (run this twice the first time)
netdbctl -a -m -debug 3
-
Check control.log for any errors
tail -f /var/log/netdb/control.log -
Check the size of the data in the database
netdb -st
-
If it's running extremely slow when you do an ARP import in to the database, you likely have a reverse DNS issue on your network. Make sure your DNS servers are properly configured or try a local caching BIND server. You can also disable DNS lookups with disable_DNS, see the netdb.conf file for ideas on how to use this.
-
If you are having issues with data showing up in the database, first start by turning debugging on in /etc/netdb.conf to level 3
-
Check to see if the MAC or ARP data is getting in to the data files arptable.txt and mactable.txt files by grepping for some device data in /opt/netdb/data/.
-
If you are not getting ARP data, make sure you append the devicelist.csv file entry as shown in the example below. Access switches usually has ARP only; however, distribution switches can have as many VRF that exists on the distribution switche.
switch1,arp switch1,arp,vrf-one,vrf-two switch1,arp,vrf-one,vrf-two
-
If data is not getting populated, you have a scraper problem. Run netdbctl with the -v or -vv option to debug any scraper issues.
-
If the data is in the files, check the database: mysql -u netdb -p -h localhost
use netdb; select * from switchports; select * from ipmac;
-
For further assistance you can create an Issue in Github