Docker swarm is container orchestration tools build and manager by Docker.
It's a native clustering tool provided by Docker which provides high-availability and high-performance for your application by distributing it to all nodes inside the swarm cluster.
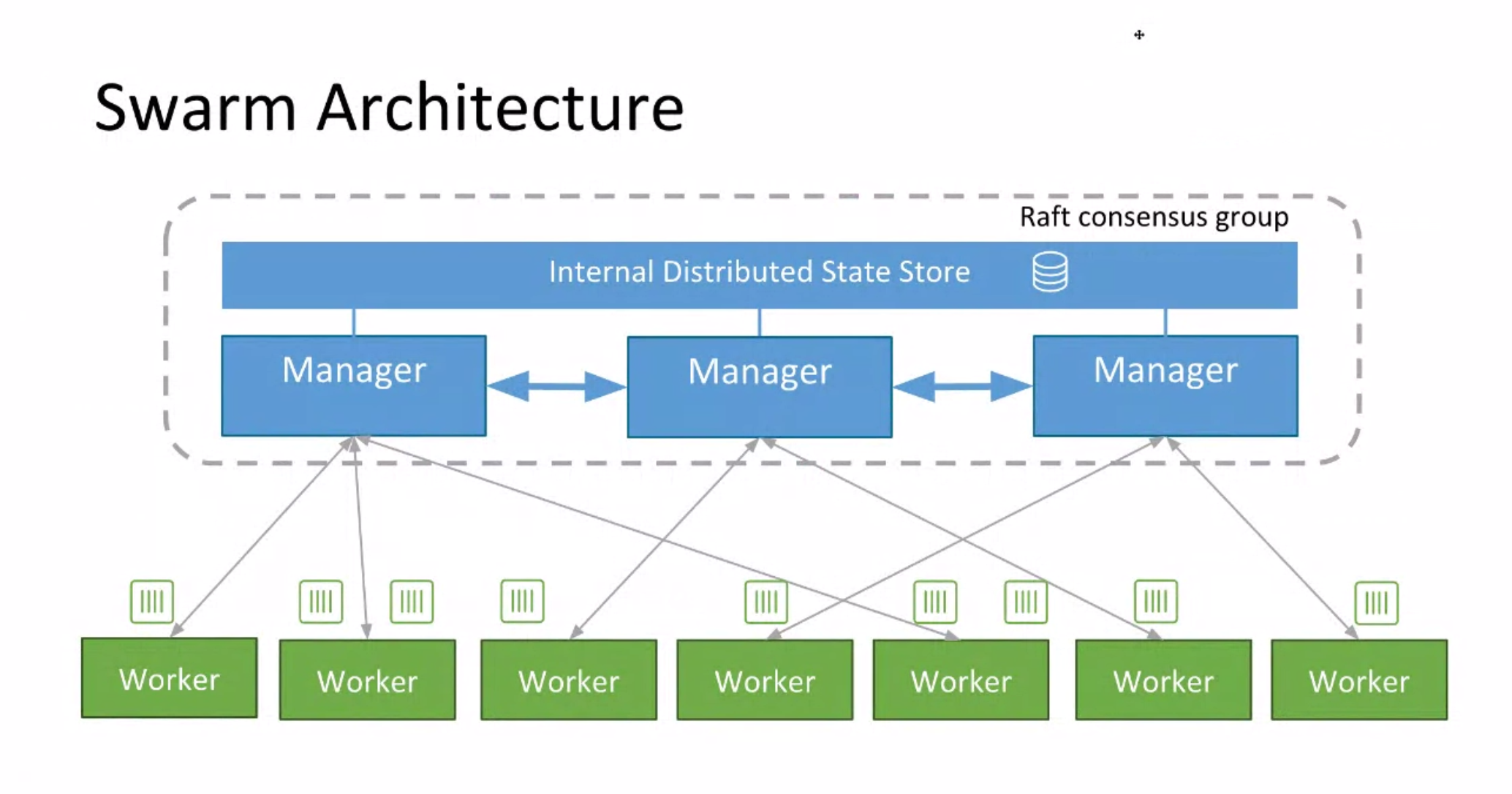
A Docker engine participating in a swarm is called a node.
Swarm uses the SwarmKit library for orchestration.
This toolkit uses Raft consensus algorithm to coordinate and decision making of a distributed system. SwarmKit is responsible for Orchestration, Scheduling and Cluster Management.
Services running on the cluster are easily scalable through a single parameter. You can declare the number of replicas a service should have and the swarm manager automatically adapts by adding or removing containers to maintain the desired state.
The swarm also provides resilience through reconciliation of the desired states. The manager continuously monitors the state of the nodes in the cluster. If a node goes offline, the manager will reconcile the difference in the desired state and the current state by redeploying the lost services on the available nodes.
Swarm manager uses ingress load balancing to expose the services you want to make available externally to the swarm..
Docker Swarm comes with great security features out of the box. When a node joins the swarm, it uses a token that not only verifies itself but also verifies it is joining the swarm you think it is. From that moment on, all communication between nodes takes place using mutual TLS encryption. This encryption is all provisioned and managed automatically by the Swarm, so you never need to worry about renewing certificates, and other typical security hassles.
-
Service : Service define the task that need to be execute on manager and workder nodes.
-
Task : Tasks are Docker containers that execute the commands you defined in the service.
-
Manager Node: It delivers work (in the form of tasks) to worker nodes. and Monitor the worker node.
-
Worker node: Worker nodes run tasks distributed by the manager node in the swarm.Each worker node runs an agent that reports back to the master node about the state of the tasks assigned to it, so the manager node can keep track of services and tasks running in the swarm.
Docker Swarm contain multiple Docker Host that running on Docker Swarm mode. Each host may be work as Master or Worker. Master Host will work as Manager or Worker.
Master Or Manager = (n-1)/2
N= Number of Nodes
docker swarm init
or
docker swarm init --advertise-addr <MANAGER-IP>
Basic Comamnd of Docker Service
create Create a new service
inspect Display detailed information on one or more services
logs Fetch the logs of a service or task
ls List services
ps List the tasks of one or more services
rm Remove one or more services
rollback Revert changes to a service's configuration
scale Scale one or multiple replicated services
update Update a service
docker service --name[nameofservice] [imagename] [action]
docker service --name pingservice alpine ping www.google.com . // New Service will create with the name of pingservice
List of service
docker service ls // Give the list of available service
Inspect the docker service
docker service inspect pingservice
Scaling the service
docker service update pingservice --replicas=3 // Create the replicas for same service
List of container runnong for that service
docker ps -a // all the running container will be visisble here
Remove any container docker service will create new container automatically
docker kill [container_name]
docker ps -a // after sometime you can see new container will created because we define that we need 4 replicas - Docker Swarm node Promote and Demote
- Docker Swarm Visualizer
- Docker Service mode (Replicated and Global)
- Docker Swarm Availablity
docker service create \
--name=viz \
--publish=8080:8080/tcp \
--constraint=node.role==manager \
--mount=type=bind,src=/var/run/docker.sock,dst=/var/run/docker.sock \
dockersamples/visualizer
demote Demote one or more nodes from manager in the swarm
inspect Display detailed information on one or more nodes
ls List nodes in the swarm
promote Promote one or more nodes to manager in the swarm
ps List tasks running on one or more nodes, defaults to current node
rm Remove one or more nodes from the swarm
update Update a nodeThere are 3 types of state present in the docker node.
- Active
- Pause
- Drain
Active - This is the default state of node. In this state node is ready to take new task from ther master or Manger node.
Pause - If Any node availability pause means that node is not ready to take new task from Master or Manager node.
Drain - Sometime if you have any planned maintanance acitity on that node so you can set the availability drain. So that node will not take any task from the master and Manger shift all the running container from that node to active node.
Change availability of node from Active state to Pause .
docker node update --availability=pauseChange availability of node from Active state to Drain .
docker node update --availability=drain